|
Cr23C6 Crystal Structure
Cr23C6 is the prototypical compound of a common crystal structure, discovered in 1933 as part of the chromium-carbon binary phase diagram. Over 85 known compounds adopt this structure type, which can be described as a NaCl-like packing of chromium cubes and cuboctahedra. Structure The space group of this structure is called Fmm (in Hermann–Mauguin notation) or "225" (in the International Tables for Crystallography). It belongs to a cubic crystal system, with Pearson symbol cF116. The shortest interatomic distances are between carbon and chromium atoms, which is expected on the basis of atomic size. The carbon atoms are in positions that cap each face of the chromium cubes and their coordination environment can be thought of as distorted square antiprisms formed from chromium atoms of both the cubes and the cuboctahedra. The closest Cr-Cr contacts are between members of a cuboctahedron, and the third closest are between members of a cube. The members of the cube, however, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cr23C6 Structure Type With Colored Polyhedra
CR or Cr may refer to: In business * Conversion rate, in marketing * Credit Record, in accounting * Crown Royal, a brand of Canadian whisky Organizations Religious organizations * Celtic reconstructionism, a form of Polytheism * Congregation of Clerics Regular of the Divine Providence (Theatines), a Roman Catholic religious order * Community of the Resurrection, an Anglican religious order * Congregation of the Resurrection, a Catholic religious order Other organizations * Choose Responsibility, a US non-profit addressing alcohol consumption by young adults * College of the Redwoods, a public two-year community college in Humboldt County, California, US * College Republicans, a college branch of the US political party * Czech Radio, a public radio broadcaster in the Czech Republic People * C. Rajagopalachari, Indian politician * Christina Ricci, American actress * Chris Rock, American comedian and actor * Cristiano Ronaldo, Portuguese footballer * Christopher Reeve, American a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Environment
In coordination chemistry, the first coordination sphere refers to the array of molecules and ions (the ligands) directly attached to the central metal atom. The second coordination sphere consists of molecules and ions that attached in various ways to the first coordination sphere. First coordination sphere The first coordination sphere refers to the molecules that are attached directly to the metal. The interactions between the first and second coordination spheres usually involve hydrogen-bonding. For charged complexes, ion pairing is important. In hexamminecobalt(III) chloride ( o(NH3)6l3), the cobalt cation plus the 6 ammonia ligands comprise the first coordination sphere. The coordination sphere of this ion thus consists of a central MN6 core "decorated" by 18 N−H bonds that radiate outwards. Second coordination sphere Metal ions can be described as consisting of series of two concentric coordination spheres, the first and second. More distant from the second coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Group Element
In chemistry and atomic physics, the main group is the group of elements (sometimes called the representative elements) whose lightest members are represented by helium, lithium, beryllium, boron, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine as arranged in the periodic table of the elements. The main group includes the elements (except hydrogen, which is sometimes not included) in groups 1 and 2 (s-block), and groups 13 to 18 (p-block). The s-block elements are primarily characterised by one main oxidation state, and the p-block elements, when they have multiple oxidation states, often have common oxidation states separated by two units. Main-group elements (with some of the lighter transition metals) are the most abundant elements on Earth, in the Solar System, and in the universe. Group 12 elements are often considered to be transition metals; however, zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd), and mercury (Hg) share some properties of both groups, and some scientists believe they should be includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rare-earth Element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides (yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous silvery-white soft heavy metals. Compounds containing rare earths have diverse applications in electrical and electronic components, lasers, glass, magnetic materials, and industrial processes. Scandium and yttrium are considered rare-earth elements because they tend to occur in the same ore deposits as the lanthanides and exhibit similar chemical properties, but have different electronic and magnetic properties. These metals tarnish slowly in air at room temperature and react slowly with cold water to form hydroxides, liberating hydrogen. They react with steam to form oxides, and at elevated temperature (400°C) ignite spontaneously. These elements and their compounds have no biological function other than in several specialized enzymes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Earth Metal
The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra).. The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure. Structurally, they (together with helium) have in common an outer s-orbital which is full; that is, this orbital contains its full complement of two electrons, which the alkaline earth metals readily lose to form cations with charge +2, and an oxidation state of +2. All the discovered alkaline earth metals occur in nature, although radium occurs only through the decay chain of uranium and thorium and not as a primordial element. There have been experiments, all unsuccessful, to try to synthesize element 120, the next potential member of the group. Characteristics Chemical As with other groups, the members of this family show patterns i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Metal
The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium (Li), sodium (Na), potassium (K),The symbols Na and K for sodium and potassium are derived from their Latin names, ''natrium'' and ''kalium''; these are still the origins of the names for the elements in some languages, such as German and Russian. rubidium (Rb), caesium (Cs), and francium (Fr). Together with hydrogen they constitute group 1, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table. All alkali metals have their outermost electron in an s-orbital: this shared electron configuration results in their having very similar characteristic properties. Indeed, the alkali metals provide the best example of group trends in properties in the periodic table, with elements exhibiting well-characterised homologous behaviour. This family of elements is also known as the lithium family after its leading element. The alkali metals are all shiny, soft, highly reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure and readil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can use d orbitals as valence orbitals to form chemical bonds. The lanthanide and actinide elements (the f-block) are called inner transition metals and are sometimes considered to be transition metals as well. Since they are metals, they are lustrous and have good electrical and thermal conductivity. Most (with the exception of group 11 and Group 12 element, group 12) are hard and strong, and have high melting and boiling temperatures. They form compounds in any of two or more different oxidation states and bind to a variety of ligands to form coordination complexes that are often coloured. They form many useful alloys and are often employed as catalysts in elemental form or in compounds such as coordination complexes and Surface prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermetallics
An intermetallic (also called an intermetallic compound, intermetallic alloy, ordered intermetallic alloy, and a long-range-ordered alloy) is a type of metallic alloy that forms an ordered solid-state compound between two or more metallic elements. Intermetallics are generally hard and brittle, with good high-temperature mechanical properties. They can be classified as stoichiometric or nonstoichiometic intermetallic compounds. Although the term "intermetallic compounds", as it applies to solid phases, has been in use for many years, its introduction was regretted, for example by Hume-Rothery in 1955. Definitions Research definition Schulze in 1967 defined intermetallic compounds as ''solid phases containing two or more metallic elements, with optionally one or more non-metallic elements, whose crystal structure differs from that of the other constituents''. Under this definition, the following are included: #Electron (or Hume-Rothery) compounds #Size packing phases. e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friauf Polyhedron
In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 equilateral triangle faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges (of two types). It can be constructed by truncating all 4 vertices of a regular tetrahedron at one third of the original edge length. A deeper truncation, removing a tetrahedron of half the original edge length from each vertex, is called rectification. The rectification of a tetrahedron produces an octahedron. A ''truncated tetrahedron'' is the Goldberg polyhedron containing triangular and hexagonal faces. A ''truncated tetrahedron'' can be called a cantic cube, with Coxeter diagram, , having half of the vertices of the cantellated cube (rhombicuboctahedron), . There are two dual positions of this construction, and combining them creates the uniform compound of two truncated tetrahedra. Area and volume The area ''A'' and the volume ''V'' of a truncated tetrahedron of edge length ''a'' are: :\begin A &= 7\sqrta^2 &&\approx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
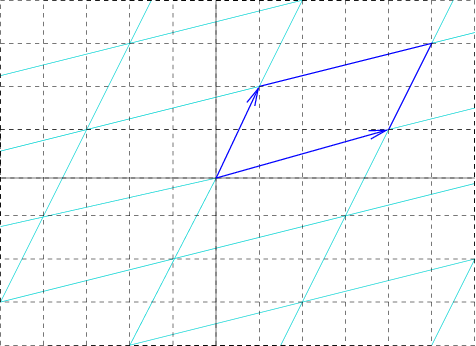
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Size
The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atom, usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the outermost isolated electron. Since the boundary is not a well-defined physical entity, there are various non-equivalent definitions of atomic radius. Four widely used definitions of atomic radius are: Van der Waals radius, ionic radius, metallic radius and covalent radius. Typically, because of the difficulty to isolate atoms in order to measure their radii separately, atomic radius is measured in a chemically bonded state; however theoretical calculations are simpler when considering atoms in isolation. The dependencies on environment, probe, and state lead to a multiplicity of definitions. Depending on the definition, the term may apply to atoms in condensed matter, covalently bonding in molecules, or in ionized and excited states; and its value may be obtained through experimental measurements, or computed from theoretical mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns that repeat along the principal directions of three-dimensional space in matter. The smallest group of particles in the material that constitutes this repeating pattern is the unit cell of the structure. The unit cell completely reflects the symmetry and structure of the entire crystal, which is built up by repetitive translation of the unit cell along its principal axes. The translation vectors define the nodes of the Bravais lattice. The lengths of the principal axes, or edges, of the unit cell and the angles between them are the lattice constants, also called ''lattice parameters'' or ''cell parameters''. The symmetry properties of the crystal are described by the concept of space groups. All possible symmetric arrangements of partic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |