 |
Cosmic Ray Energetics And Mass Experiment
Cosmic Ray Energetics and Mass (CREAM) is an experiment to determine the composition of cosmic rays up to the 1015 eV (also known as the "knee prospect") in the cosmic ray spectrum. It has been hypothesized that the knee prospect of the cosmic ray spectrum can be explained by the theoretical maximum energy that a supernova can accelerate particles to according to Fermi acceleration. The measurements are accomplished using a timing-based charge detector and transition radiation detector sent to an altitude of at least 34 km (21 mi) with aid of a high-altitude balloon. After launching from McMurdo Station in Antarctica, the balloon will stay aloft for 60–100 days gathering data on charges and energies of the unimpeded cosmic rays that strike the detectors. Expected outcomes One of the advantages of this type of experiment is that it is possible to identify the original particle that would have caused the air shower detected by ground-based detectors. Maximum detectabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk are deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Nuclear Instruments And Methods In Physics Research
''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research'' (Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res.) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier Elsevier ( ) is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell (journal), Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, .... It was established in 1957 as ''Nuclear Instruments''. It focuses on detectors descriptions and data analysis methods. History *''Nuclear Instruments'' (1957–1958) *''Nuclear Instruments and Methods'' (1959–1981) *''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research'' (1981–present) :*''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section A: Accelerators, Spectrometers, Detectors and Associated Equipment'' (1984–present) :*''Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms'' (1984–present) External links'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
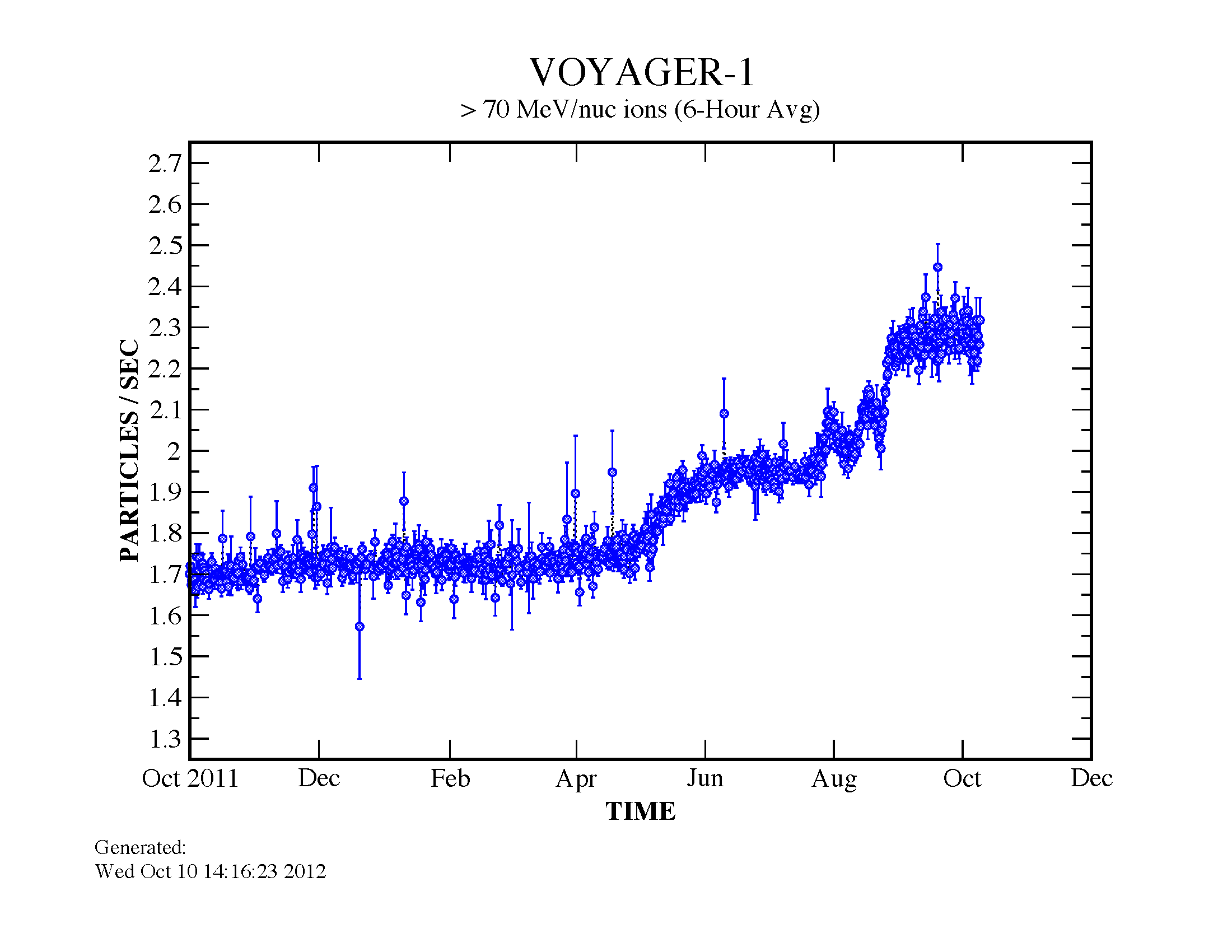 |
Cosmic Ray System
Cosmic Ray Subsystem (CRS, or Cosmic Ray System) is an instrument aboard the ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2'' spacecraft of the NASA Voyager program, and it is an experiment to detect cosmic rays. The CRS includes a High-Energy Telescope System (HETS), Low-Energy Telescope System (LETS), and The Electron Telescope (TET). It is designed to detect energetic particles and some of the requirements were for the instrument to be reliable and to have enough charge resolution. It can also detect the energetic particles like protons from the Galaxy or Earth's Sun. As of 2019, CRS is one of the active remaining instruments on both Voyager spacecraft, and it is described by as being able to detect electrons from 3–110 MeV and cosmic ray nuclei 1–500 MeV/n. All three systems used solid-state detectors. CRS is one of the five fields and particle experiments on each spacecraft, and one of the goals is to gain a deeper understanding of the solar wind. Other objects of study including elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Northern Kentucky University
Northern Kentucky University is a public university in Highland Heights, Kentucky, United States. Established in 1968, it is the youngest of Kentucky's eight public universities. The university has seven constituent colleges in arts and science, business, education, informatics, health, and the Salmon P. Chase College of Law. History  Northern Kentucky University began in 1948, when an extension campus for the University of Kentucky was opened in Covington, Kentucky, known as the UK Northern Extension Center. After 20 years in operation as an extension center for UK, it became an autonomous four-year college under the nam ...
Northern Kentucky University began in 1948, when an extension campus for the University of Kentucky was opened in Covington, Kentucky, known as the UK Northern Extension Center. After 20 years in operation as an extension center for UK, it became an autonomous four-year college under the nam ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Wallops Flight Facility
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately north-northeast of Norfolk, VA, Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, and primarily serves to support science and exploration missions for NASA and other Federal government of the United States, federal agencies. WFF includes an extensively instrumented range to support launches of more than a dozen types of sounding rockets; small expendable suborbital and orbital rockets; high-altitude balloon flights carrying scientific instruments for atmospheric and astronomical research; and, using its Research Airport, flight tests of aeronautical research aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles. There have been over 16,000 launches from the rocket testing range at Wallops since its founding in 1945 in the quest for information on the flight characteristi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C., in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959, as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC employs about 10,000 civil servants and contractors. Named for American rocket propulsion pioneer Robert H. Goddard, it is one of ten major NASA field centers. GSFC is partially within the former Goddard, Maryland, Goddard census-designated place; it has a Greenbelt, Maryland, Greenbelt mailing address.CENSUS 2000 BLOCK MAP: GODDARD CDP (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved September 1, 2018. 1990 Census map of Prince George's County [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Kyungpook National University
Kyungpook National University (; abbreviated as KNU or Kyungdae ()) is one of ten Flagship Korean National Universities representing Gyeongbuk Province in South Korea. It is located in Daegu, which used to be the capital city of the Gyeongbuk Province, South Korea. Establishment The medical school of Kyungpook National University began in 1923. Kyungpook National University was founded in September 1946 by upgrading the Colleges of Education, Medicine, and Agriculture in Daegu to a National College. In October 1951, the Colleges of Education, Medicine, Agriculture, Liberal Arts and Sciences, and Law and Political Sciences were combined into Kyungpook National University. Other departments, including Engineering and Dentistry, were established sequentially, forming the university as it is known today. Now KNU operate PPE programme. Administration As of November 20, 2021, Won-hwa Hong is the university's PresidenHe graduated from the KNU Department of Architecture and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
National Autonomous University Of Mexico
The National Autonomous University of Mexico (, UNAM) is a public university, public research university in Mexico. It has several campuses in Mexico City, and many others in various locations across Mexico, as well as a presence in nine countries. It also has 34 research institutes, 26 museums, and 18 historic sites. A portion of (University City), UNAM's main campus in Mexico City, is a UNESCO World Heritage site that was designed and decorated by some of Mexico's best-known architects and painters. The campus hosted the main events of the 1968 Summer Olympics, and was the birthplace of the Mexican Movement of 1968, student movement of 1968. All Mexican Nobel laureates have been alumni of UNAM. In 2009, the university was awarded the Princess of Asturias Awards, Prince of Asturias Award for Communication and Humanities. More than 25% of the total scientific papers published by Mexican academics come from researchers at UNAM. UNAM was founded in its modern form, on 22 Septemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Sungkyunkwan University
Sungkyunkwan University (SKKU or ''Seongdae'', ) is a private research university with campuses in Seoul and Suwon, South Korea. The institution traces its origins to the historic Sungkyunkwan founded in 1398 in central Seoul. SKKU Official Brochure 2013 As the foremost educational institution during the period, it was governed by the great code of the state administration Gyeongguk Daejeon, the great code with royal assent. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsylvania, United States. Founded in 1855 as Farmers' High School of Pennsylvania, Penn State was named the state's first land-grant university eight years later, in 1863. Its primary campus, known as Penn State University Park, is located in State College, Pennsylvania, State College and College Township, Pennsylvania, College Township. Penn State enrolls more than 89,000 students, of which more than 74,000 are undergraduates and more than 14,000 are postgraduates. In addition to its land-grant designation, the university is a National Sea Grant College Program, sea-grant, National Space Grant College and Fellowship Program, space-grant, and one of only six Sun Grant Association, sun-grant universities. It is Carnegie Classification of Instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
University Of Maryland, College Park
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD is the Flagship university, flagship institution of the University System of Maryland. It is known as the biggest university in the state of Maryland. UMD is the largest university in Maryland and the Washington metropolitan area. Its eleven schools and colleges offer over 200 degree-granting programs, including 113 undergraduate majors, 107 Master's degree, master's programs, and 83 Doctorate, doctoral programs. UMD's athletic teams are known as the Maryland Terrapins and compete in NCAA Division I as a member of the Big Ten Conference. A member of the Association of American Universities, The University of Maryland's proximity to Washington, D.C. has resulted in many research partnerships with the Federal government of the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |