|
Corpus Luteum
The corpus luteum (Latin for "yellow body"; : corpora lutea) is a temporary endocrine structure in female ovaries involved in the production of relatively high levels of progesterone, and moderate levels of estradiol, and inhibin A. It is the remains of the ovarian follicle that has released a mature ovum during a previous ovulation. The corpus luteum is colored as a result of concentrating carotenoids (including lutein) from the diet and secretes a moderate amount of estrogen that inhibits further release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and thus secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). A new corpus luteum develops with each menstrual cycle. Development and structure The corpus luteum develops from an ovarian follicle during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle or oestrous cycle, following the release of a secondary oocyte from the follicle during ovulation. The follicle first forms a corpus hemorrhagicum before it beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroma Of Ovary
The stroma of the ovary is a unique type of connective tissue abundantly supplied with blood vessels, consisting for the most part of spindle-shaped stroma cells. These appear similar to fibroblasts. The stroma also contains ordinary connective tissue such as reticular fibers and collagen. Ovarian stroma differs from typical connective tissue in that it contains a high number of cells. The stroma cells are distributed in such a way that the tissue appears to be whorled. Stromal cells associated with maturing follicles may acquire endocrine function and secrete estrogens. The entire ovarian stroma is highly vascular. On the surface of the organ this tissue is much condensed, and forms a layer ( tunica albuginea) composed of short connective-tissue fibers, with fusiform cells between them. The stroma of the ovary may contain interstitial cells resembling those of the testis. See also * stroma (other) * Stromal cell Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luteal Phase
The menstrual cycle is on average 28 days in length. It begins with Menstruation, menses (day 1–7) during the follicular phase (day 1–14), followed by ovulation (day 14) and ending with the luteal phase (day 14–28). While historically, medical experts believed the luteal phase to be relatively fixed at approximately 14 days (i.e. days 14–28), recent research suggests that there can be wide variability in luteal phase lengths not just from person to person, but from cycle to cycle within one person. The luteal phase is characterized by changes to hormone levels, such as an increase in progesterone and estrogen levels, decrease in gonadotropins such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), changes to the Endometrium, endometrial lining to promote Implantation (embryology), implantation of the fertilized egg, and development of the corpus luteum. In the absence of fertilization by sperm, the corpus luteum degenerates leading to a decrease in progeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroidogenic Acute Regulatory Protein
The steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, commonly referred to as StAR (STARD1), is a transport protein that regulates cholesterol transfer within the mitochondria, which is the rate-limiting step in the production of steroid hormones. It is primarily present in steroid-producing cells, including theca cells and luteal cells in the ovary, Leydig cells in the testis and cell types in the adrenal cortex. Function Cholesterol needs to be transferred from the outer mitochondrial membrane to the inner membrane where cytochrome P450scc enzyme (CYP11A1) cleaves the cholesterol side chain, which is the first enzymatic step in all steroid synthesis. The aqueous phase between these two membranes cannot be crossed by the lipophilic cholesterol, unless certain proteins assist in this process. A number of proteins have historically been proposed to facilitate this transfer including: sterol carrier protein 2 (SCP2), steroidogenic activator polypeptide (SAP), peripheral benzodiazepine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of serine-threonine kinases whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulation of glycogen, sugar, and lipid metabolism. It should not be confused with 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMP-activated protein kinase). History Protein kinase A, more precisely known as adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP)-dependent protein kinase, abbreviated to PKA, was discovered by chemists Edmond H. Fischer and Edwin G. Krebs in 1968. They won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1992 for their work on phosphorylation and dephosphorylation and how it relates to PKA activity. PKA is one of the most widely researched Protein kinase, protein kinases, in part because of its uniqueness; out of 540 different protein kinase genes that make up the human kinome, only one other protein kinase, casein kinase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-density Lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density naming convention), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to Cell (biology), cells. LDL has been associated with the progression of atherosclerosis. Overview Lipoproteins transfer lipids (fats) around the body in the extracellular fluid, making fats available to body cells for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins, typically 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by a single apolipoprotein B for LDL and the larger particles). A single LDL particle is about 22–27.5 nanometers in diameter, typically transporting 3,000 to 6,000 fat molecules per part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granulosa Cell
A granulosa cell or follicular cell is a somatic cell of the sex cord that is closely associated with the developing female gamete (called an oocyte or egg) in the ovary of mammals. Structure and function In the Folliculogenesis#Primordial, primordial ovarian follicle, and later in follicle development (folliculogenesis), granulosa cells advance to form a multilayered cumulus oophorus surrounding the oocyte in the preovulatory or antral follicle, antral (or Graafian) follicle. The major functions of granulosa cells include the production of sex steroids, as well as myriad growth factors thought to interact with the oocyte during its development. The sex steroid production begins with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary, stimulating granulosa cells to convert androgens (coming from the thecal cells) to estradiol by aromatase during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. However, after ovulation the granulosa cells turn into granulosa lutein cells th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theca Cell
The theca folliculi comprise a layer of the ovarian follicles. They appear as the follicles become secondary follicles. The theca are divided into two layers, the theca interna and the theca externa. Theca cells are a group of endocrine cells in the ovary made up of connective tissue surrounding the follicle. They have many diverse functions, including promoting folliculogenesis and recruitment of a single follicle during ovulation. Theca cells and granulosa cells together form the stroma of the ovary. Androgen synthesis Theca cells are responsible for synthesizing androgens, providing signal transduction between granulosa cells and oocytes during development by the establishment of a vascular system, providing nutrients, and providing structure and support to the follicle as it matures. Theca cells are responsible for the production of androstenedione, and indirectly the production of 17β estradiol, also called E2, by supplying the neighboring granulosa cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallopian Tube
The fallopian tubes, also known as uterine tubes, oviducts or salpinges (: salpinx), are paired tubular sex organs in the human female body that stretch from the Ovary, ovaries to the uterus. The fallopian tubes are part of the female reproductive system. In other vertebrates, they are only called oviducts. Each tube is a muscular hollow organ that is on average between in length, with an external diameter of . It has four described parts: the intramural part, isthmus, ampulla, and infundibulum with associated fimbriae. Each tube has two openings: a proximal opening nearest to the uterus, and a distal opening nearest to the ovary. The fallopian tubes are held in place by the mesosalpinx, a part of the broad ligament mesentery that wraps around the tubes. Another part of the broad ligament, the mesovarium suspends the ovaries in place. An ovum, egg cell is transported from an ovary to a fallopian tube where it may be human fertilization, fertilized in the ampulla of the tube. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore. History German zoologists Oscar Hertwig, Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. In multicellular organisms The zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other Anisogamy, anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm, sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. The formation of a cell potency, totipotent zygote with the potential to produce a whole organism depends on epigenetics, epigenetic reprogramming. DNA demethyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
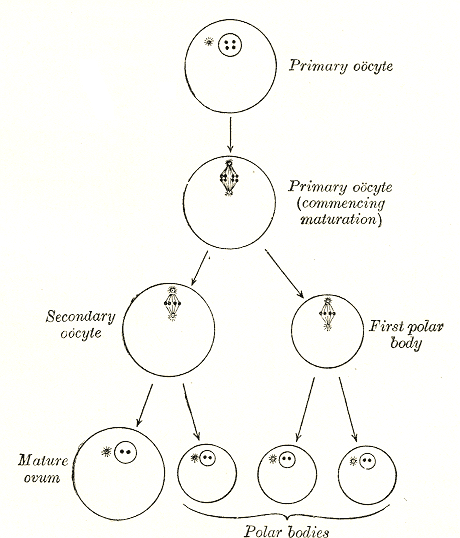
Oocyte
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |