|
Count Anton Alexander Von Auersperg
Count Anton Alexander von Auersperg, also known under the name Anastasius Grün (11 April 180612 September 1876), was an Austrian poet and liberal politician from Carniola, a former Habsburg crown land in today's Slovenia. Early life He was born in Laibach (Ljubljana), and was head of the Thurn am Hart/Krain branch of the Carniolan line of the House of Auersperg. Anton Alexander was the only child of his parents, Count Alexander Maria Josef Riegfried Joachim von Auersperg (1770-1818) and his wife, Baroness Maria Rosalia Cecilia von Billichgrätz zu Baumkircherthurm und Hilzenegkh (1786-1836). Anton's maternal uncle in law, and also paternal first cousin, was Count Rihard Ursini von Blagay, a Slovene aristocrat, botanist and patron of the arts. He received his education first at the University of Graz and then at Vienna, where he studied jurisprudence. In Vienna, he met with fellow Carniolan countryman France Prešeren, who would later become the national poet of the Sloven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
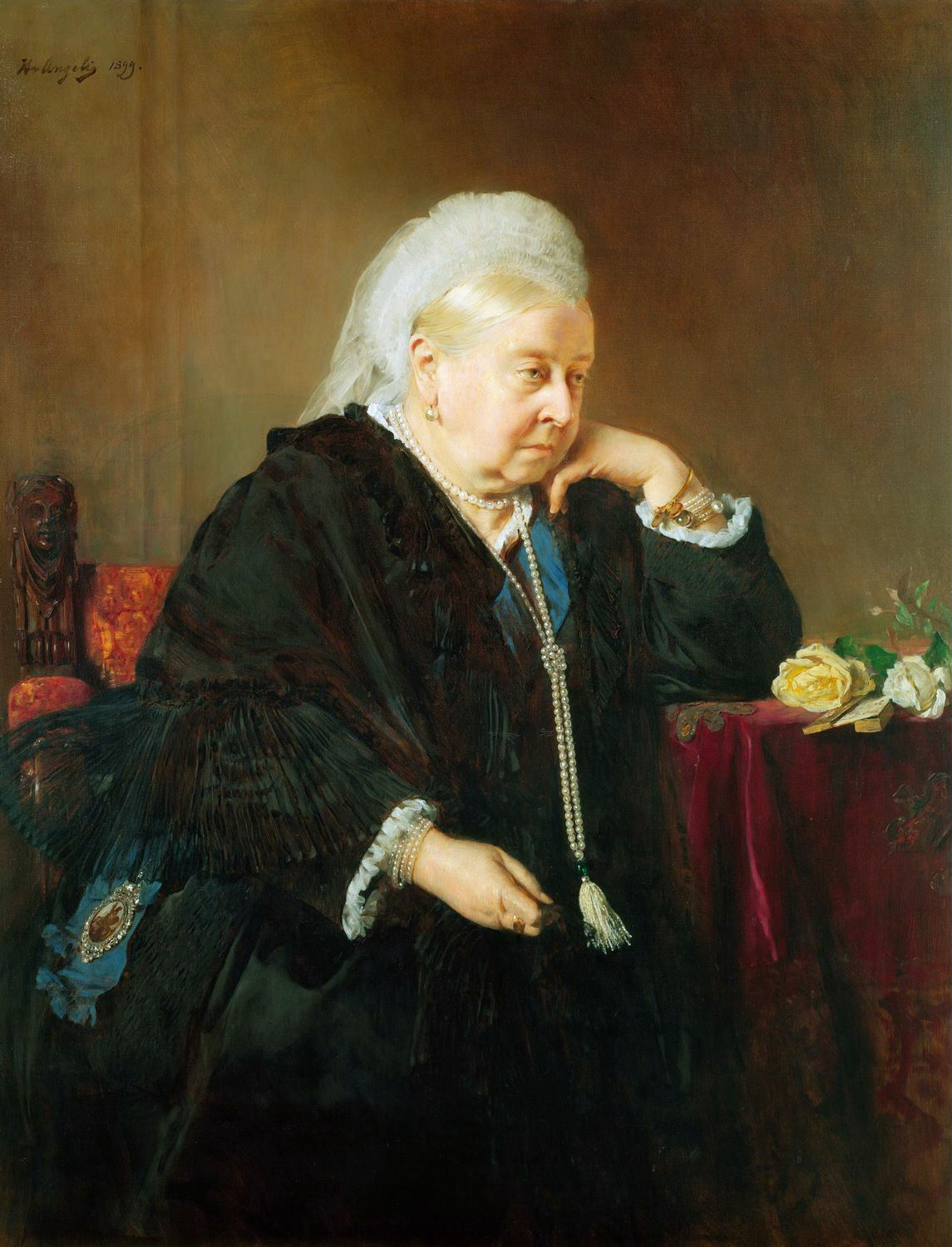
Heinrich Von Angeli
Heinrich Anton von Angeli (8 July 1840 – 21 October 1925) was an Austrian historian and portrait painter. Life The Angeli family was originally from Venice and was ennobled by the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian II in 1565.Braun-Ronsdorf (1953), p. 288 Angeli was born in 1840 in Ödenburg, then part of the Austrian empire, now known as Sopron in Hungary. He studied at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna, the Kunstakademie Düsseldorf, and in Munich, before moving back to Vienna in 1862. From 1870 he travelled between Berlin, London, and Vienna, producing portraits. The success of Angeli at painting society portraits was partly due to his skill in depicting uniforms, pearls, and other jewels. Unlike painters such as Franz Xaver Winterhalter, Angeli worked in a naturalistic style and preferred to portray his sitters as they were. His 1875 portrait of Queen Victoria earned him praise from the monarch for its honesty. As well as royal figures and politicians, he painted other notabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohemian Style
The Bohemian style, often termed 'Boho chic', is a fashion and lifestyle choice characterized by its unconventional and free-spirited essence. While its precise origins are debated, Bohemian style is believed to have been influenced by the nomadic lifestyle of the Romani people during the late 19th century to the early 20th century. The term 'Bohemian' itself derives from the French 'Bohémien,' originally associated with the Roma community due to a historical misconception that they originated from Bohemia, a region in the Czech Republic. Throughout history, Bohemian fashion has undergone significant transformations, reflecting the cultural shifts and influences of each era. Today, contemporary Bohemian fashion embraces flowing fabrics, vibrant colors, and natural, woven materials instead of knits. This style draws inspiration from various sources, including the counterculture movements of the 1960s and 1970s, reminiscent of the attire worn by attendees of the inaugural W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Deschmann
Karl may refer to: People * Karl (given name), including a list of people and characters with the name * Karl der Große, commonly known in English as Charlemagne * Karl of Austria, last Austrian Emperor * Karl (footballer) (born 1993), Karl Cachoeira Della Vedova Júnior, Brazilian footballer * Karl (surname) In myth * Karl (mythology), in Norse mythology, a son of Rig and considered the progenitor of peasants (churl) * ''Karl'', giant in Icelandic myth, associated with Drangey island Vehicles * Opel Karl, a car * ST ''Karl'', Swedish tugboat requisitioned during the Second World War as ST ''Empire Henchman'' Other uses * Karl, Germany, municipality in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany * ''Karl-Gerät'', AKA Mörser Karl, 600mm German mortar used in the Second World War * KARL project, an open source knowledge management system * Korean Amateur Radio League, a national non-profit organization for amateur radio enthusiasts in South Korea * KARL, a radio station in Minnesota * Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diet (assembly)
In politics, a diet ( ) is a formal deliberative assembly or legislature. The term is used for some assemblies such as the German Imperial Diet (the general assembly of the Imperial Estates of the Holy Roman Empire), as well as a designation for modern-day legislative bodies of certain countries and states such as the National Diet of Japan, or the German Bundestag, the Federal Diet. Etymology The term (also in the nutritional sense) might be derived from Medieval Latin ', meaning both "parliamentary assembly" and "daily food allowance", from earlier Latin , possibly from the Greek ("arbitration"), or transcribing Classical Greek (), meaning "way of living", and hence also "diet" (regular food), "regular (daily) work". Through a false etymology, reflected in Latin spelling change in medieval Europe that replaced the ''ae'' with ''e'', the word ''diaeta'' came to be associated with another Latin word , which means "day". Day thus came to be used in postclassical Europe in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realism (arts)
Realism in the arts is generally the attempt to Representation (arts), represent subject-matter truthfully, without artificiality, exaggeration, or speculative fiction, speculative or supernatural elements. The term is often used interchangeably with naturalism, although these terms are not necessarily synonymous. Naturalism, as an idea relating to visual representation in Western art, seeks to depict objects with the least possible amount of distortion and is tied to the development of linear perspective and illusionism in Renaissance Europe. Realism, while predicated upon naturalistic representation and a departure from the idealization of earlier academic art, often refers to a Realism (art movement), specific art historical movement that originated in France in the aftermath of the French Revolution of 1848. With artists like Gustave Courbet capitalizing on the mundane, ugly or sordid, realism was motivated by the renewed interest in the commoner and the rise of leftist polit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
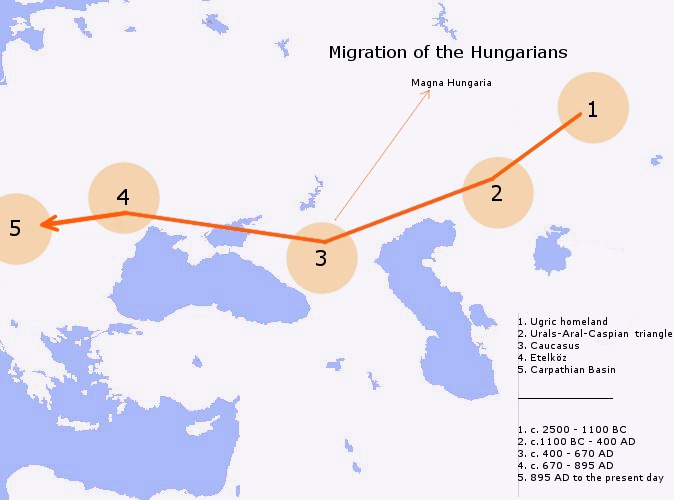
Magyars
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common culture, language and history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric branch of the Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty and Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. In addition, significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina, and therefore constitute the Hungarian diaspo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
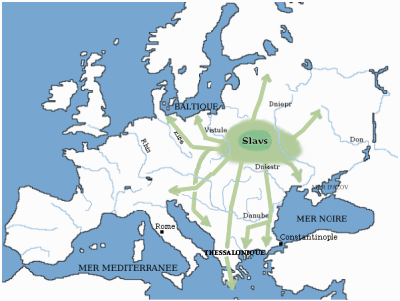
Slavic Peoples
The Slavs or Slavic people are groups of people who speak Slavic languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout the northern parts of Eurasia; they predominantly inhabit Central Europe, Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe, and North Asia, Northern Asia, though there is a large Slavic minority scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and a substantial Slavic diaspora in the Americas, Western Europe, and Northern Europe. Early Slavs lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately from the 5th to the 10th century AD), and came to control large parts of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe between the sixth and seventh centuries. Beginning in the 7th century, they were gradually Christianization of the Slavs, Christianized. By the 12th century, they formed the core population of a number of medieval Christian states: East Slavs in the Kievan Rus', South Slavs in the First Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsrat (Austria)
The Imperial Council was the legislature of the Austrian Empire from 1861 until 1918. It was a bicameral body: the upper house was the House of Lords (Austria), House of Lords (), and the lower house was the House of Deputies (Austria), House of Deputies (). To become law, bills had to be passed by both houses, signed by the government minister responsible, and then granted royal assent by the Emperor of Austria, Emperor. After having been passed, laws were published in the ''Reichsgesetzblatt'' (lit. Reich Law Government gazette, Gazette). In addition to the Imperial Council, the fifteen individual Cisleithania#Crown lands, crown lands of Cisleithania had their own Landtag, diets (). The seat of the Imperial Council from 4 December 1883 was in the Austrian Parliament Building, Parliament Building on Vienna Ring Road, Ringstraße in Vienna. Prior to the completion of this building, the House of Lords met in the Estates House of Lower Austria, and the House of Deputies met in a temp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frankfurt Parliament
The Frankfurt National Assembly () was the first freely elected parliament for all German Confederation, German states, including the German-populated areas of the Austrian Empire, elected on 1 May 1848 (see German federal election, 1848). The session was held from 18 May 1848 to 30 May 1849 in the St. Paul's Church, Frankfurt am Main, Paulskirche at Frankfurt am Main. Its existence was both part of and the result of the Revolutions of 1848 in the German states, "March Revolution" within the states of the German Confederation. After long and controversial debates, the assembly produced the so-called Frankfurt Constitution (''Paulskirchenverfassung'' or St. Paul's Church Constitution, officially the ''Verfassung des Deutschen Reiches'') which proclaimed a German Empire (1848–1849), German Empire based on the principles of parliamentary democracy. This constitution fulfilled the main demands of the liberal and Nation-state, nationalist Social movement, movements of the Vormärz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolution Of 1848
The revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the springtime of the peoples or the springtime of nations, were a series of revolutions throughout Europe over the course of more than one year, from 1848 to 1849. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in European history to date. The revolutions were essentially democratic and liberal in nature, with the aim of removing the old monarchical structures and creating independent nation-states, as envisioned by romantic nationalism. The revolutions spread across Europe after an initial revolution began in Italy in January 1848. Over 50 countries were affected, but with no significant coordination or cooperation among their respective revolutionaries. Some of the major contributing factors were widespread dissatisfaction with political leadership, demands for more participation in government and democracy, demands for freedom of the press, other demands made by the working class for economic rights, the upsurge of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diet (assembly)
In politics, a diet ( ) is a formal deliberative assembly or legislature. The term is used for some assemblies such as the German Imperial Diet (the general assembly of the Imperial Estates of the Holy Roman Empire), as well as a designation for modern-day legislative bodies of certain countries and states such as the National Diet of Japan, or the German Bundestag, the Federal Diet. Etymology The term (also in the nutritional sense) might be derived from Medieval Latin ', meaning both "parliamentary assembly" and "daily food allowance", from earlier Latin , possibly from the Greek ("arbitration"), or transcribing Classical Greek (), meaning "way of living", and hence also "diet" (regular food), "regular (daily) work". Through a false etymology, reflected in Latin spelling change in medieval Europe that replaced the ''ae'' with ''e'', the word ''diaeta'' came to be associated with another Latin word , which means "day". Day thus came to be used in postclassical Europe in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |