|
Credit Crunch
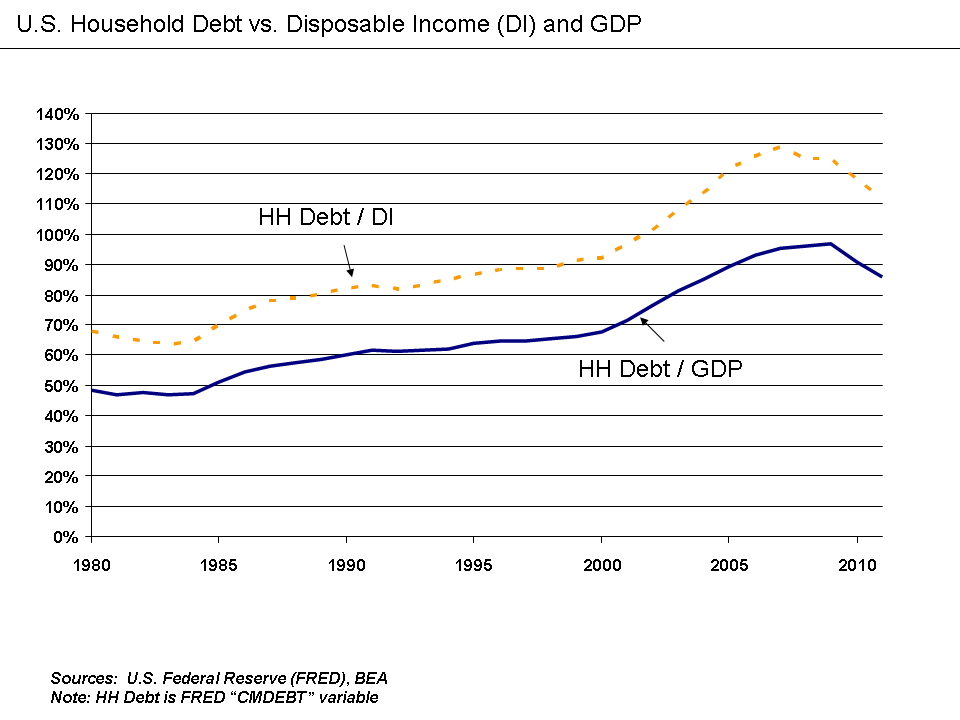
A credit crunch (a credit squeeze, credit tightening or credit crisis) is a sudden reduction in the general availability of loans (or credit) or a sudden tightening of the conditions required to obtain a loan from banks. A credit crunch generally involves a reduction in the availability of credit independent of a rise in official interest rates. In such situations the relationship between credit availability and interest rates changes. Credit becomes less available at any given official interest rate, or there ceases to be a clear relationship between interest rates and credit availability (i.e. credit rationing occurs). Many times, a credit crunch is accompanied by a flight to quality by lenders and investors, as they seek less risky investments (often at the expense of small to medium size enterprises). Causes A credit crunch is often caused by a sustained period of careless and inappropriate lending which results in losses for lending institutions and investors in debt when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money Loan, borrowed or otherwise withheld from another party, the creditor. Debt may be owed by a sovereign state or country, local government, company, or an individual. Commercial debt is generally subject to contractual terms regarding the amount and timing of repayments of #Principal, principal and interest. Loans, bond (finance), bonds, notes, and Mortgage loan, mortgages are all types of debt. In financial accounting, debt is a type of financial transaction, as distinct from equity (finance), equity. The term can also be used metaphorically to cover morality, moral obligations and other interactions not based on a monetary value. For example, in Western cultures, a person who has been helped by a second person is sometimes said to owe a "debt of gratitude" to the second person. Etymology The English term "debt" was first used in the late 13th century and comes by way of Old French from the Latin verb ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyman Minsky
Hyman Philip Minsky (September 23, 1919 – October 24, 1996) was an American economist and economy professor at Washington University in St. Louis. A distinguished scholar at the Levy Economics Institute of Bard College, his research was intent on providing explanations to the characteristics of financial crises, which he attributed to swings in a potentially fragile financial system. Minsky is often described as a post-Keynesian economist because, in the Keynesian tradition, he supported some government intervention in financial markets, opposed some of the financial deregulation of the 1980s, stressed the importance of the Federal Reserve as a lender of last resort and argued against the over-accumulation of private debt in the financial markets. Minsky's economic theories were largely ignored for decades, until the subprime mortgage crisis of 2008 caused a renewed interest in them. Education A native of Chicago, Illinois, Minsky was born into a Jewish family of Menshevik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor. Bankrupt is not the only legal status that an insolvent person may have, meaning the term ''bankruptcy'' is not a synonym for insolvency. Etymology The word ''bankruptcy'' is derived from Italian language, Italian , literally meaning . The term is often described as having originated in Renaissance Italy, where there allegedly existed the tradition of smashing a banker's bench if he defaulted on payment. However, the existence of such a ritual is doubted. History In Ancient Greece, bankruptcy did not exist. If a man owed and he could not pay, he and his wife, children or servants were forced into "debt slavery" until the creditor recouped losses through their Manual labour, physical labour. Many city-states in ancient Greece lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreclosure
Foreclosure is a legal process in which a lender attempts to recover the balance of a loan from a borrower who has Default (finance), stopped making payments to the lender by forcing the sale of the asset used as the Collateral (finance), collateral for the loan. Formally, a Mortgage law#Mortgage lender, mortgage lender (mortgagee), or other lienholder, obtains a termination of a Mortgage law#Borrower, mortgage borrower (mortgagor)'s Equity of redemption, equitable right of redemption, either by court order or by operation of law (after following a specific statutory procedure). Usually, a lender obtains a security interest from a borrower who mortgages or pledges an asset like a house to secure the loan. If the borrower default (finance), defaults and the lender tries to Repossession, repossess the property, courts of equity can grant the borrower the Equity of redemption, equitable right of redemption if the borrower repays the debt. While this equitable right exists, it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Crisis
A financial crisis is any of a broad variety of situations in which some financial assets suddenly lose a large part of their nominal value. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, many financial crises were associated with Bank run#Systemic banking crises, banking panics, and many recessions coincided with these panics. Other situations that are often called financial crises include stock market crashes and the bursting of other financial Economic bubble, bubbles, currency crisis, currency crises, and sovereign defaults. Financial crises directly result in a loss of paper wealth but do not necessarily result in significant changes in the real economy (for example, the crisis resulting from the famous tulip mania bubble in the 17th century). Many economists have offered theories about how financial crises develop and how they could be prevented. There is little consensus and financial crises continue to occur from time to time. It is apparent however that a consistent feature of bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Biases
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the objective input, may dictate their behavior in the world. Thus, cognitive biases may sometimes lead to perceptual distortion, inaccurate judgment, illogical interpretation, and irrationality. While cognitive biases may initially appear to be negative, some are adaptive. They may lead to more effective actions in a given context. Furthermore, allowing cognitive biases enables faster decisions which can be desirable when timeliness is more valuable than accuracy, as illustrated in heuristics. Other cognitive biases are a "by-product" of human processing limitations, resulting from a lack of appropriate mental mechanisms (bounded rationality), the impact of an individual's constitution and biological state (see embodied cognition), or simply from a limited c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Kahneman
Daniel Kahneman (; ; March 5, 1934 – March 27, 2024) was an Israeli-American psychologist best known for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making as well as behavioral economics, for which he was awarded the 2002 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences together with Vernon L. Smith. Kahneman's published empirical findings challenge the assumption of human rationality prevailing in modern economic theory. Kahneman became known as the "grandfather of behavioral economics." With Amos Tversky and others, Kahneman established a cognitive basis for common human errors that arise from heuristics and biases, and developed prospect theory. In 2011, Kahneman was named by ''Foreign Policy'' magazine in its list of top global thinkers. In the same year, his book '' Thinking, Fast and Slow'', which summarizes much of his research, was published and became a best seller. In 2015, ''The Economist'' listed him as the seventh most influential economist in the world. Kah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moral Hazard
In economics, a moral hazard is a situation where an economic actor has an incentive to increase its exposure to risk because it does not bear the full costs associated with that risk, should things go wrong. For example, when a corporation is insured, it may take on higher risk knowing that its insurance will pay the associated costs. A moral hazard may occur where the actions of the risk-taking party change to the detriment of the cost-bearing party after a financial transaction has taken place. Moral hazard can occur under a type of information asymmetry where the risk-taking party to a transaction knows more about its intentions than the party paying the consequences of the risk and has a tendency or incentive to take on too much risk from the perspective of the party with less information. One example is a principal–agent approach (also called agency theory), where one party, called an agent, acts on behalf of another party, called the principal. However, a principa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subprime Mortgage Crisis
The American subprime mortgage crisis was a multinational financial crisis that occurred between 2007 and 2010, contributing to the 2008 financial crisis. It led to a severe economic recession, with millions becoming unemployed and many businesses going bankrupt. The U.S. government intervened with a series of measures to stabilize the financial system, including the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA). The collapse of the United States housing bubble and high interest rates led to unprecedented numbers of borrowers missing mortgage repayments and becoming delinquent. This ultimately led to mass foreclosures and the devaluation of housing-related securities. The housing bubble preceding the crisis was financed with mortgage-backed securities (MBSes) and collateralized debt obligations (CDOs), which initially offered higher interest rates (i.e. better returns) than government securities, along with attractive risk ratin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long-term Capital Management
Long-Term Capital Management L.P. (LTCM) was a highly leveraged hedge fund. In 1998, it received a $3.6 billion bailout from a group of 14 banks, in a deal brokered and put together by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York. LTCM was founded in 1994 by John Meriwether, the former vice-chairman and head of bond trading at Salomon Brothers. Members of LTCM's board of directors included Myron Scholes and Robert C. Merton, who three years later in 1997 shared the Nobel Prize in Economics for having developed the Black–Scholes model of financial dynamics.''A financial History of the United States Volume II: 1970–2001'', Jerry W. Markham, Chapter 5: "Bank Consolidation", M. E. Sharpe, Inc., 2002 LTCM was initially successful, with annualized returns (after fees) of around 21% in its first year, 43% in its second year and 41% in its third year. However, in 1998 it lost $4.6 billion in less than four months due to a combination of high leverage and exposure to the 1997 Asian fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and business failures around the world. The economic contagion began in 1929 in the United States, the largest economy in the world, with the devastating Wall Street stock market crash of October 1929 often considered the beginning of the Depression. Among the countries with the most unemployed were the U.S., the United Kingdom, and Weimar Republic, Germany. The Depression was preceded by a period of industrial growth and social development known as the "Roaring Twenties". Much of the profit generated by the boom was invested in speculation, such as on the stock market, contributing to growing Wealth inequality in the United States, wealth inequality. Banks were subject to laissez-faire, minimal regulation, resulting in loose lending and wides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist and philosopher whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in mathematics, he built on and greatly refined earlier work on the causes of business cycles. One of the most influential economists of the 20th century, he produced writings that are the basis for the schools of economic thought, school of thought known as Keynesian economics, and its various offshoots. His ideas, reformulated as New Keynesianism, are fundamental to mainstream economics, mainstream macroeconomics. He is known as the "father of macroeconomics". During the Great Depression of the 1930s, Keynes spearheaded Keynesian Revolution, a revolution in economic thinking, challenging the ideas of neoclassical economics that held that free markets would, in the short to medium term, automatically provide full employment, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |