|
Common Carotid Artery
In anatomy, the left and right common carotid arteries (carotids) () are artery, arteries that supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood; they divide in the neck to form the external carotid artery, external and internal carotid artery, internal carotid arteries. Structure The common carotid arteries are present on the left and right sides of the body. These arteries originate from different arteries but follow symmetrical courses. The right common carotid originates in the neck from the brachiocephalic trunk; the left from the aortic arch in the thorax. These split into the external and internal carotid arteries at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage, at around the level of the fourth cervical vertebra. The left common carotid artery can be thought of as having two parts: a thoracic (chest) part and a cervical (neck) part. The right common carotid originates in or close to the neck and contains only a small thoracic portion. There are studies in the bioengineering l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aorta
The aorta ( ; : aortas or aortae) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the Ventricle (heart), left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at the aortic bifurcation into two smaller arteries (the common iliac artery, common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes Oxygen saturation (medicine), oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word ''sternum'' originates from Ancient Greek στέρνον (''stérnon'') 'chest'. Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed nerve that originates from the C3–C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also a contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerve roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic nerve or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibers and serves as a major pathway that connects the brain to various organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. As a key part of the parasympathetic nervous system, the vagus nerve helps regulate essential involuntary functions like heart rate, breathing, and digestion. By controlling these processes, the vagus nerve contributes to the body's "rest and digest" response, helping to calm the body after stress, lower heart rate, improve digestion, and maintain homeostasis. The vagus nerve consists of two branches: the right and left vagus nerves. In the neck, the right vagus nerve contains approximately 105,000 fibers, while the left vagus nerve has about 87,000 fibers, according to one source. However, other sources report slig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
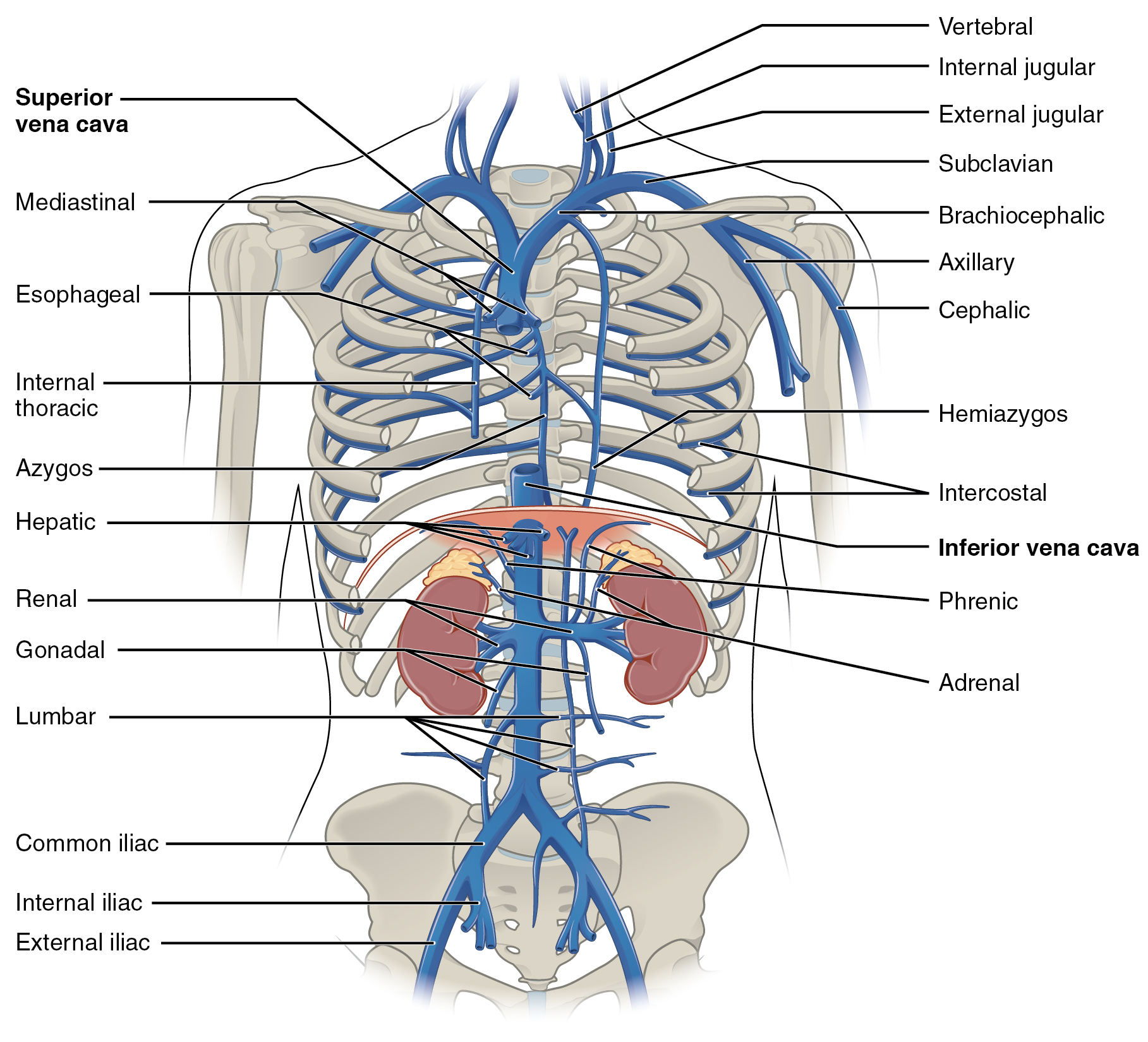
Inferior Thyroid Vein
The inferior thyroid veins appear two, frequently three or four, in number, and arise in the venous plexus on the thyroid gland, communicating with the middle and superior thyroid veins. While the superior and middle thyroid veins serve as direct tributaries to the internal jugular vein, the inferior thyroid veins drain directly to the brachiocephalic veins. The inferior thyroid veins form a plexus in front of the trachea, behind the sternothyroid muscle. From this plexus, the left vein descends and joins the left brachiocephalic vein, and the right vein passes obliquely downward and to the right across the brachiocephalic artery to open into the right brachiocephalic vein, just at its junction with the superior vena cava The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vei ...; s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct (also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal'') is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system (the other being the right lymphatic duct). The thoracic duct usually begins from the upper aspect of the cisterna chyli, passing out of the abdomen through the aortic hiatus into first the posterior mediastinum and then the superior mediastinum, extending as high up as the root of the neck before descending to drain into the systemic (blood) circulation at the venous angle. The thoracic duct carries chyle, a liquid containing both lymph and emulsified fats, rather than pure lymph. It also collects most of the lymph in the body other than from the right thorax, arm, head, and neck (which are drained by the right lymphatic duct). When the duct ruptures, the resulting flood of liquid into the pleural cavity is known as chylothorax. Structure In adults, the thoraci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve
The recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN), also known as nervus recurrens, is a branch of the vagus nerve ( cranial nerve X) that supplies all the intrinsic muscles of the larynx, with the exception of the cricothyroid muscles. There are two recurrent laryngeal nerves, right and left. The right and left nerves are not symmetrical, with the left nerve looping under the aortic arch, and the right nerve looping under the right subclavian artery, then traveling upwards. They both travel alongside the trachea. Additionally, the nerves are among the few nerves that follow a ''recurrent'' course, moving in the opposite direction to the nerve they branch from, a fact from which they gain their name. The recurrent laryngeal nerves supply sensation to the larynx below the vocal cords, give cardiac branches to the deep cardiac plexus, and branch to the trachea, esophagus and the inferior constrictor muscles. The posterior cricoarytenoid muscles, the only muscles that can open the vocal fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, is an Organ (anatomy), organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by Peristalsis, peristaltic contractions, from the Human pharynx, pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a :wiktionary:fibromuscular, fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and human heart, heart, passes through the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''esophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, "I carry") + ἔφαγον ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate Trachea
The trachea (: tracheae or tracheas), also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all animals' lungs. The trachea extends from the larynx and branches into the two primary bronchi. At the top of the trachea, the cricoid cartilage attaches it to the larynx. The trachea is formed by a number of horseshoe-shaped rings, joined together vertically by overlying ligaments, and by the trachealis muscle at their ends. The epiglottis closes the opening to the larynx during swallowing. The trachea begins to form in the second month of embryo development, becoming longer and more fixed in its position over time. Its epithelium is lined with column-shaped cells that have hair-like extensions called cilia, with scattered goblet cells that produce protective mucins. The trachea can be affected by inflammation or infection, usually as a result of a viral illness affectin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus (: thymuses or thymi) is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, T cells mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with Major histocompatibility complex, MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is the largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the Thymic involuti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiocephalic Vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the Thorax, upper chest, formed by the union of the ipsilateral internal jugular vein and subclavian vein (the so-called venous angle) behind the sternoclavicular joint. The left brachiocephalic vein is more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein. These veins merge to form the superior vena cava, a great vessel, posterior to the junction of the first costal cartilage with the Manubrium, manubrium of the sternum. The brachiocephalic veins are the major veins returning blood to the superior vena cava. Left and right veins Left brachiocephalic vein The left brachiocephalic vein is about 6cm, more than twice the length of the right brachiocephalic vein. and is formed by the confluence of the left subclavian vein, subclavian and left internal jugular veins. In addition the left vein receives drainage from the following tributaries: * The left vertebral vein, internal thor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the Thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes Animal communication#Auditory, vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |