|
Compound Probability Distribution
In probability and statistics, a compound probability distribution (also known as a mixture distribution or contagious distribution) is the probability distribution that results from assuming that a random variable is distributed according to some parametrized distribution, with (some of) the parameters of that distribution themselves being random variables. If the parameter is a scale parameter, the resulting mixture is also called a scale mixture. The compound distribution ("unconditional distribution") is the result of marginalizing (integrating) over the ''latent'' random variable(s) representing the parameter(s) of the parametrized distribution ("conditional distribution"). Definition A compound probability distribution is the probability distribution that results from assuming that a random variable X is distributed according to some parametrized distribution F with an unknown parameter \theta that is again distributed according to some other distribution G. The resulting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an event is to occur."Kendall's Advanced Theory of Statistics, Volume 1: Distribution Theory", Alan Stuart and Keith Ord, 6th ed., (2009), .William Feller, ''An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications'', vol. 1, 3rd ed., (1968), Wiley, . This number is often expressed as a percentage (%), ranging from 0% to 100%. A simple example is the tossing of a fair (unbiased) coin. Since the coin is fair, the two outcomes ("heads" and "tails") are both equally probable; the probability of "heads" equals the probability of "tails"; and since no other outcomes are possible, the probability of either "heads" or "tails" is 1/2 (which could also be written as 0.5 or 50%). These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
F-test
An F-test is a statistical test that compares variances. It is used to determine if the variances of two samples, or if the ratios of variances among multiple samples, are significantly different. The test calculates a Test statistic, statistic, represented by the random variable F, and checks if it follows an F-distribution. This check is valid if the null hypothesis is true and standard assumptions about the errors (ε) in the data hold. F-tests are frequently used to compare different statistical models and find the one that best describes the population (statistics), population the data came from. When models are created using the least squares method, the resulting F-tests are often called "exact" F-tests. The F-statistic was developed by Ronald Fisher in the 1920s as the variance ratio and was later named in his honor by George W. Snedecor. Common examples Common examples of the use of ''F''-tests include the study of the following cases * The hypothesis that the Arithme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Prior Distribution
A prior probability distribution of an uncertain quantity, simply called the prior, is its assumed probability distribution before some evidence is taken into account. For example, the prior could be the probability distribution representing the relative proportions of voters who will vote for a particular politician in a future election. The unknown quantity may be a parameter of the model or a latent variable rather than an observable variable. In Bayesian statistics, Bayes' rule prescribes how to update the prior with new information to obtain the posterior probability distribution, which is the conditional distribution of the uncertain quantity given new data. Historically, the choice of priors was often constrained to a conjugate family of a given likelihood function, so that it would result in a tractable posterior of the same family. The widespread availability of Markov chain Monte Carlo methods, however, has made this less of a concern. There are many ways to constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Prior Predictive Distribution
In Bayesian statistics, the posterior predictive distribution is the distribution of possible unobserved values conditional on the observed values. Given a set of ''N'' i.i.d. observations \mathbf = \, a new value \tilde will be drawn from a distribution that depends on a parameter \theta \in \Theta, where \Theta is the parameter space. :p(\tilde, \theta) It may seem tempting to plug in a single best estimate \hat for \theta, but this ignores uncertainty about \theta, and because a source of uncertainty is ignored, the predictive distribution will be too narrow. Put another way, predictions of extreme values of \tilde will have a lower probability than if the uncertainty in the parameters as given by their posterior distribution is accounted for. A posterior predictive distribution accounts for uncertainty about \theta. The posterior distribution of possible \theta values depends on \mathbf: : p(\theta, \mathbf) And the posterior predictive distribution of \tilde given \ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Posterior Distribution
The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule. From an epistemological perspective, the posterior probability contains everything there is to know about an uncertain proposition (such as a scientific hypothesis, or parameter values), given prior knowledge and a mathematical model describing the observations available at a particular time. After the arrival of new information, the current posterior probability may serve as the prior in another round of Bayesian updating. In the context of Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability distribution usually describes the epistemic uncertainty about statistical parameters conditional on a collection of observed data. From a given posterior distribution, various point and interval estimates can be derived, such as the maximum a posteriori (MAP) or the highest posterior density interval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Bayesian Inference
Bayesian inference ( or ) is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to calculate a probability of a hypothesis, given prior evidence, and update it as more information becomes available. Fundamentally, Bayesian inference uses a prior distribution to estimate posterior probabilities. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability". Introduction to Bayes' rule Formal explanation Bayesian inference derives the posterior probability as a consequence of two antecedents: a prior probability and a "likelihood function" derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Beta-binomial Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the beta-binomial distribution is a family of discrete probability distributions on a finite support of non-negative integers arising when the probability of success in each of a fixed or known number of Bernoulli trials is either unknown or random. The beta-binomial distribution is the binomial distribution in which the probability of success at each of ''n'' trials is not fixed but randomly drawn from a beta distribution. It is frequently used in Bayesian statistics, empirical Bayes methods and classical statistics to capture overdispersion in binomial type distributed data. The beta-binomial is a one-dimensional version of the Dirichlet-multinomial distribution as the binomial and beta distributions are univariate versions of the multinomial and Dirichlet distributions respectively. The special case where ''α'' and ''β'' are integers is also known as the negative hypergeometric distribution. Motivation and derivation As a compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Beta Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the beta distribution is a family of continuous probability distributions defined on the interval [0, 1] or (0, 1) in terms of two positive Statistical parameter, parameters, denoted by ''alpha'' (''α'') and ''beta'' (''β''), that appear as exponents of the variable and its complement to 1, respectively, and control the shape parameter, shape of the distribution. The beta distribution has been applied to model the behavior of random variables limited to intervals of finite length in a wide variety of disciplines. The beta distribution is a suitable model for the random behavior of percentages and proportions. In Bayesian inference, the beta distribution is the conjugate prior distribution, conjugate prior probability distribution for the Bernoulli distribution, Bernoulli, binomial distribution, binomial, negative binomial distribution, negative binomial, and geometric distribution, geometric distributions. The formulation of the beta dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Binomial Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution with parameters and is the discrete probability distribution of the number of successes in a sequence of statistical independence, independent experiment (probability theory), experiments, each asking a yes–no question, and each with its own Boolean-valued function, Boolean-valued outcome (probability), outcome: ''success'' (with probability ) or ''failure'' (with probability ). A single success/failure experiment is also called a Bernoulli trial or Bernoulli experiment, and a sequence of outcomes is called a Bernoulli process; for a single trial, i.e., , the binomial distribution is a Bernoulli distribution. The binomial distribution is the basis for the binomial test of statistical significance. The binomial distribution is frequently used to model the number of successes in a sample of size drawn with replacement from a population of size . If the sampling is carried out without replacement, the draws ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Negative Binomial Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the negative binomial distribution, also called a Pascal distribution, is a discrete probability distribution that models the number of failures in a sequence of independent and identically distributed Bernoulli trials before a specified/constant/fixed number of successes r occur. For example, we can define rolling a 6 on some dice as a success, and rolling any other number as a failure, and ask how many failure rolls will occur before we see the third success (r=3). In such a case, the probability distribution of the number of failures that appear will be a negative binomial distribution. An alternative formulation is to model the number of total trials (instead of the number of failures). In fact, for a specified (non-random) number of successes , the number of failures is random because the number of total trials is random. For example, we could use the negative binomial distribution to model the number of days (random) a certain machin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
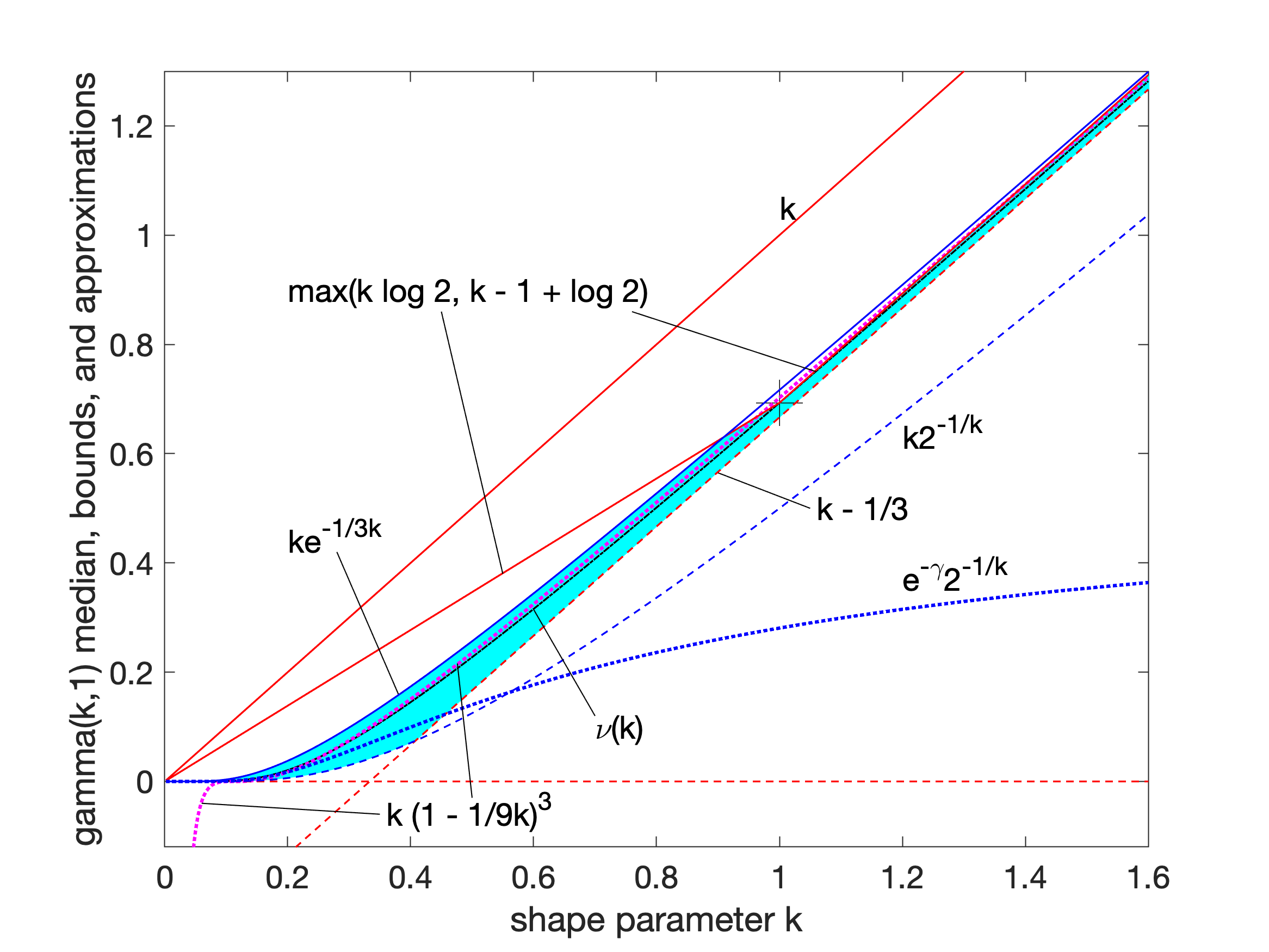 |
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a versatile two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-squared distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: # With a shape parameter and a scale parameter # With a shape parameter \alpha and a rate parameter In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The distribution has important applications in various fields, including econometrics, Bayesian statistics, and life testing. In econometrics, the (''α'', ''θ'') parameterization is common for modeling waiting times, such as the time until death, where it often takes the form of an Erlang distribution for integer ''α'' values. Bayesian statisticians prefer the (''α'',''λ'') parameterization, utilizing the gamma distribution as a conjugate prior for several inverse scale parameters, facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |