|
Create, Read, Update And Delete
In computer programming, create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) are the four basic operations (actions) of persistent storage. CRUD is also sometimes used to describe user interface conventions that facilitate viewing, searching, and changing information using computer-based forms and reports. History The term ''C.R.U.D'' was likely first popularized in 1983 by James Martin in his book ''Managing the data-base environment''. Conceptual Data can be put in a ''location/area'' of a storage mechanism. * The fundamental feature of a storage location is that its ''content'' is both ''readable'' and ''updatable''. * Before a storage location can be read or updated it needs to be ''created''; that is allocated and initialized with content. * At some later point, the storage location may need to be ''destructed''; that is finalized and deallocated. Together these four operations make up the basic operations of storage management known as CRUD: ''Create'', ''Read'', ''Update'' and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Computer Programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of procedures, by writing source code, code in one or more programming languages. Programmers typically use high-level programming languages that are more easily intelligible to humans than machine code, which is directly executed by the central processing unit. Proficient programming usually requires expertise in several different subjects, including knowledge of the Domain (software engineering), application domain, details of programming languages and generic code library (computing), libraries, specialized algorithms, and Logic#Formal logic, formal logic. Auxiliary tasks accompanying and related to programming include Requirements analysis, analyzing requirements, Software testing, testing, debugging (investigating and fixing problems), imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
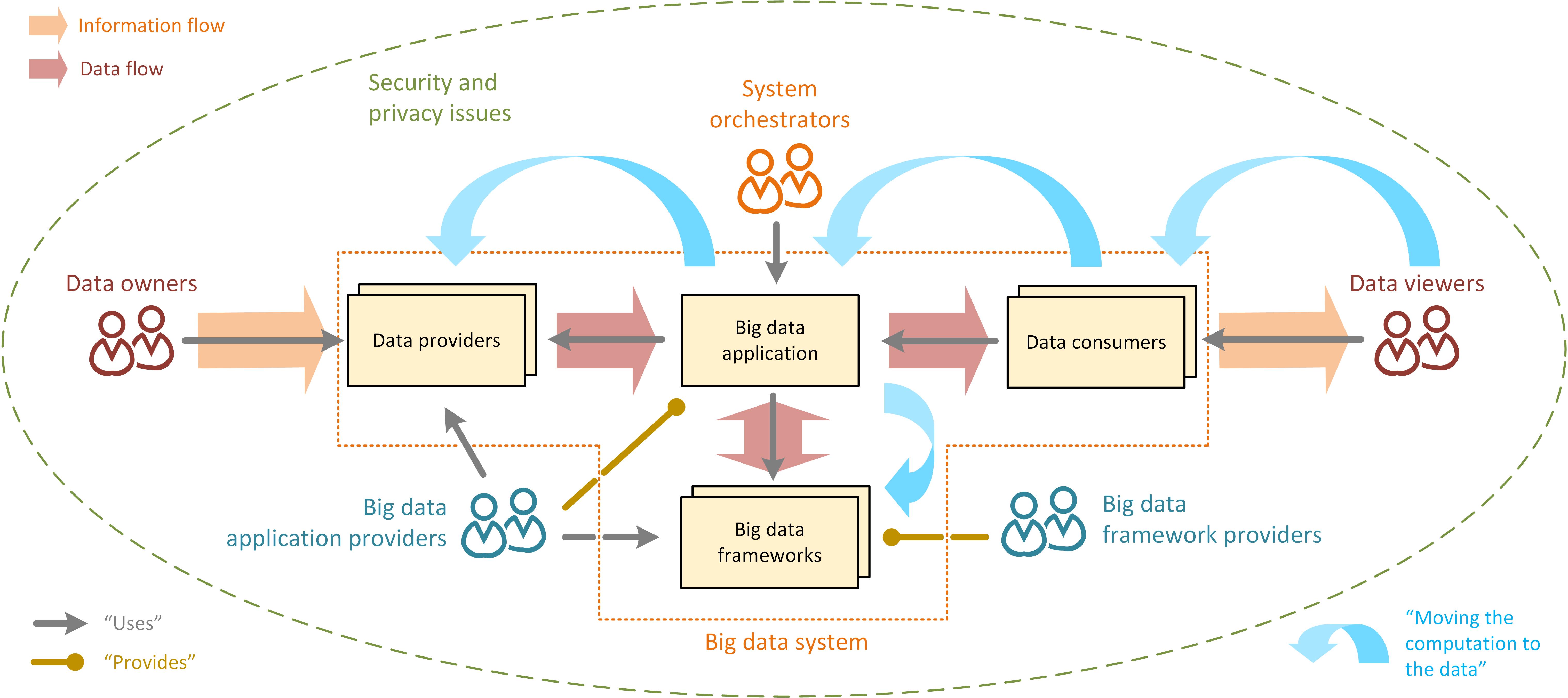 |
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Command–query Separation
Command-query separation (CQS) is a principle of imperative computer programming. It was devised by Bertrand Meyer as part of his pioneering work on the Eiffel programming language. It states that every method should either be a ''command'' that performs an action, or a ''query'' that returns data to the caller, but not both. In other words, ''asking a question should not change the answer''. More formally, methods should return a value only if they are referentially transparent and hence possess no side effects. Connection with design by contract Command-query separation is particularly well suited to a design by contract (DbC) methodology, in which the design of a program is expressed as assertions embedded in the source code, describing the state of the program at certain critical times. In DbC, assertions are considered design annotations—not program logic—and as such, their execution should not affect the program state. CQS is beneficial to DbC because any value-retu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Query By Example
Query by Example (QBE) is a database query language for relational databases. History Query by Example was devised by Moshé M. Zloof at IBM Research during the mid-1970s, in parallel to the development of SQL, and influenced by the work on relational databases of Edgar Codd. It is the first graphical query language, using visual tables where the user would enter commands, example elements and conditions. Many graphical front-ends for databases use the ideas from QBE today. Originally limited only for the purpose of retrieving data, QBE was later extended to allow other operations, such as inserts, deletes and updates, as well as creation of temporary tables. The motivation behind QBE is that a parser can convert the user's actions into statements expressed in a database manipulation language, such as SQL. Behind the scenes, it is this statement that is actually executed. A suitably comprehensive front-end can minimize the burden on the user to remember the finer details of SQ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
ACID
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Input/output
In computing, input/output (I/O, i/o, or informally io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, such as another computer system, peripherals, or a human operator. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to "perform I/O" is to perform an input or output operation. are the pieces of hardware used by a human (or other system) to communicate with a computer. For instance, a keyboard or computer mouse is an input device for a computer, while monitors and printers are output devices. Devices for communication between computers, such as modems and network cards, typically perform both input and output operations. Any interaction with the system by an interactor is an input and the reaction the system responds is called the output. The designation of a device as either input or output depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Data Manipulation Language
A data manipulation language (DML) is a computer programming language used for adding (inserting), deleting, and modifying (updating) data in a database. A DML is often a sublanguage of a broader database language such as SQL, with the DML comprising some of the operators in the language. Read-only selecting of data is sometimes distinguished as being part of a separate data query language (DQL), but it is closely related and sometimes also considered a component of a DML; some operators may perform both selecting (reading) and writing. A popular data manipulation language is that of Structured Query Language (SQL), which is used to retrieve and manipulate data in a relational database. SQL92 Other forms of DML are those used by IMS/DLI, CODASYL databases, such as IDMS and others. SQL In SQL, the data manipulation language comprises the ''SQL-data change'' statements, which modify stored data but not the schema or database objects. Manipulation of persistent database obje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Active Record Pattern
In software engineering, the active record pattern is an architectural pattern. It is found in software that stores in-memory object data in relational databases. It was named by Martin Fowler in his 2003 book ''Patterns of Enterprise Application Architecture''. The interface of an object conforming to this pattern would include functions such as Insert, Update, and Delete, plus properties that correspond more or less directly to the columns in the underlying database table. The active record pattern is an approach to accessing data in a database. A database table or view is wrapped into a class. Thus, an object instance is tied to a single row in the table. After creation of an object, a new row is added to the table upon save. Any object loaded gets its information from the database. When an object is updated, the corresponding row in the table is also updated. The wrapper class implements accessor methods or properties for each column in the table or view. This pattern is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Software Documentation
Software documentation is written text or illustration that accompanies computer software or is embedded in the source code. The documentation either explains how the software operates or how to use it, and may mean different things to people in different roles. Documentation is an important part of software engineering. Types of documentation include: * Requirements – Statements that identify attributes, capabilities, characteristics, or qualities of a system. This is the foundation for what will be or has been implemented. * Architecture/Design – Overview of software. Includes relations to an environment and construction principles to be used in design of software components. * Technical – Documentation of code, algorithms, interfaces, and APIs. * End user – Manuals for the end-user, system administrators and support staff. * Marketing – How to market the product and analysis of the market demand. Types Requirements documentation Requirements documentation is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
User Agent
On the Web, a user agent is a software agent responsible for retrieving and facilitating end-user interaction with Web content. This includes all web browsers, such as Google Chrome and Safari A safari (; originally ) is an overland journey to observe wildlife, wild animals, especially in East Africa. The so-called big five game, "Big Five" game animals of Africa – lion, African leopard, leopard, rhinoceros, African elephant, elep ..., some email clients, standalone download managers like youtube-dl, and other command-line utilities like cURL. The user agent is the client in a client–server system. The HTTP User-Agent header is intended to clearly identify the agent to the server. However, this header can be omitted or spoofed, so some websites use other detection methods. References Clients (computing) {{Web-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
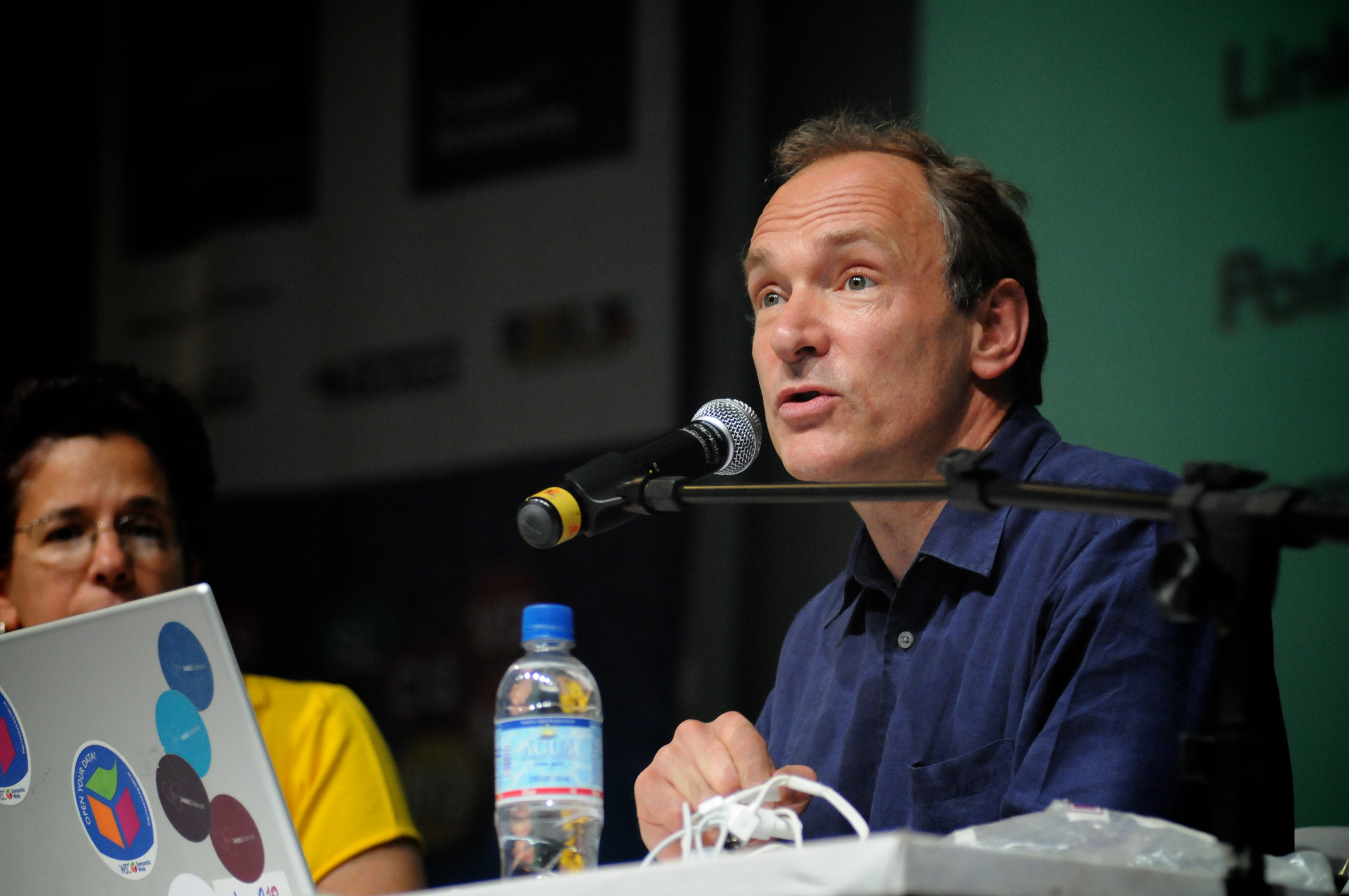 |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser. Development of HTTP was initiated by Tim Berners-Lee at CERN in 1989 and summarized in a simple document describing the behavior of a client and a server using the first HTTP version, named 0.9. That version was subsequently developed, eventually becoming the public 1.0. Development of early HTTP Requests for Comments (RFCs) started a few years later in a coordinated effort by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), with work later moving to the IETF. HTTP/1 was finalized and fully documented (as version 1.0) in 1996. It evolved ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |