|
Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation
Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation is a technique used in assisted reproduction involving the use of fertility medications to induce ovulation by multiple ovarian follicles. These multiple follicles can be taken out by oocyte retrieval (egg collection) for use in ''in vitro'' fertilisation (IVF), or be given time to ovulate, resulting in superovulation which is the ovulation of a larger-than-normal number of eggs, generally in the sense of at least two. When ovulated follicles are fertilised ''in vivo'', whether by natural or artificial insemination, there is a very high risk of a multiple pregnancy. In this article, unless otherwise specified, hyperstimulation will refer to hyperstimulation as part of IVF. In contrast, ovulation induction is ovarian stimulation without subsequent IVF, with the aim of developing one or two ovulatory follicles. Procedure Response prediction Response predictors determine the protocol for ovulation suppression as well as dosage of medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assisted Reproduction
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), and cryopreservation of gametes and embryos, and the use of fertility medication. When used to address infertility, ART may also be referred to as fertility treatment. ART mainly belongs to the field of reproductive endocrinology and infertility. Some forms of ART may be used with regard to fertile couples for genetic purpose (see preimplantation genetic diagnosis). ART may also be used in surrogacy arrangements, although not all surrogacy arrangements involve ART. The existence of sterility will not always require ART to be the first option to consider, as there are occasions when its cause is a mild disorder that can be solved with more conventional treatments or with behaviors based on promoting health and reproductive habits. Procedures General With ART, the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
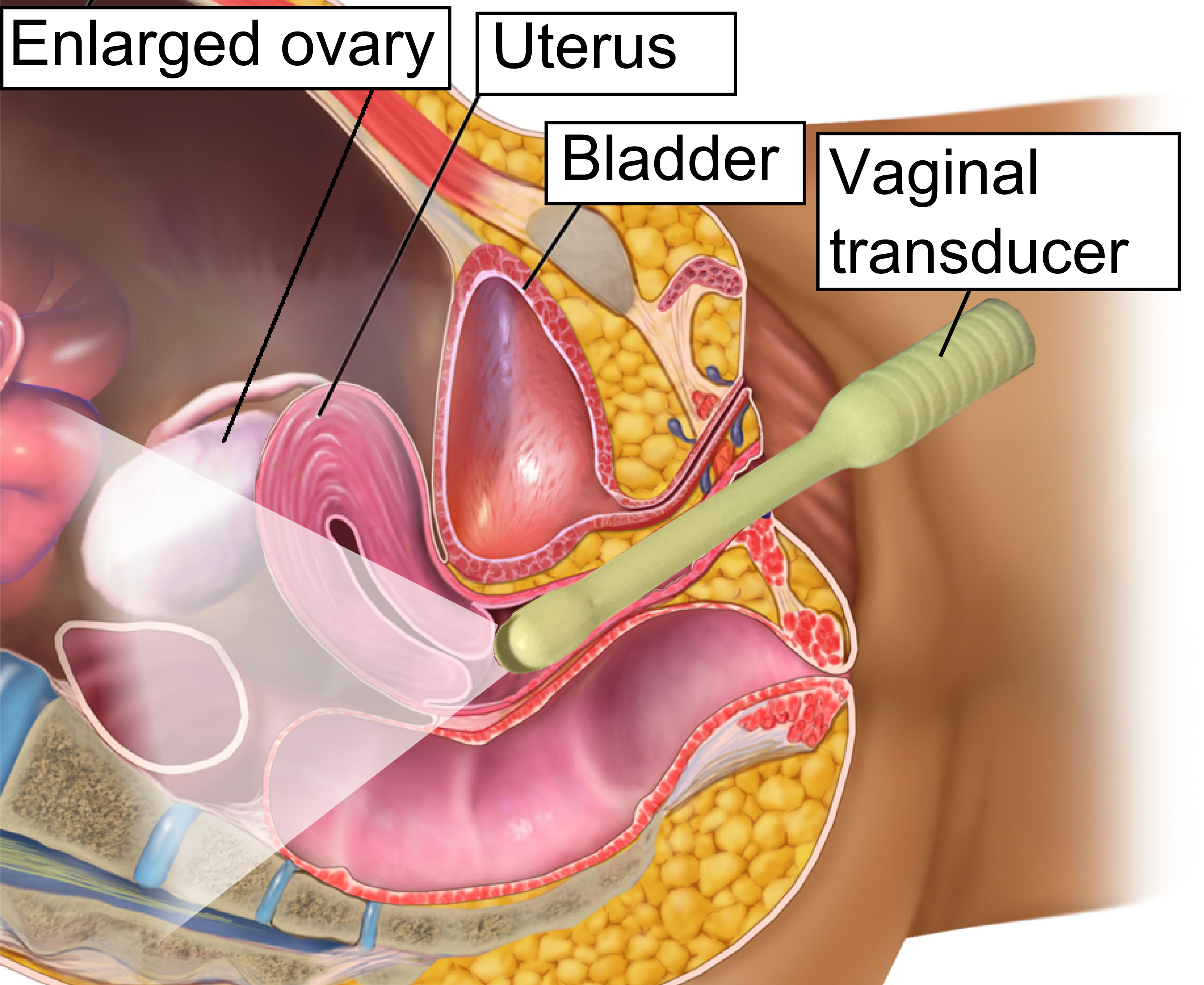
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is a medical condition that can occur in some women who take fertility medication to stimulate egg growth, and in other women in sporadic cases. Most cases are mild, but rarely the condition is severe and can lead to serious illness or even death. Signs and symptoms Mild symptoms include abdominal bloating and feeling of fullness, nausea, diarrhea, and slight weight gain. Moderate symptoms include weight gain greater than per day, increased abdominal girth, vomiting, diarrhea, darker urine, decreased urine output, excessive thirst, and skin and/or hair feeling dry (in addition to mild symptoms). Severe symptoms are fullness/bloating above the waist, shortness of breath, pleural effusion, urination significantly darker or diminished in quantity, calf and chest pain, marked abdominal bloating or distention, and lower abdominal pain. Complications OHSS may be complicated by ovarian torsion or rupture, venous thromboembolism, acute respirator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FSH Preparations
Gonadotropin preparations are drugs that mimic the physiological effects of gonadotropins, used therapeutically mainly as fertility medication for ovarian hyperstimulation and ovulation induction. For example, the so-called menotropins consist of LH and FSH extracted from human urine from menopausal women. There are also recombinant variants. FSH and LH preparations hMG (human Menopausal Gonadotrophins), FSH and LH prepared from human urine collected from postmenopausal women. First extracted in 1953. Injected intra-muscularily (IM) or subcutaneously (SC). Generic : menotropins for injections, USP Brands :* Menopur, 5 mL vials containing 75 IU FSH and 75 IU LH. :* Repronex, vials containing either 75 IU FSH and 75 IU LH, or 150 IU FSH and 150 IU LH. Common side effects of preparations containing FSH and LH are: * Mild bloating * Pain, swelling, or irritation injection site * Rash at injection site or other part of body * Stomach pain or pelvic pain FSH preparations P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomogram For FSH Dosage By AMH
A nomogram (), also called a nomograph, alignment chart, or abac, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function. The field of nomography was invented in 1884 by the French engineer Philbert Maurice d'Ocagne (1862–1938) and used extensively for many years to provide engineers with fast graphical calculations of complicated formulas to a practical precision. Nomograms use a parallel coordinate system invented by d'Ocagne rather than standard Cartesian coordinates. A nomogram consists of a set of n scales, one for each variable in an equation. Knowing the values of n-1 variables, the value of the unknown variable can be found, or by fixing the values of some variables, the relationship between the unfixed ones can be studied. The result is obtained by laying a straightedge across the known values on the scales and reading the unknown value from where it crosses the scale for that va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days. Menarche (the onset of the first period) usually occurs around the age of 12 years; menstrual cycles continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining ( endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Mass Index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is expressed in Units of measurement, units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms (kg) and height in metres (m). The BMI may be determined first by measuring its components by means of a weighing scale and a stadiometer. The multiplication and division may be carried out directly, by hand or using a calculator, or indirectly using a lookup table (or chart). The table displays BMI as a function of mass and height and may show other units of measurement (converted to Metric system, metric units for the calculation). The table may also show contour lines or colours for different BMI categories. The BMI is a convenient rule of thumb used to broadly categorize a person as based on tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) and height. Major adult B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro Fertilization
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a process of fertilisation in which an egg is combined with sperm in vitro ("in glass"). The process involves monitoring and stimulating the ovulatory process, then removing an ovum or ova (egg or eggs) from the ovaries and enabling sperm to fertilise them in a culture medium in a laboratory. After a fertilised egg (zygote) undergoes embryo culture for 2–6 days, it is transferred by catheter into the uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy. IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to treat infertility, enable gestational surrogacy, and, in combination with pre-implantation genetic testing, avoid the transmission of abnormal genetic conditions. When a fertilised egg from egg and sperm donors implants in the uterus of a genetically unrelated surrogate, the resulting child is also genetically unrelated to the surrogate. Some countries have banned or otherwise regulated the availability of IVF treatme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Insemination
Artificial insemination is the deliberate introduction of sperm into a female's cervix or uterine cavity for the purpose of achieving a pregnancy through in vivo fertilization by means other than sexual intercourse. It is a fertility treatment for humans, and is a common practice in animal breeding, including dairy cattle (see frozen bovine semen) and pigs. Artificial insemination may employ assisted reproductive technology, sperm donation and animal husbandry techniques. Artificial insemination techniques available include intracervical insemination (ICI) and intrauterine insemination (IUI). Where gametes from a third party are used, the procedure may be known as 'assisted insemination'. Humans History The first recorded case of artificial insemination was John Hunter in 1790, who helped impregnate a linen draper's wife. The first reported case of artificial insemination by donor occurred in 1884: William H. Pancoast, a professor in Philadelphia, took sperm from his "bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Maternal Age
Advanced maternal age, in a broad sense, is the instance of a woman being of an older age at a stage of reproduction, although there are various definitions of specific age and stage of reproduction. The variability in definitions is in part explained by the effects of increasing age occurring as a continuum rather than as a threshold effect. Average age at first childbirth has been increasing, especially in OECD countries, among which the highest average age is 32.6 years (South Korea) followed by 32.1 years (Ireland and Spain). In a number of European countries (Spain), the mean age of women at first childbirth has crossed the 30 year threshold. This process is not restricted to Europe. Asia, Japan and the United States are all seeing average age at first birth on the rise, and increasingly the process is spreading to countries in the developing world such as China, Turkey and Iran. In the U.S., the average age of first childbirth was 26.9 in 2018. Advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) work together in the reproductive system. Structure FSH is a 35.5 kDa glycoprotein heterodimer, consisting of two polypeptide units, alpha and beta. Its structure is similar to those of luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The alpha subunits of the glycoproteins LH, FSH, TSH, and hCG are identical and consist of 96 amino acids, while the beta subunits vary. Both subunits are required for biological activity. FSH has a beta subunit of 111 amino acids (FSH β), which confers its specific biologic action, and is responsible for interaction with the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor. The sugar p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |