|
Commissioners Of Supply
Commissioners of Supply were local administrative bodies in Scotland from 1667 to 1930. Originally established in each sheriffdom to collect tax, they later took on much of the responsibility for the local government of the counties of Scotland. In 1890 they ceded most of their duties to the county councils created by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889. They were finally abolished in 1930. Creation The Parliament of Scotland passed legislation creating Commissioners of Supply for each of the shires or sheriffdoms in 1667. The act specified that the commissioners for each sheriffdom should consist partly of ''ex officio'' members: all privy councillors and senators of the College of Justice "within the severall respective shyres wher any part of ther lands and estates doeth ly", and partly of nominated members: a number of named prominent landowners in each shire.The sheriffdoms listed were Edinburgh (i.e. Midlothian), Hadingtoun (i.e. East Lothian), Berwick, Roxburgh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjacent Islands of Scotland, islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. To the south-east, Scotland has its Anglo-Scottish border, only land border, which is long and shared with England; the country is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the north-east and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. The population in 2022 was 5,439,842. Edinburgh is the capital and Glasgow is the most populous of the cities of Scotland. The Kingdom of Scotland emerged as an independent sovereign state in the 9th century. In 1603, James VI succeeded to the thrones of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, forming a personal union of the Union of the Crowns, three kingdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Union 1707
The Acts of Union refer to two acts of Parliament, one by the Parliament of Scotland in March 1707, followed shortly thereafter by an equivalent act of the Parliament of England. They put into effect the international Treaty of Union agreed on 22 July 1706, which politically joined the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland into a single "political state" named Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, with Anne, Queen of Great Britain, Queen Anne as its sovereign. The English and Scottish acts of ratification took effect on 1 May 1707, creating the new kingdom, with Parliament of Great Britain, its parliament based in the Palace of Westminster. The two countries had shared a monarch since the "personal" Union of the Crowns in 1603, when James VI of Scotland inherited the English throne from his cousin Elizabeth I to become (in addition) 'James I of England', styled James VI and I. Attempts had been made to try to unite the two separate countries, in 1606, 1667, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1667 In Politics
Events January–March * January 11 – Aurangzeb, monarch of the Mughal Empire, orders the removal of Rao Karan Singh as Maharaja of the Bikaner State (part of the modern-day Rajasthan state of India) because of Karan's dereliction of duty in battle. * January 19 – The town of Anzonico in Switzerland is destroyed by an avalanche. * January 27 – The 2,000 seat Opernhaus am Taschenberg, a theater in Dresden (capital of the Electorate of Saxony) opens with its first production, Pietro Andrea Ziani, Pietro Ziani's opera ''Il teseo''. * February 5 – In the Second Anglo-Dutch War, the English Royal Navy warship HMS Saint Patrick, HMS ''Saint Patrick'' is captured less than nine months after being launched, when it fights a battle off the coast of England and North Foreland, North Foreland, Kent. Captain Robert Saunders and 8 of his crew are killed while fighting the Dutch ships ''Delft'' and ''Shakerlo''. The Dutch Navy renames the ship the ''Zwane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Commissions And Inquiries
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including: *Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland *Scottish English *Scottish national identity, the Scottish identity and common culture *Scottish people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland * Scots language, a West Germanic language spoken in lowland Scotland *Symphony No. 3 (Mendelssohn), a symphony by Felix Mendelssohn known as ''the Scottish'' See also *Scotch (other) *Scotland (other) *Scots (other) *Scottian (other) *Schottische The schottische is a partnered country dance that apparently originated in Bohemia. It was popular in Victorian-era ballrooms as a part of the Bohemian folk-dance craze and left its traces in folk music of countries such as Argentina (Spanish ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ca:Escocès ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
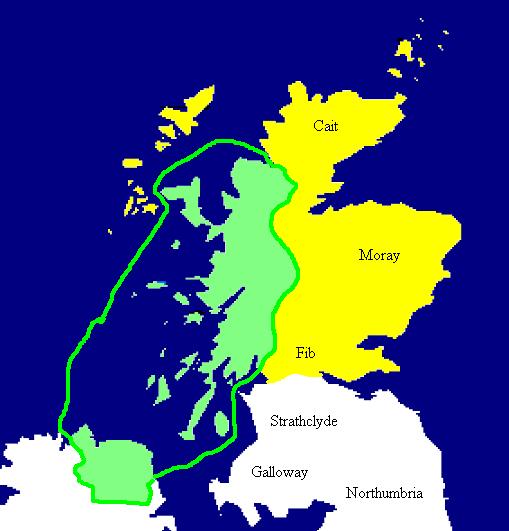
History Of Local Government In Scotland
The history of local government in Scotland is a complex tale of largely ancient and long established Scottish political units being replaced after the mid 20th century by a frequently changing series of different local government arrangements. Origins Anciently, the territory now referred to as ''Scotland'' belonged to a mixture of Brythonic groups (Picts and Cumbrians) and Angles. The Picts were based north of the Forth– Clyde line, traditionally in seven kingdoms: * Cat (the far north) * Ce (from Deeside to Speyside) * Circinn (southeast of the Cairngorms, roughly between the Isla and Dee) * Fib (the Fife peninsula) * Fotla (an expanded Atholl) * Fortriu (the areas to the north and west of the Grampians, including the Great Glen, and extending to the Atlantic coast, and as far north as the Dornoch Firth) *Fidach (unknown location). In later legends Albanactus, the legendary founder of Scotland, had seven sons, who each founded a kingdom. ''De Situ Albanie' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929
The Local Government (Scotland) Act 1929 ( 19 & 20 Geo. 5. c. 25) reorganised local government in Scotland from 1930, introducing joint county councils, large and small burghs and district councils. The Act also abolished the Scottish poor law system with institutions passing to the local authorities. The Act was drafted by Walter Elliot, the Unionist (Conservative) politician who became later (1936) Secretary of State for Scotland. Parish councils and poor law The parish councils that had been introduced by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1894 were dissolved. Their responsibilities regarding poor law passed to the county council, other powers passing to the new district councils. Another major effect of the Act was the ending of the Poor Law system, which had largely been administered by the parish councils. Their responsibilities in this area – now known as "Public Assistance" – passed to the county councils, large burghs and counties of cities. Abolition of Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland, the , which is commonly translated to English as ''sheriff''. Description In British English, the political or legal office of a sheriff, term of office of a sheriff, or jurisdiction of a sheriff, is called a shrievalty in England and Wales, and a sheriffdom in Scotland. In modern times, the specific combination of legal, political and ceremonial duties of a sheriff varies greatly from country to country. * In England, Northern Ireland, or Wales, a sheriff (or high sheriff) is a ceremonial county or city official. * In Scotland, sheriffs are judges. * In the Republic of Ireland, in some counties and in the cities of Dublin and Cork, sheriffs are legal officials similar to bailiffs. * In the United States The United States of America (USA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioners Of Highland Roads And Bridges
The Commissioners of Highland Roads and Bridges (formally the Commissioners for Roads and Bridges in the Highlands of Scotland) was created in 1803 to take responsibility for the construction and maintenance of the long-distance roads in the Scottish Highlands. The commission was created following the 1802 inspection by Thomas Telford (on behalf of the government) of the state of the roads. The Scottish Highland Roads and Bridges Act 1803 (43 Geo. 3. c. 80) established the commission. The initial commissioners, named in section 4 of the 1803 Act, were the Speaker of the House of Commons, the Chancellor of the Exchequer, and His Majesty's Advocate for Scotland, all for the Time being, the Rt Hon William Dundas, Sir William Pulteney, Bt, Isaac Hawkins Browne, Nicholas Vansittart, Charles Grant, William Smith, and Charles Dundas. The commission was dissolved by the Highland Roads and Bridges Act 1862 with effect from 31 December of that year, and the roads managed by the Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Police Burghs
A police burgh was a Scottish burgh which had adopted a "police system" for governing the town. They existed from 1833 to 1975. The 1833 act The first police burghs were created under the Burgh Police (Scotland) Act 1833 ( 3 & 4 Will. 4. c. 46). This act enabled existing royal burghs, burghs of regality, and burghs of barony to adopt powers of paving, lighting, cleansing, watching, supplying with water and improving their communities. This preceded the Municipal Corporations Act 1835, which introduced a similar reform in England and Wales, by two years. Forming a police burgh In order for the act to be adopted in any burgh, an application by householders in the town had to be made for a poll to be held. If three-quarters of qualified voters were in favour, the act would come into force in the burgh. Inhabitants were also free to choose which parts of the act to adopt. Boundaries Boundaries for the police burgh were to be set out, which could be extended up to in any dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Police (Scotland) Act 1857
The Police (Scotland) Act 1857 ( 20 & 21 Vict. c. 72) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was one of the Police (Scotland) Acts 1857 to 1890. The legislation made the establishment of a police force mandatory in the counties of Scotland, and also allowed existing burgh police forces to be consolidated with a county force. Establishment of county police forces The Commissioners of Supply for each county were required to form a police committee to administer a police force for their area. The committee was to consist of not more than 15 commissioners, plus the lord lieutenant and sheriff of the county (or their deputies). The police force forces were to come into existence on 15 March 1858. A chief constable was to be appointed to each police force by the committee. It was, however, permitted for two or more adjoining counties to appoint a single chief constable. The chief constable was to run the day-to-day activities of the force, and to appoint and dismiss co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |