|
Cromlech D
A cromlech (sometimes also spelled "cromleh" or "cromlêh"; cf Welsh ''crom'', "bent"; ''llech'', "slate") is a megalithic construction made of large stone blocks. The word applies to two different megalithic forms in English, the first being an altar tomb (frequently called a "dolmen"), as William Borlase first denoted in 1769. A good example is at . The second meaning of the name "cromlech" in English refers to large stone circles such as those found among the Carnac stones in Brittany, France. Unlike in English, the word "cromlech" in many other languages (such as Azerbaijani, Armenian, French, Greek, Indonesian, Italian, Romanian, and Spanish) exclusively denotes a megalithic stone circle, whereas the word "dolmen" is used to refer to the type of megalithic altar tomb sometimes indicated by the English "cromlech". Also, more recently in English, scholars such as Aubrey Burl use "cromlech" as a synonym for "megalithic stone circle".Aubrey Burl: ''A Guide to the Stone Circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically from Sweden in the north to the Mediterranean Sea in the south. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words " mega" for great and " lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. Types and definitions While "megalith" is often used to describe a single piece of stone, it also can be used to denote one or more rocks hewn in definite shapes for special purposes. It has been used to describe structures built by people from many parts of the world living in many different periods. The most widely known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalithic Monuments In Europe
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging geographically from Sweden in the north to the Mediterranean Sea in the south. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words " mega" for great and " lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. Types and definitions While "megalith" is often used to describe a single piece of stone, it also can be used to denote one or more rocks hewn in definite shapes for special purposes. It has been used to describe structures built by people from many parts of the world living in many different periods. The most widely known m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crom Dubh
Crom Dubh (, ; meaning ":wikt:dubh, black :wikt:crom, crooked [one]"; also ''Crum Dubh'', ''Dark Crom'') is a mythological and folkloric figure of Ireland, based on the god ''Crom Cruach'', mentioned in the 12th-century ''Metrical Dindshenchas, dinnseanchas'' of Magh Slécht. Folklore Conflict with Saint Patrick According to one legend, Cainnech of Aghaboe saw a number of demons flying past and when he inquired of their errand, one of them told him that Crom Dubh had died and they were after collecting his soul. Cainnech bid him on their return to tell him how they had fared. Some time later the demon returned limping badly. He told Cainnech that they were just about to seize Crom Dubh's soul when St. Patrick appeared with a host of angels and saints and drove them off, Crom Dubh's good works having outweighed his sins. Another location associated with Crom Dubh is Downpatrick Head in County Mayo. According to Irish legend, St. Patrick came to the headland to confront Crom Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolni Glavanak Cromlech
The Dolni Glavanak Cromlech is an oval stone circle located 2 kilometres west of village of Dolni Glavanak, some 12 kilometres from town of Madzharovo, in Bulgaria. The site is referred to as a cromlech by analogy with similar monuments in Western Europe, but it is the only structure of its kind known in the country. Description The site is situated on a low ridge-top above the left bank of the Arda river. It is enclosed on all sides and isolated from external influences. The circle consists of vertical, roughly-shaped, blocks of local hard volcanic rock (rhyodacite). The blocks are trapezoidal in shape, and are approximately 1.2 to 1.5 metres tall, and around 0.9 to 1.2 metres wide at the base, and 0.4 to 0.6 metres thick. Nine blocks still stand and three are now fallen. The vertical blocks are spaced at regular intervals, with smaller stones placed horizontally between them. The circle has an internal diameter of about 10 metres. There is an entrance on the southeast side. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinas Cromlech
Dinas Cromlech or Dinas y Gromlech is a distinctive rhyolite rock outcrop at the Llanberis Pass, in Snowdonia, northwest Wales, which has a distinctive "open book" shape that is clearly visible from the road ( A4086), and is very popular location for rock climbers and contains some of Britain's most famous and notable rock climbing routes, several of which are important in the history of rock climbing. Climbing history The obvious traditional climbing route up the deep ninety-degree angled corner resisted attempts for many years until it was climbed by Joe Brown in 1952, and called ''Cenotaph Corner'' (1952, E1 5c, with Doug Belshaw), and is regarded as one of Britain's most famous rock climbing routes. The outcrop is an important rock climbing venue in Britain, and the corner includes some of the famous traditional climbing routes in British rock climbing history, including ''Cemetery Gates'' ( E1 5b) by Don Whillans in 1951, ''Left Wall'' ( E2 5c) by Ron Moseley in 1956, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
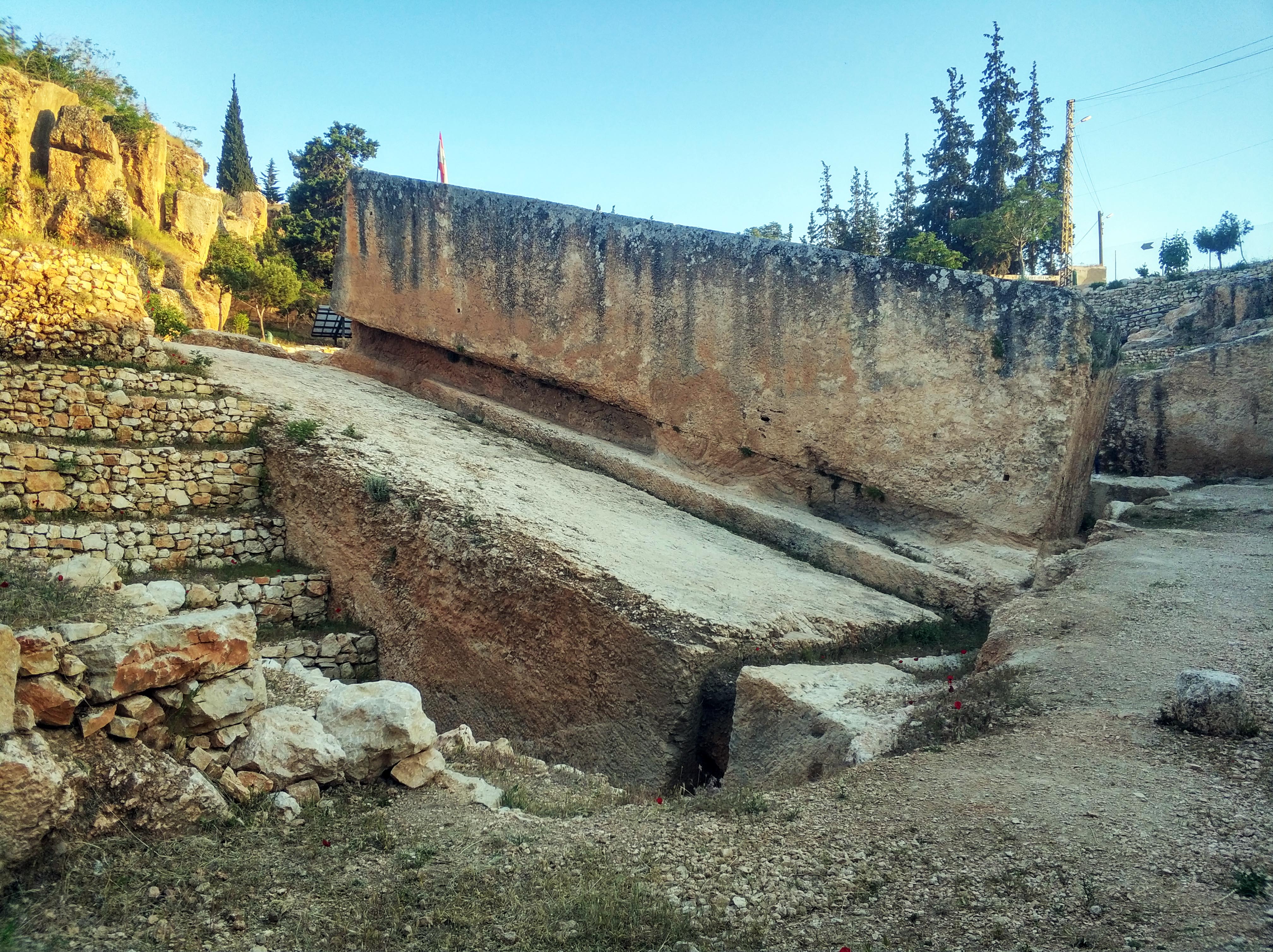
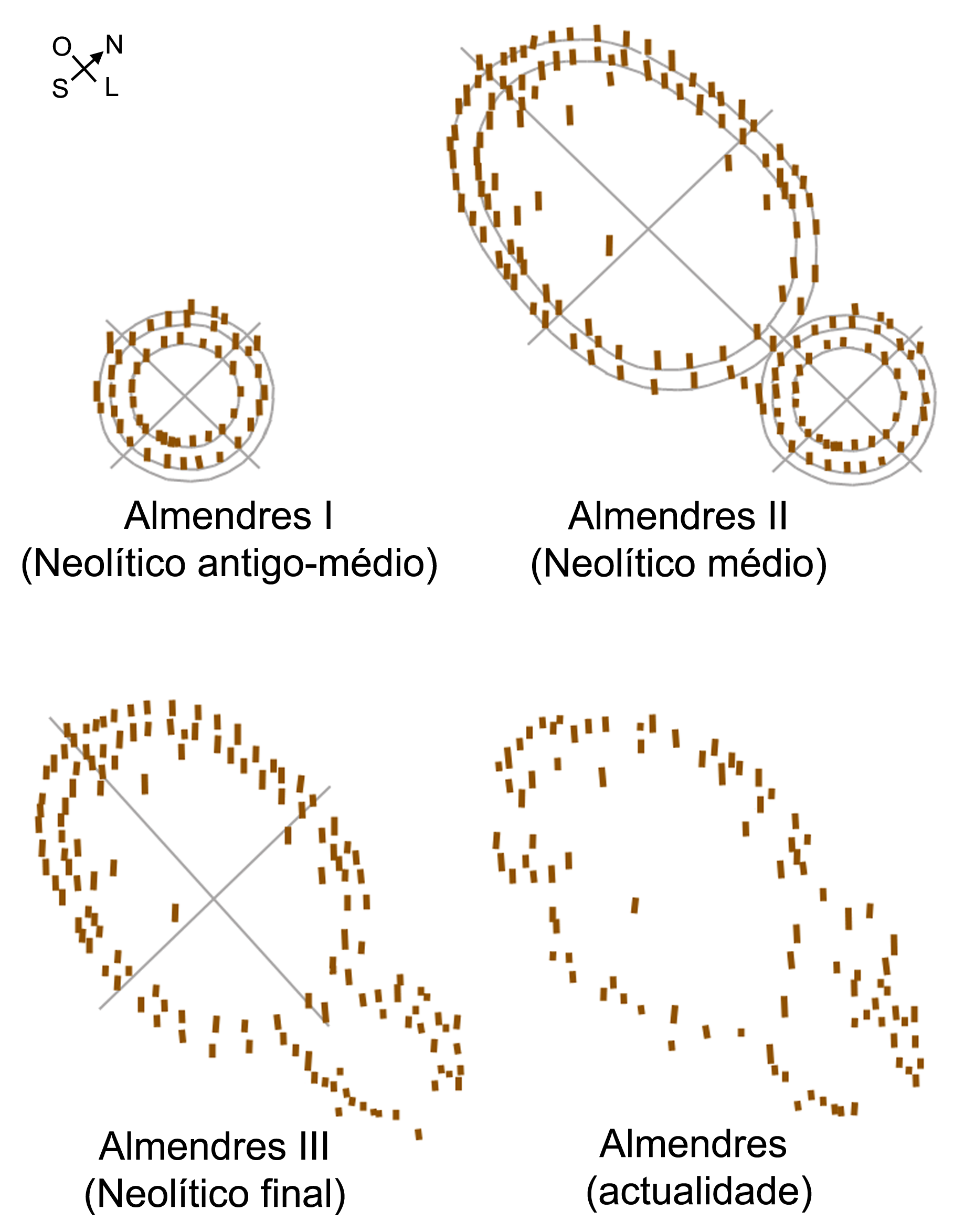
Almendres Cromlech
The Cromlech of the Almendres () is a megalithic complex (commonly known as the ''Almendres Cromlech''), located 4.5 road km WSW of the village of Nossa Senhora de Guadalupe, in the civil parish of Nossa Senhora da Tourega e Nossa Senhora de Guadalupe, municipality of Évora, in the Portuguese Alentejo. The largest existing group of structured menhirs in the Iberian Peninsula (and one of the largest in Europe), this archaeological site consists of several megalithic structures: cromlechs and menhir stones, that belong to the so-called ''"megalithic universe of Évora"'', with clear parallels to other cromlechs in Évora District, such as Portela Mogos and the Vale Maria do Meio Cromlech. History The construction of these structures dates back to the 6th millennium BC. They were rediscovered in 1966 by Henrique Leonor Pina, who was carrying out field work relating to the country's geological charts. The excavation of the site unearthed a series of both megalithic and neolithic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aubrey Burl
Harry Aubrey Woodruff Burl (24 September 1926 – 8 April 2020) was a British archaeologist best known for his studies into megalithic monuments and the nature of prehistoric rituals associated with them. Before retirement, he was Principal Lecturer in Archaeology, Hull College, East Riding of Yorkshire. Burl received a volume edited in his honour. He was called by ''The New York Times'', "the leading authority on British stone circles". Burl's work, while considering the astronomical roles of many megalithic monuments, was cautious of embracing the more tenuous claims of archaeoastronomy. In ''Prehistoric Avebury'' Burl proposed that Circles and Henge monuments, far from being astronomical observatories for a class of "astronomer priests" were more likely used for ritualistic practices, connected with death and fertility rites, and ancestor worship, similar to practices observed in other agricultural cultures (in particular the rituals of Native North American Tribes such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Circle
A stone circle is a ring of megalithic standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially Stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built between 3300 and 2500 BC. The best known examples include those at the henge monument at Avebury, the Rollright Stones, Castlerigg, and elements within the ring of standing stones at Stonehenge. Scattered examples exist from other parts of Europe. Later, during the Iron Age, stone circles were built in southern Scandinavia. The archetypical stone circle is an uncluttered enclosure, large enough to congregate inside, and composed of megalithic stones. Often similar structures are named 'stone circle', but these names are either historic, or incorrect. Examples of commonly misinterpreted stone circles are ring cairns, burial mounds, and kerb cairns. Although it is often assumed there are thousands of stone circles across the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |