|
Copernican Assumption
In physical cosmology, the Copernican principle states that humans are not privileged observers of the universe, that observations from the Earth are representative of observations from the average position in the universe. Named for Copernican heliocentrism, it is a working assumption that arises from a modified cosmological extension of Copernicus' argument of a moving Earth. Origin and implications Hermann Bondi named the principle after Copernicus in the mid-20th century, although the principle itself dates back to the 16th–17th century paradigm shift away from the Ptolemaic system, which placed Earth at the center of the universe. Copernicus proposed that the motion of the planets could be explained by reference to an assumption that the Sun is centrally located and stationary in contrast to the geocentrism. He argued that the apparent retrograde motion of the planets is an illusion caused by Earth's movement around the Sun, which the Copernican model placed at the cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactocentrism
In astronomy, galactocentrism is the theory that the Milky Way Galaxy, home of Earths Solar System, is at or near the center of the Universe. The galactocentric model was the standard model of cosmology from the decline of heliocentrism onward, but was reliant on the assumption that the Milky Way is the only such galactic structure in the universe, surrounded by a starless void only occasionally populated by extragalactic nebulae. Thomas Wright and Immanuel Kant first speculated that fuzzy patches of light called nebulae were actually distant "island universes" consisting of many stellar systems. The shape of the solar system's own parent galaxy was expected to resemble such "island universes," but "scientific arguments were marshalled against such a possibility," and this view was rejected by almost all scientists until Edwin Hubble's measurements in 1924. William Herschel's heliocentric model of the universe, which was regarded as the standard model of cosmology in the 19th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it, with more than 150 Nobel Prize-winners being featured since its inception. In print since 1845, it is the oldest continuously published magazine in the United States. ''Scientific American'' is owned by Springer Nature, which is a subsidiary of Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History ''Scientific American'' was founded by inventor and publisher Rufus Porter (painter), Rufus Porter in 1845 as a four-page weekly newspaper. The first issue of the large-format New York City newspaper was released on August 28, 1845. Throughout its early years, much emphasis was placed on reports of what was going on at the United States Patent and Trademark Office, U.S. Patent Office. It also reported on a broad range of inventions including perpetual motion machines, an 1860 devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
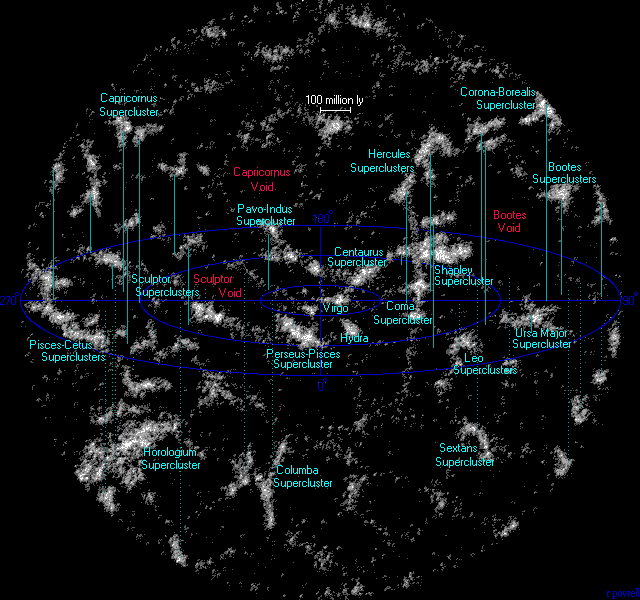
Galaxy Cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. Clusters consist of galaxies, heated gas, and dark matter. They are the second-largest known gravitationally bound structures in the universe after superclusters. They were believed to be the largest known structures in the universe until the 1980s, when superclusters were discovered. Small aggregates of galaxies are referred to as galaxy groups rather than clusters of galaxies. Together, galaxy groups and clusters form superclusters. Basic properties Galaxy clusters typically have the following properties: * They contain 100 to 1,000 galaxies, hot X-ray emitting gas and large amounts of dark matter. Details are described in the "Composition" section. * They have total masses of 1014 to 1015 solar masses. * They typically have diameters from 1 to 5 Mpc ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (AU), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 AU subtended angle, subtends an angle of one arcsecond ( of a degree (angle), degree). The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about from the Sun: from that distance, the gap between the Earth and the Sun spans slightly less than one arcsecond. Most Naked-eye stars, stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand parsecs, and the Andromeda Galaxy at over 700,000 parsecs. The word ''parsec'' is a shortened form of ''a distance corresponding to a parallax of one second'', coined by the British astronomer Herbert Hall Turner in 1913. The unit was introduced to simplify the calculation of astronomical distances from raw observational data. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambda-CDM Model
The Lambda-CDM, Lambda cold dark matter, or ΛCDM model is a mathematical model of the Big Bang theory with three major components: # a cosmological constant, denoted by lambda (Λ), associated with dark energy; # the postulated cold dark matter, denoted by CDM; # ordinary matter. It is the current ''standard model'' of Big Bang cosmology, as it is the simplest model that provides a reasonably good account of: * the existence and structure of the cosmic microwave background; * the large-scale structure in the distribution of galaxies; * the observed abundances of hydrogen (including deuterium), helium, and lithium; * the accelerating expansion of the universe observed in the light from distant galaxies and supernovae. The model assumes that general relativity is the correct theory of gravity on cosmological scales. It emerged in the late 1990s as a concordance cosmology, after a period when disparate observed properties of the universe appeared mutually inconsistent, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Void (astronomy)
Cosmic voids (also known as dark space) are vast spaces between Galaxy filament, filaments (the largest-scale structures in the universe), which contain void galaxy, very few or no Galaxy, galaxies. In spite of their size, most galaxies are not located in voids. This is because most galaxies are gravitationally bound together, creating huge cosmic structures known as galaxy filaments. The cosmological evolution of the void regions differs drastically from the evolution of the universe as a whole: there is a long stage when Shape_of_the_universe#Curvature_of_the_universe, the curvature term dominates, which prevents the formation of galaxy clusters and massive galaxies. Hence, although even the emptiest regions of voids contain more than ~15% of the average matter density of the universe, the voids look almost empty to an observer. Voids typically have a diameter of 10 to 100 Parsec#Megaparsecs and gigaparsecs, megaparsecs (30 to 300 million light-years); particularly large void ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Filament
In cosmology, galaxy filaments are the largest known structures in the universe, consisting of walls of galactic superclusters. These massive, thread-like formations can commonly reach 50 to 80 megaparsecs ()—with the largest found to date being the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall at around in length—and form the boundaries between voids. Due to the accelerating expansion of the universe, the individual clusters of gravitationally bound galaxies that make up galaxy filaments are moving away from each other at an accelerated rate; in the far future they will dissolve. Galaxy filaments form the cosmic web and define the overall structure of the observable universe. Discovery Discovery of structures larger than superclusters began in the late 1980s. In 1987, astronomer R. Brent Tully of the University of Hawaii's Institute of Astronomy identified what he called the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex. The CfA2 Great Wall was discovered in 1989, followed by the Sloa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn is part of the Virgo Supercluster, which is part of the Laniakea Supercluster, which is part of the Pisces–Cetus Supercluster Complex. The large size and low density of superclusters means that they, unlike clusters, expand with the Hubble expansion. The number of superclusters in the observable universe is estimated to be 10 million. Existence The existence of superclusters indicates that the galaxies in the Universe are not uniformly distributed; most of them are drawn together in groups and clusters, with groups containing up to some dozens of galaxies and clusters up to several thousand galaxies. Those groups and clusters and additional isolated galaxies in turn form even larger structures called superclusters. Their existence was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity And Heterogeneity
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, income, disease, temperature, radioactivity, architectural design, etc.); one that is heterogeneous is distinctly nonuniform in at least one of these qualities. Etymology and spelling The words ''homogeneous'' and ''heterogeneous'' come from Medieval Latin ''homogeneus'' and ''heterogeneus'', from Ancient Greek ὁμογενής (''homogenēs'') and ἑτερογενής (''heterogenēs''), from ὁμός (''homos'', "same") and ἕτερος (''heteros'', "other, another, different") respectively, followed by γένος (''genos'', "kind"); -ous is an adjectival suffix. Alternate spellings omitting the last ''-e-'' (and the associated pronunciations) are common, but mistaken: ''homogenous'' is strictly a biological/pathological term whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological Principle
In modern physical cosmology, the cosmological principle is the notion that the spatial distribution of matter in the universe is uniformly isotropic and homogeneous when viewed on a large enough scale, since the forces are expected to act equally throughout the universe on a large scale, and should, therefore, produce no observable inequalities in the large-scale structuring over the course of evolution of the matter field that was initially laid down by the Big Bang. Definition Astronomer William Keel explains: The cosmological principle is usually stated formally as 'Viewed on a sufficiently large scale, the properties of the universe are the same for all observers.' This amounts to the strongly philosophical statement that the part of the universe which we can see is a fair sample, and that the same physical laws apply throughout. In essence, this in a sense says that the universe is knowable and is playing fair with scientists. As Andrew Liddle puts it, "the cosmologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneity (physics)
In physics, a homogeneous material or system has the same properties at every point; it is uniform without irregularities. (accessed November 16, 2009). Tanton, James. "homogeneous." Encyclopedia of Mathematics. New York: Facts On File, Inc., 2005. Science Online. Facts On File, Inc. "A polynomial in several variables p(x,y,z,…) is called homogeneous [...] more generally, a function of several variables f(x,y,z,…) is homogeneous [...] Identifying homogeneous functions can be helpful in solving differential equations [and] any formula that represents the mean of a set of numbers is required to be homogeneous. In physics, the term homogeneous describes a substance or an object whose properties do not vary with position. For example, an object of uniform density is sometimes described as homogeneous." James. homogeneous (math). (accessed: 2009-11-16) A uniform electric field (which has the same strength and the same direction at each point) would be compatible with homogeneity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |