|
Comparison Of Space Station Cargo Vehicles
A number of different spacecraft have been used to carry cargo to and from space stations. This list does not include crewed spacecraft. Notes See also * Comparison of crewed space vehicles *Comparison of orbital launch systems *Comparison of orbital rocket engines This page is an incomplete list of orbital rocket engine data and specifications. Current, upcoming, and in-development rocket engines Retired and canceled rocket engines See also * Comparison of orbital launch systems * Comparison of ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Space station cargo vehicle comparison * Technological comparisons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncrewed Spacecraft
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which they have a pre-programmed list of operations that will be executed unless otherwise instructed. A robotic spacecraft for scientific measurements is often called a space probe or space observatory. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather than crewed operation, due to lower cost and risk factors. In addition, some planetary destinations such as Venus or the vicinity of Jupiter are too hostile for human survival, given current technology. Outer planets such as Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune are too distant to reach with current crewed spaceflight technology, so telerobotic probes are the only way to explore them. Telerobotics also allows exploration of regions that are vulnerable to contamination by Earth micro-organisms sinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the company has made numerous advancements in rocket propulsion, reusable launch vehicles, human spaceflight and satellite constellation technology. , SpaceX is the world's dominant space launch provider, its launch cadence eclipsing all others, including private competitors and national programs like the Chinese space program. SpaceX, NASA, and the United States Armed Forces work closely together by means of Government contractor, governmental contracts. SpaceX was founded by Elon Musk in 2002 with a vision of decreasing the costs of space launches, paving the way to SpaceX ambition of colonizing Mars, a sustainable colony on Mars. In 2008, Falcon 1 successfully launched into orbit after three failed launch attempts. The company then pivoted towar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress-MS
The Progress MS (; GRAU: 11F615A61) is the latest version of the Russian Progress spacecraft series, first launched in 2015. The "MS" stands for "modernized systems," reflecting upgrades primarily focused on the communications and navigation subsystems. An evolution of the Progress M spacecraft, the Soyuz MS features minimal external changes, mainly in the placement of antennas, sensors, and thrusters. It is used by Roscosmos for cargo spaceflight missions. Progress MS-01 conducted its maiden flight on 21 December 2015, heading to the International Space Station (ISS). Design Like all previous variants, the Progress MS spacecraft consists of three distinct sections: * Cargo Section: This pressurized carries supplies for the crew, including maintenance items, prepackaged and fresh food, scientific equipment, and clothing. Its docking drogue, similar to that of the Soyuz, features ducting that enables fuel transfer (described below). * Tanker Section: Replacing the Soyuz's r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long March 7
The Long March 7 (), or Chang Zheng 7 in pinyin, abbreviated LM-7 for export or CZ-7 within China, originally Long March 2F/H or Chang Zheng 2F/H, nicknamed Bingjian (), is a Chinese liquid-fuelled launch vehicle of the Long March family, developed by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CAST). It made its inaugural flight on 25 June 2016. Designed as a replacement of the Long March 2F, Long March 7 and its variants was expected to be the workhorse of the fleet, projected to account for around 70% of all Chinese launches. Long March 7 plays a critical role in the Chinese Space Station program: it is used to launch the Tianzhou robotic cargo and resupply spacecraft to the station. The rocket was intended to replace the Long March 2F as China's crew-rated launch vehicle in the future, although by 2023 this role has apparently been taken over by the under-development Long March 10 and Long March 10A. Since 2020, in addition to the base Long March 7 config ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Academy Of Space Technology
The China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) () is a Chinese space agency and subordinate of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC). The agency was founded on 20 February 1968, and is the main spacecraft development and production facility in China. On 24 April 1970, CAST successfully launched China's first artificial satellite Dong Fang Hong I. Space flight programmes CAST designs and manufactures the Dong Fang Hong satellites. U.S. sanctions CAST is the majority shareholder of listed company China Spacesat. On 30 June 2020, CAST owns 51.46% of China Spacesat Co. In August 2020, the United States Department of Defense published the names of companies linked to the People's Liberation Army operating directly or indirectly in the United States. China Spacesat Co. was included on the list. In November 2020, Donald Trump issued an executive order prohibiting any American company or individual from owning shares in companies that the United States Depar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tianzhou (spacecraft)
The Tianzhou () is a Chinese automated cargo spacecraft developed from China's first prototype space station Tiangong-1 to resupply its modular space station. It was first launched ( Tianzhou 1) on the Long March 7 rocket from Wenchang on April 20, 2017 and demonstrated autonomous propellant transfer ( space refueling). The first version of Tianzhou has a mass of 13,500 kg and can carry 6,500 kg of cargo. Tianzhou-6 is the first improved version of the spacecraft to be launched into orbit; it has a mass of about 14,000 kg and can transport 7,400 kg of cargo. Function Based on the Tiangong-1 space station, the Tianzhou functions as the main automated cargo spacecraft for the Tiangong space station. It has pressurized, semi-pressurized and unpressurized cargo capabilities, and is able to transport airtight cargo, large extravehicular payloads and experiment platforms. It was first launched on the new Long March 7 rocket from Wenchang on April 20, 2017. Name The China Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national Aeronautics, air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into Geocentric orbit, orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kounotori 7
, also known as HTV-7, was the seventh flight of the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), an uncrewed cargo spacecraft launched on 22 September 2018 to resupply the International Space Station. Spacecraft specification Major changes from previous Kounotori include: * Inclusion of the HTV Small Re-entry Capsule (HSRC). * Reduction of primary batteries to five units, down from six on Kounotori 6, and seven on Kounotori 2 through Kounotori 5 * Replacement of Hardware Control Panel (HCP) by Portable Computer System (PCS), a dedicated control command box which allowed ISS crew to send control commands to Kounotori via a portable (laptop) computer. To enable HSRC retrieval, the destructive re-entry of Kounotori 7 and the splashdown of HSRC was planned to take place in the northwestern Pacific Ocean near Minami-Tori-shima (Marcus Island), east of the Bonin Islands and the Northern Mariana Islands, instead of the South Pacific used by the previous missions. Reentry capsule Along with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
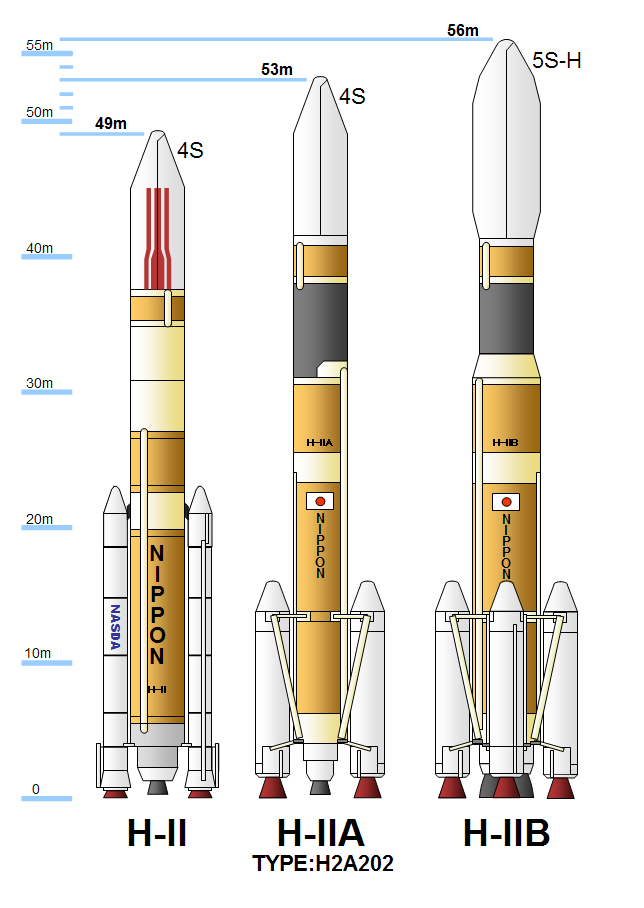
H-IIB
H-IIB (H2B) was an expendable space launch system jointly developed by the Japanese government's space agency JAXA and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. It was used to launch the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV, or ''Kōnotori'') cargo spacecraft for the International Space Station. The H-IIB was a liquid-fueled rocket, with solid-fuel strap-on boosters and was launched from the Tanegashima Space Center in southern Japan. H-IIB made its first flight in 2009, and had made a total of nine flights through 2020 with no failures. H-IIB was able to carry a payload of up to to Geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), compared with the payload of 4000–6000 kg for the H-IIA, a predecessor design. Its performance to low Earth orbit (LEO) was sufficient for the H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV). The first H-IIB was launched in September 2009 and the last H-IIB was launched in May 2020. Development The H-IIB was a space launch vehicle jointly designed, manufactured and operated by JAXA and Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
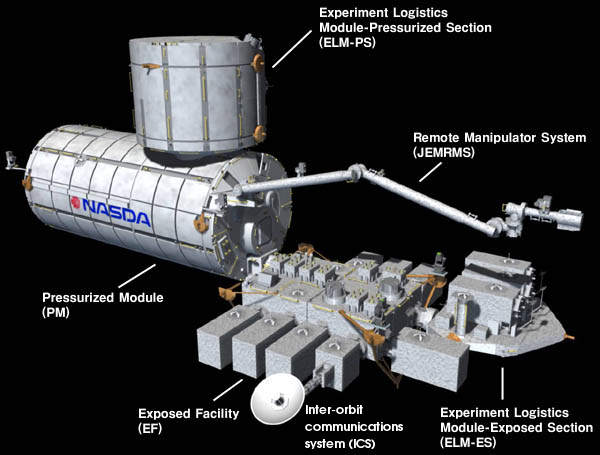
H-II Transfer Vehicle
The H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV), also called , is an Expendable launch system, expendable Japanese Cargo spacecraft, automated cargo spacecraft designed for International Space Station (ISS) resupply missions, particularly the Kibo (ISS module), ''Kibō'' Japanese Experiment Module (JEM). Development of the spacecraft began in the early 1990s and the HTV's first mission, HTV-1, was launched on 10September 2009 on an H-IIB launch vehicle. The name ''Kounotori'' was chosen because "a white stork carries an image of conveying an important thing (a baby, happiness, and other joyful things), therefore, it precisely expresses the HTV's mission to transport essential materials to the ISS". The HTV is crucial for ISS resupply, especially after the retirement of the Space Shuttle, as it's the only vehicle capable of transporting large International Standard Payload Racks (ISPR) and disposing of old ones within the ISS's US Orbital Segment. The final HTV mission, Kounotori 9, was laun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a retired European heavy-lift space launch vehicle operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It was launched from the Guiana Space Centre (CSG) in French Guiana. It was used to deliver payloads into geostationary transfer orbit (GTO), low Earth orbit (LEO) or further into space. The launch vehicle had a streak of 82 consecutive successful launches between 9 April 2003 and 12 December 2017. Since 2014, Ariane 6, a direct successor system, first launched in 2024. The system was designed as an expendable launch vehicle by the ''Centre national d'études spatiales'' (CNES), the French government's space agency, in cooperation with various European partners. Despite not being a direct derivative of its predecessor launch vehicle program, it was classified as part of the Ariane rocket family. Aérospatiale, and later ArianeGroup, was the prime contractor for the manufacturing of the vehicles, leading a multi-country consortium of other European con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |