|
Cramond
Cramond Village (; ) is a village and suburb in the north-west of Edinburgh, Scotland, at the mouth of the River Almond where it enters the Firth of Forth. The Cramond area has evidence of Mesolithic, Bronze Age and Roman activity. In modern times, it was the birthplace of the Scottish economist John Law (1671–1729). Cramond was incorporated into the City of Edinburgh by the Edinburgh Boundaries Extension and Tramways Act 1920 ( 10 & 11 Geo. 5. c. lxxxvii). Etymology It was once believed that Cramond Roman Fort was known to the Romans as ''Alaterva''. A stone altar was dug up in the grounds of Cramond House dedicated "To the Alatervan Mothers and the Mothers of the Parade-ground."Site Record for Cramond Edinburgh, Cramond Roman Fort Details – Royal Commission on the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
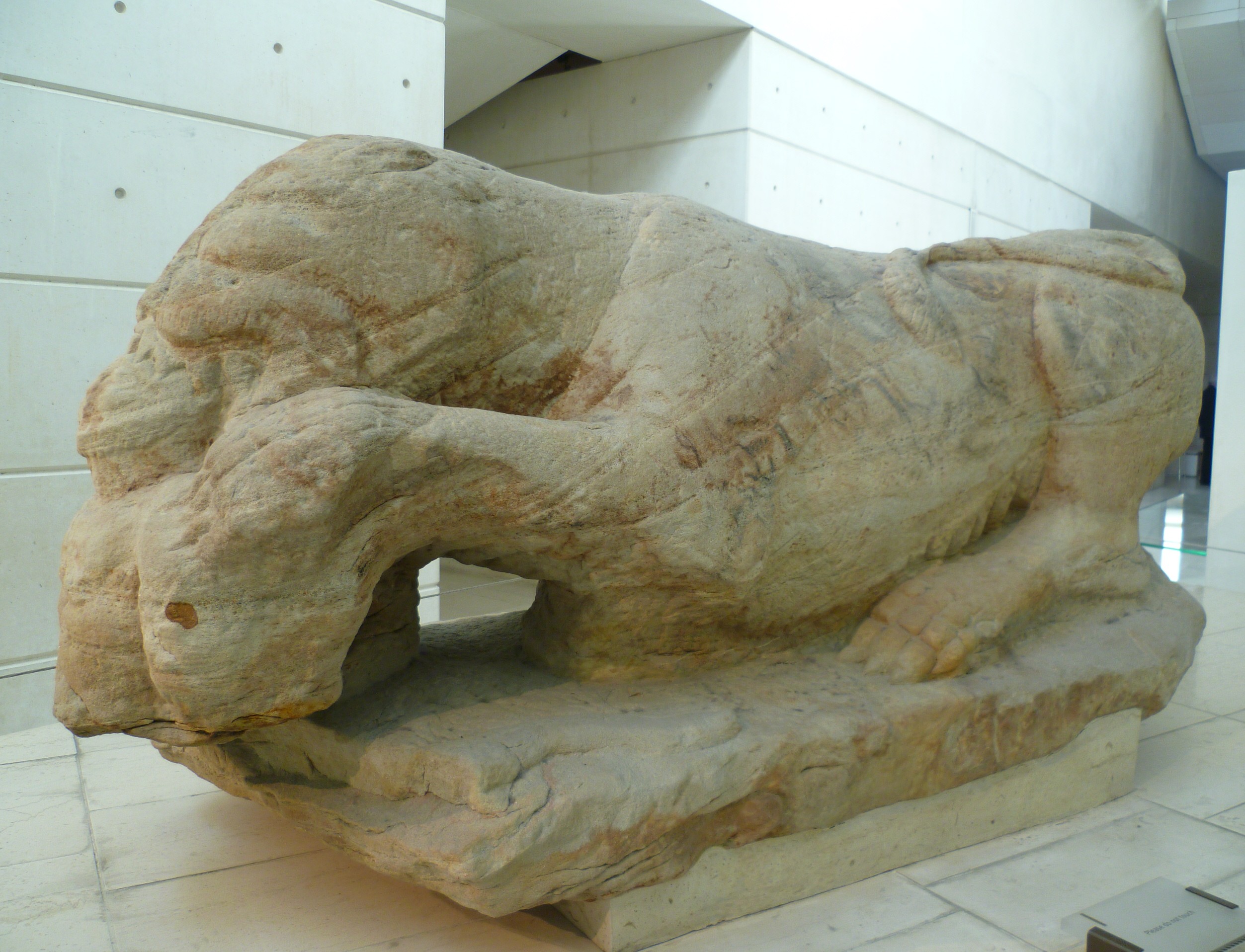
Cramond Roman Fort
Cramond Roman Fort is a Roman-Era archaeological site at Cramond, Edinburgh, Scotland. The settlement may be the "Rumabo" listed in the 7th-century ''Ravenna Cosmography''. The fort was established around 140 AD and occupied until around 170 AD, with a further period of occupation from around 208 to 214 AD. Among the many archaeological finds, one of the most famous is a sculpture known as the Cramond Lioness. History The fort at Cramond was located on the River Almond at the point where it flows into the Forth. In Roman times, there was probably a natural harbour here. One suggested interpretation is that Cramond formed a chain of Lothian forts along with Carriden and Inveresk. The fort was established around 140 AD during the building of the Antonine Wall, and remained in use until around 170 AD when the Romans retreated south to Hadrian's Wall. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Almond, Lothian
The River Almond is a river in Lothian, Scotland. It is approximately 28 miles (45 km) long, rising at Hirst Hill in Lanarkshire near Shotts, running through West Lothian and draining into the Firth of Forth at Cramond, Edinburgh. The name Almond/Amon is simply old Celtic for "river". Environment Running through areas that were dominated for much of the 20th century by heavy industry and shale- and coal mining, the River Almond has long been notorious for its high levels of pollution. With the demise of mining and heavy industry in Central Scotland, the river became cleaner, and it is being actively repopulated by wildlife: there is a healthy population of brown trout and there are improving runs of both Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar'') and sea trout (''Salmo trutta''). There is also a good array of birds to be seen around the river banks, including dippers, kingfishers and grey herons, and increasing numbers of otters are being reported. The river is still the primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh West (UK Parliament Constituency)
Edinburgh West is a burgh constituency of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, first contested at the 1885 United Kingdom general election, 1885 general election. It has been represented since 2017 by Christine Jardine of the Scottish Liberal Democrats, Liberal Democrats. Prior to the 2005 United Kingdom general election, 2005 general election, the boundaries were the same as the Edinburgh West (Scottish Parliament constituency), eponymous constituency of the Scottish Parliament, which had been created in 1999. History This commuter belt seat, distinctively in the city, was Unionist Party (Scotland), Unionist/Scottish Conservatives, Conservative for over 65 years, from the 1931 United Kingdom general election, 1931 general election until the 1997 United Kingdom general election, 1997 general election, although the Liberal/SDP Alliance and later the Liberal Democrats repeatedly came close to winning in the 1980s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firth Of Forth
The Firth of Forth () is a firth in Scotland, an inlet of the North Sea that separates Fife to its north and Lothian to its south. Further inland, it becomes the estuary of the River Forth and several other rivers. Name ''Firth'' is a cognate of ''fjord'', a Norse word meaning a narrow inlet. ''Forth'' stems from the name of the river; this is ('slow running') in Proto-Celtic, yielding in Old Gaelic and in Welsh. It was known as ' in Roman Empire, Roman times and was referred to as ' in Ptolemy's ''Geography_(Ptolemy), Geography''. In the Norse mythology, Norse sagas it was known as the . An early Welsh language, Welsh name is , or the 'sea of '. Geography and geology Geologically, the Firth of Forth is a fjord, formed by the Forth Glacier in the last glacial period. The drainage basin for the Firth of Forth covers a wide geographic area including places as far from the shore as Ben Lomond, Cumbernauld, Harthill, Scotland, Harthill, Penicuik and the edges of Gleneagles H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Scotland
Scotland during the Roman Empire refers to the protohistory, protohistorical period during which the Roman Empire interacted within the area of modern Scotland. Despite sporadic attempts at conquest and government between the first and fourth centuries AD, most of modern Scotland, inhabited by the Caledonians and the Maeatae, was not incorporated into the Roman Empire with Roman control over the area fluctuating. In the Roman imperial period (chronology), Roman imperial period, the area of Caledonia lay north of the River Forth, while the area now called England was known as ''Britannia'', the name also given to the Roman province roughly consisting of modern England and Wales and which replaced the earlier Ancient Greek designation as ''Albion''. Roman legions arrived in the territory of modern Scotland around AD 71, having conquered the Celtic Britons of southern Britannia over the preceding three decades. Aiming to complete the Roman conquest of Britannia, the Roman a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Edinburgh Council Area
The City of Edinburgh Council (Scottish Gaelic: ''Comhairle Baile Dhùn Èideann'') is the Local government in Scotland, local government authority covering the City of Edinburgh council area. Almost half of the council area is the built-up area of Edinburgh, capital of Scotland. With a population of in , it is Subdivisions of Scotland#Council areas, the second most populous local authority area in Scotland. The council took on its current form in 1996 under the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994, replacing the City of Edinburgh District Council of the Lothian region, which had been created in 1975. The history of local government in Edinburgh, however, stretches back much further. Around 1130, David I of Scotland, David I made the town a royal burgh and a burgh council, based at the Old Tolbooth, Edinburgh, Old Tolbooth is recorded continuously from the 14th century. The council is currently based in Edinburgh City Chambers with a main office nearby at Waverley Court. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Edinburgh Council
The City of Edinburgh Council (Scottish Gaelic: ''Comhairle Baile Dhùn Èideann'') is the local government authority covering the City of Edinburgh council area. Almost half of the council area is the built-up area of Edinburgh, capital of Scotland. With a population of in , it is the second most populous local authority area in Scotland. The council took on its current form in 1996 under the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994, replacing the City of Edinburgh District Council of the Lothian region, which had been created in 1975. The history of local government in Edinburgh, however, stretches back much further. Around 1130, David I made the town a royal burgh and a burgh council, based at the Old Tolbooth is recorded continuously from the 14th century. The council is currently based in Edinburgh City Chambers with a main office nearby at Waverley Court. History Origins The date of Edinburgh's formation as a burgh is unknown, but it is referred to as a royal burgh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Millennium BC
The 9th millennium BC spanned the years 9000 BC to 8001 BC (11 to 10 thousand years ago). In chronological terms, it is the first full millennium of the current Holocene epoch that is generally reckoned to have begun by 9700 BC (11.7 thousand years ago). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological and anthropological analysis, or by radiometric dating. In the Near East, especially in the Fertile Crescent, the transitory Epipalaeolithic age was gradually superseded by the Neolithic with evidence of agriculture across the Levant to the Zagros Mountains in modern-day Iran. The key characteristic of the Neolithic is agricultural settlement, albeit with wooden and stone tools and weapons still in use. It is believed that agriculture had begun in China by the end of the millennium. Elsewhere, especially in Europe, the Palaeolithic continued. Global environment In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh Boundaries Extension And Tramways Act 1920
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh had a population of in , making it the second-most populous city in Scotland and the seventh-most populous in the United Kingdom. The wider metropolitan area had a population of 912,490 in the same year. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament, the highest courts in Scotland, and the Palace of Holyroodhouse, the official residence of the British monarch in Scotland. It is also the annual venue of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sciences, and engineering. The University of Edinburgh was founded in 1582 and is now one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Law (economist)
John Law (pronounced in French in the traditional approximation of ''Laws'', the colloquial Scottish form of the name; 21 April 1671 – 21 March 1729) was a Scottish-French economist and financier. He rose to power in France where he created a novel financial scheme for French public finances known as Law's System () with two institutions at its core, John Law's Bank and John Law's Company (also known as the Mississippi company), ending in the devastating boom and bust "Mississippi Bubble" of 1720. Born in Scotland, Law was an accomplished gambler with an interest in the rules of probability. After killing a man in a duel and being sentenced to death, he fled to mainland Europe. He read economics and made the acquaintance of Philippe II, Duke of Orléans, who became regent for the juvenile Louis XV of France in 1715. In 1716 Philippe approved Law's plan to create a private bank which would take gold deposits in return for bank notes, loaning out the gold. It was structured as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
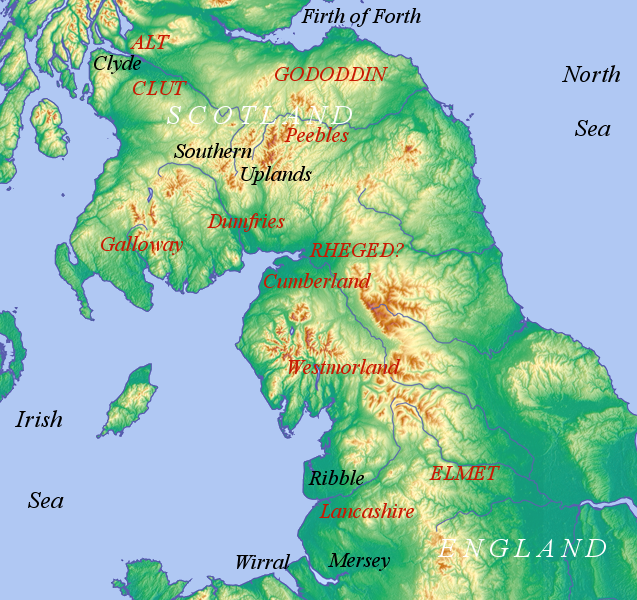
Cumbric Language
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Borough of Pendle, Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in Epipaleolithic Near East, the Levant and Epipaleolithic Caucasus, Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and the Middle East, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 Before Present, BP; in the Middle East (the Epipalaeolithic Near East) roughly 20,000 to 10,000 Before Present, BP. The term is less used of areas farther east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa. The type of culture associated with the Mesolithic varies between areas, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |