|
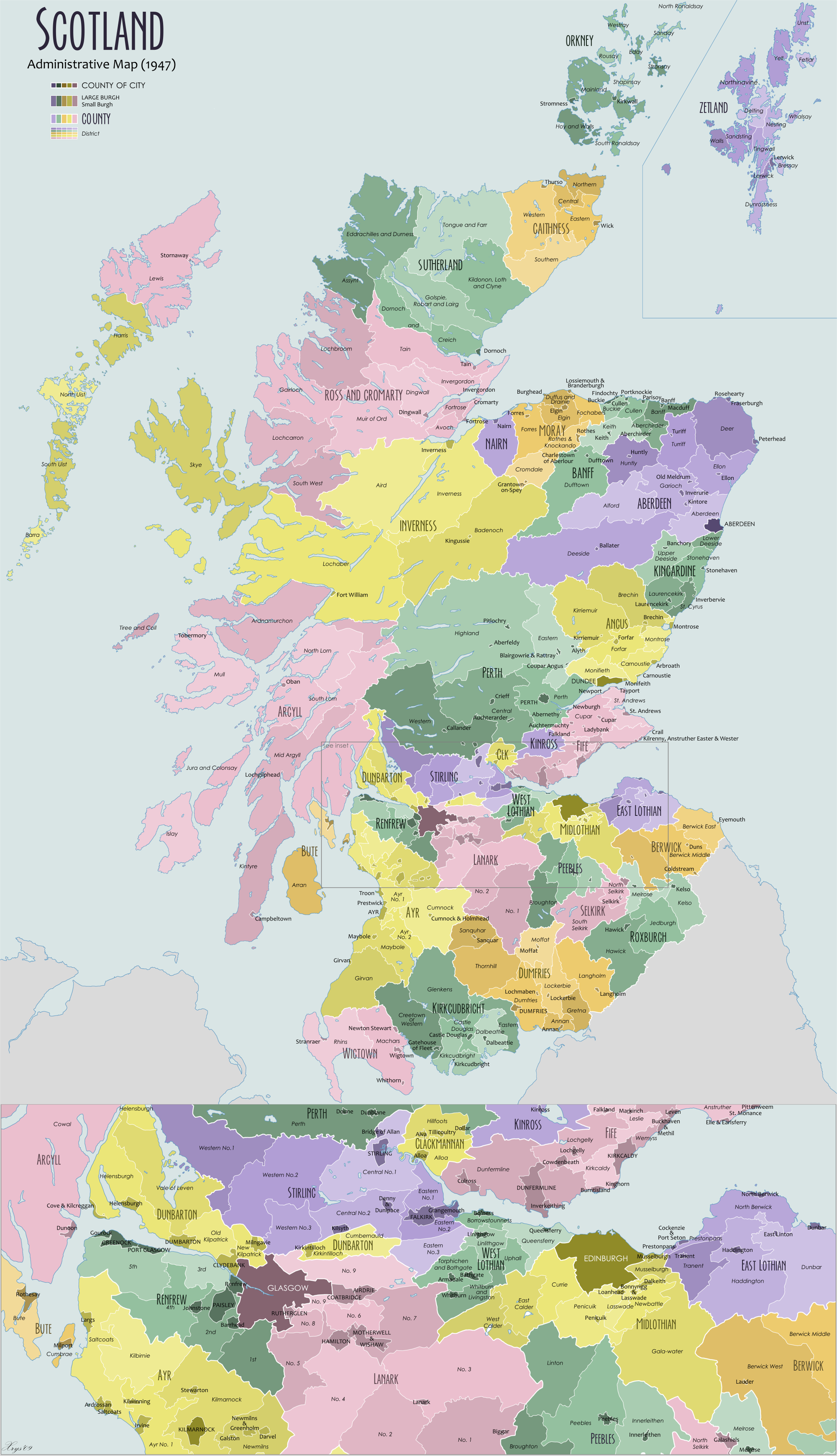
County Of Dumfries
Dumfriesshire or the County of Dumfries or Shire of Dumfries () is a Counties of Scotland, historic county and registration county in southern Scotland. The Dumfries lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area covers a similar area to the historic county. In terms of historic counties it borders Kirkcudbrightshire to the west, Ayrshire to the north-west, Lanarkshire, Peeblesshire and Selkirkshire to the north, and Roxburghshire to the east. To the south is the coast of the Solway Firth, and on the other side of the border between Scotland and England the England, English county of Cumberland. Dumfriesshire has three traditional subdivisions, based on the three main valleys in the county: Annandale, Dumfries and Galloway, Annandale, Eskdale, Scotland, Eskdale and Nithsdale. These had been independent provinces of Scotland, provinces in medieval times but were gradually superseded as administrative areas by the area controlled by the sheriff principal, sheriff of Dumfries, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shires Of Scotland
The counties or shires of Scotland () were historic subdivisions of Scotland. The shires were originally established in the Middle Ages for judicial purposes, being territories over which a Sheriff principal, sheriff had jurisdiction. They were distinct from the various older mormaerdoms, earldoms and other territories into which Scotland was also divided, which are collectively termed the provinces of Scotland by modern historians. The provinces gradually lost their functions, whereas the shires gradually gained functions. From the 16th century, the shires served as county constituency, constituencies, electing shire commissioners to the Parliament of Scotland. From 1667 each shire had Commissioners of Supply, commissioners of supply responsible for collecting local taxes; the commissioners of supply were subsequently given various local government functions as well. From 1797, the shires also served as areas for organising the militia, which was the responsibility of a lord-li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annandale, Dumfries And Galloway
Annandale is a district of Dumfriesshire, Scotland, centred on the dale or valley of the River Annan. It runs north–south through the Southern Uplands from Annanhead (north of Moffat) to Annan, Dumfries and Galloway, Annan on the Solway Firth. It is bordered by Nithsdale to the west and Eskdale, Scotland, Eskdale to the east. The Annandale Way runs the length of the valley, a distance of some . History Annandale is famous for its connection with Robert I of Scotland, Robert the Bruce, as the de Brus family was given this land by David I of Scotland, David I in 1124 as one of the border lordships when David became David, Prince of the Cumbrians, Prince of the Cumbrians. Along with Carrick, Scotland, Carrick, these lands acted as a buffer between the quasi-independent Lordship or Kingdom of Galloway and David's lands of Strathclyde and Cumbria. See also *Annandale distillery *Annadale, Shimla *Lord of Annandale, The Lordship of Annandale References External linksHistoric map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longbridge Moor
Longbridge is an area in the south-west of Birmingham, England, located near the border with Worcestershire, historically being within this place. Public transport Longbridge is described as a hub for public transport with a number of bus services run by Kev's Coaches and National Express West Midlands passing through it with destinations including Birmingham City Centre, West Bromwich and the Queen Elizabeth Hospital in Edgbaston. West Midlands Railway serves Longbridge railway station on the Cross City Line, with destinations at Redditch or Bromsgrove and Four Oaks or Lichfield with connections to Hereford and Nottingham at University station or nationwide at Birmingham New Street station. In 2020 a large multi-storey carpark was built near Longbridge station as a park and ride facility to reduce car journeys into the city centre. Some improvements to Longbridge station were also carried out in 2020 though one side of the station remains without a lift facility. Situa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lochar Moss
Lochar may refer to: * Lochar (ward) Lochar is one of the thirteen wards used to elect members of the Dumfries and Galloway Council. It elects four Councillors. Councillors Election results 2022 election 2017 election 2017 Dumfries and Galloway Council election 2 ..., Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland * Lochar Moss Torc, an Iron Age brass torc * Lochar Thistle F.C., Dumfries, Scotland * Lochar Water, a stream in Dumfries and Galloway See also * Locher (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Craigs Moss
Craigs (, "The Rocks") is a townland in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is part of the Finvoy Civil Parish situated in the history Barony of Kilconway. It is a relatively large townland at a 4.38 square miles (2,800 acres), making it the ninth largest townland in County Antrim. Modern archaeological excavations at Craigs found pottery and evidence of sod homes from the medieval period. Craigs is a former civil parish and ecclesiastical parish within the Church of Ireland that consisted of the townland of Craigs, Cullybackey Cullybackey or Cullybacky () is a large village in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It lies 3 miles north-west of Ballymena, on the banks of the River Main, and is part of Mid and East Antrim district. It had a population of 2,569 people in th ... and Dreen. References Geography of County Antrim {{Antrim-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holm (island)
There are numerous islands containing the word ''holm'', mainly in northern Europe. In many cases the name is derived from the Old Norse ''holmr'', meaning "a small and rounded islet". These include: Denmark * Bornholm * Hørsholm * Munkholm * Slotsholmen Germany * Dänholm * Holm (Flensburg), Holm in Flensburg * Holm (Schleswig), Holm in Schleswig Greenland * Holm Ø Ireland * Holmpatrick (the original name for the town of Skerries, County Dublin, and one of its islands Sweden *Stockholm (originally the islet Helgeandsholmen in central Stockholm) *Djursholm (suburb of Stockholm) *Tureholm (island), Tureholm *There are hundreds of islets in the Stockholm archipelago containing the word "holm" United Kingdom England *Holm Island in the River Thames *Steep Holm in the Bristol Channel *Portholme in the River Great Ouse *Holme-next-the-Sea in Norfolk Northern Ireland *Ballynahinch, County Down () Orkney, Scotland *Glimps Holm *Helliar Holm *Holm of Papa *Lamb Holm *Linga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table (landform)
A tableland is an area containing elevated landforms characterized by a distinct, flat, nearly level, or gently undulating surface. They often exhibit steep, cliff-like edges, known as escarpments, that separate them from surrounding lowlands. Depending on either their size, other physical characteristics, or geographic location, the landforms comprising a tableland are individually referred to by a number of names including butte, mesa, plateau, potrero, tepui, or tuya. A homologous landform under the sea is called either a tablemount or guyot. Sedimentary tablelands Sedimentary tablelands are tablelands that typically have developed from the erosion of coarse-grained, clastic, sedimentary rocks in the form of relatively flat-lying sandstones and conglomerates that have not been strongly deformed by tectonics. The primary control on the geomorphology of sedimentary tablelands is the dip of the layers of the sandstones, conglomerates, and associated sedimentary strata. Sedim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands () are the southernmost and least populous of mainland Scotland's three major geographic areas (the others being the Central Lowlands and the Highlands). The term is used both to describe the geographical region and to collectively denote the various ranges of hills and mountains within this region. An overwhelmingly rural and agricultural region, the Southern Uplands are partly forested and contain many areas of open moorland - the hill names in the area are congruent with these characteristics. Geology The Southern Uplands consist mainly of Silurian sedimentary deposits deposited in the Iapetus Ocean 420 million years ago. These rocks were pushed up from the sea bed into an accretionary wedge during the Caledonian orogeny, roughly 400 million years ago ( Ma), when the continents and terranes of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia collided. The Caledonian orogeny is named for Caledonia, a Latin name for Scotland. The majority of the rocks are weak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridle Path To Enterkin Pass
A bridle is a piece of equipment used to direct a horse. As defined in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the "bridle" includes both the that holds a Bit (horse), bit that goes in the mouth of a horse, and the reins that are attached to the bit (horse), bit. It provides additional control and communication through rein pressure (Oxford English Dictionary, n.d., para. 1). Headgear without a bit that uses a noseband to control a horse is called a hackamore, or, in some areas, a bitless bridle. There are many different designs with many different name variations, but all use a noseband that is designed to exert pressure on sensitive areas of the animal's face to provide direction and control. The bridle was devised by Indo-European herders of the Pontic-Caspian steppes to control horses between 3000 BC and 2000 BC. Parts The bridle consists of the following elements: * Crownpiece: The crownpiece, headstall (US) or headpiece (UK) goes over the horse's head just behind the anima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Areas Of Scotland
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" (), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Gaelic Names) (Scotland) Act 1997 of being known (but not re-designated) as a "''comhairle''" when opting for a Gaelic name; only ''Comhairle nan Eilean Siar'' (Council of the Western Isles) has chosen this option, whereas the Highland Council (''Comhairle na Gàidhealtachd'') has adopted its Gaelic form alongside its English equivalent, informally. The council areas have been in existence since 1 April 1996, under the provisions of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994. Historically, Scotland was divided into 34 counties or shires. Although these no longer have any administrative function, they are still used to some extent in Scotland for cultural and geographical purposes, and some of the current council areas are named after them. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries And Galloway
Dumfries and Galloway (; ) is one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland, located in the western part of the Southern Uplands. It is bordered by East Ayrshire, South Ayrshire, and South Lanarkshire to the north; Scottish Borders to the north-east; the English county of Cumbria, the Solway Firth, and the Irish Sea to the south, and the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel to the west. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, located to the west of Dumfries on the North Channel coast. Dumfries and Galloway corresponds to the counties of Scotland, historic shires of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the last two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The three counties were combined in 1975 to form a single regions and districts of Scotland, region, with four districts within it. The districts were abolished in 1996, since when Dumfries and Galloway has been a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheriff Principal
In Scotland a sheriff principal (''pl''. sheriffs principal) () is a judge in charge of a sheriffdom with judicial, quasi-judicial, and administrative responsibilities. Sheriffs principal have been part of the judiciary of Scotland since the 11th century. Sheriffs principal were originally appointed by the monarch of Scotland, and evolved into a heritable jurisdiction before appointment was again vested in the Crown and the monarch of the United Kingdom following the passage of the Heritable Jurisdictions (Scotland) Act 1746. Under the Sheriff Courts (Scotland) Act 1971 (as amended), each sheriff principal is appointed by the monarch of the United Kingdom on the advice of the First Minister of Scotland, who is advised by the Judicial Appointments Board for Scotland. As of May 2017 there were six sheriffs principal, each of whom has responsibility not only as a judge, but for the administration of justice in their respective sheriffdoms. Sheriffs principal have to ensure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |