|
Confederation Of Madja-as
Madja-as was a legendary precolonial confederacy on the island of Panay in the Philippines. It was mentioned in Pedro Monteclaro's book titled Maragtas. It was supposedly created by Datu Sumakwel to exercise his authority over all the other datus of Panay. Like the Maragtas and the Code of Kalantiaw, the historical authenticity of the confederation is disputed. The ''Maragtas'' legend Background The book of Maragtas The Maragtas is a work by Pedro Alcantara Monteclaro titled (in English translation) ''History of Panay from the first inhabitants and the Bornean immigrants, from which they descended, to the arrival of the Spaniards''. The work is in mixed Hiligaynon language, Hiligaynon and Kinaray-a language, Kinaray-a languages in Iloilo City#Period of Malay Mass Migration, Iloilo written in 1901 and published in 1907. It is an original work based on written and oral sources available to the author. While the work is disputed, the notion that the Maragtas is an orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
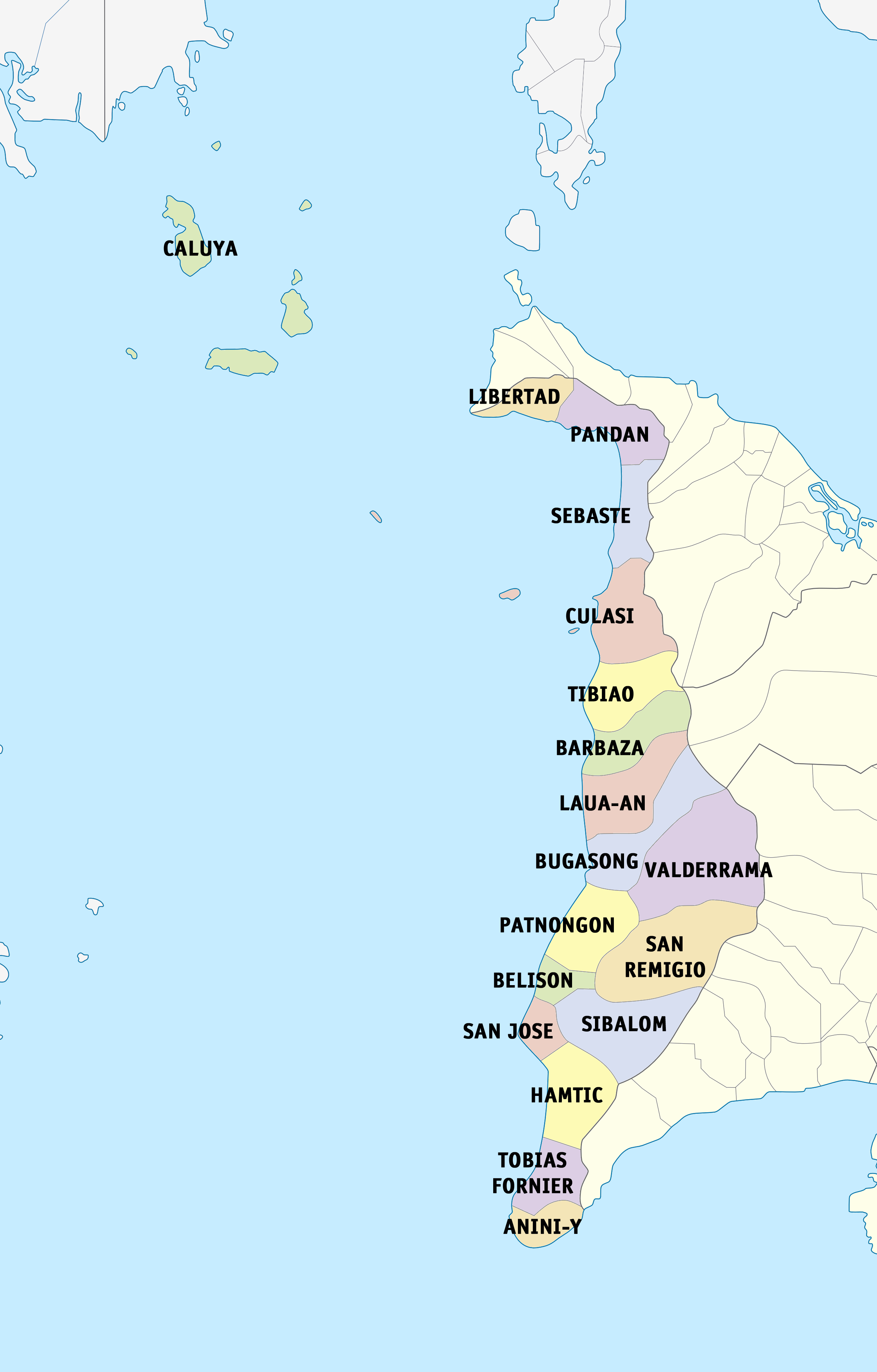
Hamtic
Hamtic, officially the Municipality of Hamtic (; ; ), is a municipality of the Philippines, municipality in the Philippine Province, province of Antique (province), Antique, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 52,685 people, making it the third most populous municipality in the province of Antique. Etymology Hantik was named after the humming big black ants that produce the sound "tik" when they bite. History Hamtic was formerly named ''Antique'', after which the province was named. It is the oldest town and the first capital of the province before it was transferred to San Jose de Buenavista in 1802. Hamtic was created from portions of San Jose de Buenavista, through Executive Order No. 3 signed by President Ramon Magsaysay on January 5, 1954. Geography Hamtic is from the provincial capital, San Jose de Buenavista. According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, the municipality has a land area of constituting of the total area of Antique. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinaray-a Language
The Karay-a language (, or ; ) is an Austronesian regional language in the Philippines spoken by the Karay-a people, mainly in Antique. It is one of the Bisayan languages, along with Aklanon/Malaynon, Capiznon, Cebuano, and Hiligaynon. History Kinaray-a, Kinaray-a Bukidnon, or Hiniraya, possibly deriving from "Iraya." It was the primary language spoken by the majority of the Panay people whom the first Spanish colonizers encountered upon their arrival and subsequent settlement in Ogtong (now Oton, Iloilo) between the late 16th and early 17th centuries. This was before the linguistic evolution that eventually led to the Hiligaynon language of Iloilo gaining dominance as the common language over Kinaray-a on the island. However, in modern times, Kinaray-a remains in use as a primary language in the province of Antique and the western part of Iloilo province. Geographical distribution Kinaray-a is spoken mainly in Antique. It is also spoken in Iloilo province as a prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly or other form of organization. A committee may not itself be considered to be a form of assembly or a decision-making body. Usually, an assembly or organization sends matters to a committee as a way to explore them more fully than would be possible if the whole assembly or organization were considering them. Committees may have different functions and their types of work differ depending on the type of organization and its needs. A member of a legislature may be delegated a committee assignment, which gives them the right to serve on a certain committee. Purpose A deliberative assembly or other organization may form a committee (or "commission") consisting of one or more persons to assist with the work of the assembly. For larger organizations, much work is done in committees. They can be a way to formally draw together people of relevant expertise from different parts of an organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antique
An antique () is an item perceived as having value because of its aesthetic or historical significance, and often defined as at least 100 years old (or some other limit), although the term is often used loosely to describe any object that is old. An antique is usually an item that is collected or desirable because of its age, beauty, rarity, condition, utility, personal emotional connection and/or other unique features. It is an object that represents a previous era or time period in human history. Vintage and collectible are used to describe items that are old, but do not meet the 100-year criterion. Antiques are usually objects of the decorative arts that show some degree of craftsmanship, collectability, or an attention to design, such as a desk or an vintage car, early automobile. They are bought at antique shops, estate sales, auction houses, online auctions and other venues, or estate inherited. Antiques dealers often belong to national trade associations, many of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamtik
Antique (), officially the Province of Antique, is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital and most populous town is San Jose de Buenavista. The province is situated in the western section of Panay Island and borders Aklan, Capiz, and Iloilo to the east, while facing the Sulu Sea to the west. The province is home to the indigenous Iraynun-Bukidnon, speakers of a dialect of the Kinaray-a language, who have crafted the only rice terrace clusters in the Visayas through indigenous knowledge and sheer vernacular capabilities. The rice terraces of the Iraynun-Bukidnon are divided into four terraced fields, namely, General Fullon rice terraces, Lublub rice terraces, Bakiang rice terraces, and San Agustin rice terraces. All of the rice terrace clusters have been researched by the National Commission for Culture and the Arts and various scholars from the University of the Philippines. There have been campaigns to nominate the Iraynun-Bukidnon Rice Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salakot
Salakot is a traditional lightweight headgear from the Philippines commonly used for protection against the sun and rain. Variants occur among ethnic groups, but all are shaped like a dome or cone and can range in size from having very wide brims to being almost helmet-like. Made from various materials including bamboo, rattan, nito ferns, and bottle gourd, the salakot is held in place by an inner headband and a chinstrap. The tip of the crown commonly has a spiked or knobbed finial made of metal or wood. The salakot is the direct precursor to the pith helmet (also called '' salacot'' in Spanish and ''salacco'' in French) widely used by European military forces in the colonial era. Description Salakot is a general term for a range of related traditional headgear used by virtually all ethnic groups of the Philippines. It is usually dome-shaped or cone-shaped, but various other styles also exist, including versions with dome-shaped, cone-shaped, or flat crowns with a flat or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negrito
The term ''Negrito'' (; ) refers to several diverse ethnic groups who inhabit isolated parts of Southeast Asia and the Andaman Islands. Populations often described as Negrito include: the Andamanese peoples (including the Great Andamanese, the Onge, the Jarawas (Andaman Islands), Jarawa, and the Sentinelese) of the Andaman Islands, the Semang peoples (among them, the Batek people) of Peninsular Malaysia, the Maniq people of Southern Thailand, as well as the Aeta people, Aeta of Luzon, the Ati people, Ati and Suludnon, Tumandok of Panay, the Mamanwa of Mindanao, and about 30 other officially recognized ethnic groups in the Philippines. Etymology The word ''Negrito,'' the Spanish diminutive of ''negro'', is used to mean "little black person." This usage was coined by 16th-century Spanish Catholic Church and the Age of Discovery, missionaries operating in the Philippines, and was borrowed by other European travellers and colonialists across Austronesia to label various peoples pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visayans
Visayans ( Cebuano: ''mga Bisayà'' ) are a Philippine ethnolinguistic family group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, to the southernmost islands south of Luzon, and to a significant portion of Mindanao. They are composed of numerous distinct ethnic groups. When taken as a single group, they number around 33.5 million. The Visayans, like the Luzon Lowlanders (Tagalogs, Bicolanos, Ilocanos, etc.) were originally predominantly animist-polytheists and broadly share a maritime culture until the 16th century when the Spanish Empire enforced Catholicism as the state religion. In more inland or otherwise secluded areas, ancient animistic-polytheistic beliefs and traditions either were reinterpreted within a Roman Catholic framework or syncretized with the new religion. Visayans are generally speakers of one or more of the distinct Bisayan languages, the most widely spoken being Cebuano, followed by Hiligaynon (Ilonggo) and Waray-Waray. Terminology "Visayan" is the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalaur River
The Jalaur River, also known as Jalaud River, is the second longest river on Panay island in the Philippines, with a total length of and the second largest by drainage basin after Panay River in Capiz. The Jalaur has a drainage area of . Its source is in the Central Panay Mountain Range, west of Calinog, and the river traverses east to southeast before emptying into the Guimaras Strait. It drains the eastern portion of Panay and courses through Passi City and the towns of Leganes, Zarraga, Dumangas, Barotac Nuevo, Pototan, Dingle, San Enrique, Dueñas, and Calinog, all in Iloilo province. The river provides irrigation to farmlands as well as providing a source of potable water. The river is the site of the Jalaur Mega Dam project that begun in 2019. Etymology ''Jalaur'', also known by its variant form ''Jalaud'', seems to be a Hispanicized form of Halawod, the river which serves as the core setting of ''Hinilawod'', an epic poem from Panay. Geography The Jalaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ati People
The Ati are a Negrito ethnic group and indigenous peoples in the Visayan Islands of the Philippines. Their small numbers are principally concentrated on the islands of Boracay, Panay and Negros. They are genetically related to other Negrito ethnic groups in the Philippines such as the Aeta of Luzon, the Batak of Palawan, the Agta of the Sierra Madres, and the Mamanwa of Mindanao. History The Negritos are the descendants of the same early East Eurasian meta-population, which also gave rise to modern East Asians and Australasians, among other populations of the Asia-Pacific region. The earliest modern human migrations into the Philippine archipelago were during the Paleolithic, around 40,000 years ago, followed by two other migration waves between 25,000 and 12,000 years ago, through the Sundaland land bridges that linked the islands with the Asian mainland. The latest migration wave is associated with the Austronesian peoples (c. 7,000 years ago) from Taiwan. The Philippine Neg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Joaquin, Iloilo
San Joaquin, officially the Municipality of San Joaquin (; ; , ), is a municipality of the Philippines, municipality in the Philippine Province, province of Iloilo, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 52,617 people. Geography San Joaquin is located in the southern tip of Iloilo Province. One of the rivers that traverse the town is the Siwaragan River with Barangay Siwaragan and Bucaya situated in its mouth. It is the southernmost municipality in the province and is from the provincial capital, Iloilo City, and is from San Jose de Buenavista, the capital of Antique. Climate Barangays San Joaquin is subdivided into 85 barangays. Each barangay consists of puroks and some have sitios. * Amboyu-an * Andres Bonifacio * Antalon * Bad-as * Bagumbayan * Balabago * Baybay * Bayunan, also known as Panday Ora * Bolbogan * Bonga * Bulho * Bucaya * Cadluman * Cadoldolan * Camia * Camaba-an * Cata-an * Crossing Dapuyan * Cubay * Cumarascas * Dacdacanan * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Sarawak
The History of Sarawak can be traced as far as 40,000 years ago to the Paleolithic period where the earliest evidence of human settlement is found in the Niah caves. A series of Chinese ceramics dated from the 8th to 13th century AD was uncovered at the archeological site of Santubong. The coastal regions of Sarawak came under the influence of the Bruneian Empire in the 16th century. In 1839, James Brooke, a British explorer, first arrived in Sarawak. Sarawak was later governed by the Brooke family between 1841 and 1946. During World War II, it was occupied by the Japanese for three years. After the war, the last White Rajah, Charles Vyner Brooke, ceded Sarawak to Britain, and in 1946 it became a British Crown Colony. On 22 July 1963, Sarawak was granted self-government by the British. Following this, it became one of the founding members of the Federation of Malaysia, established on 16 September 1963. However, the federation was opposed by Indonesia, and this led to the three-ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |