|
Colombia's History
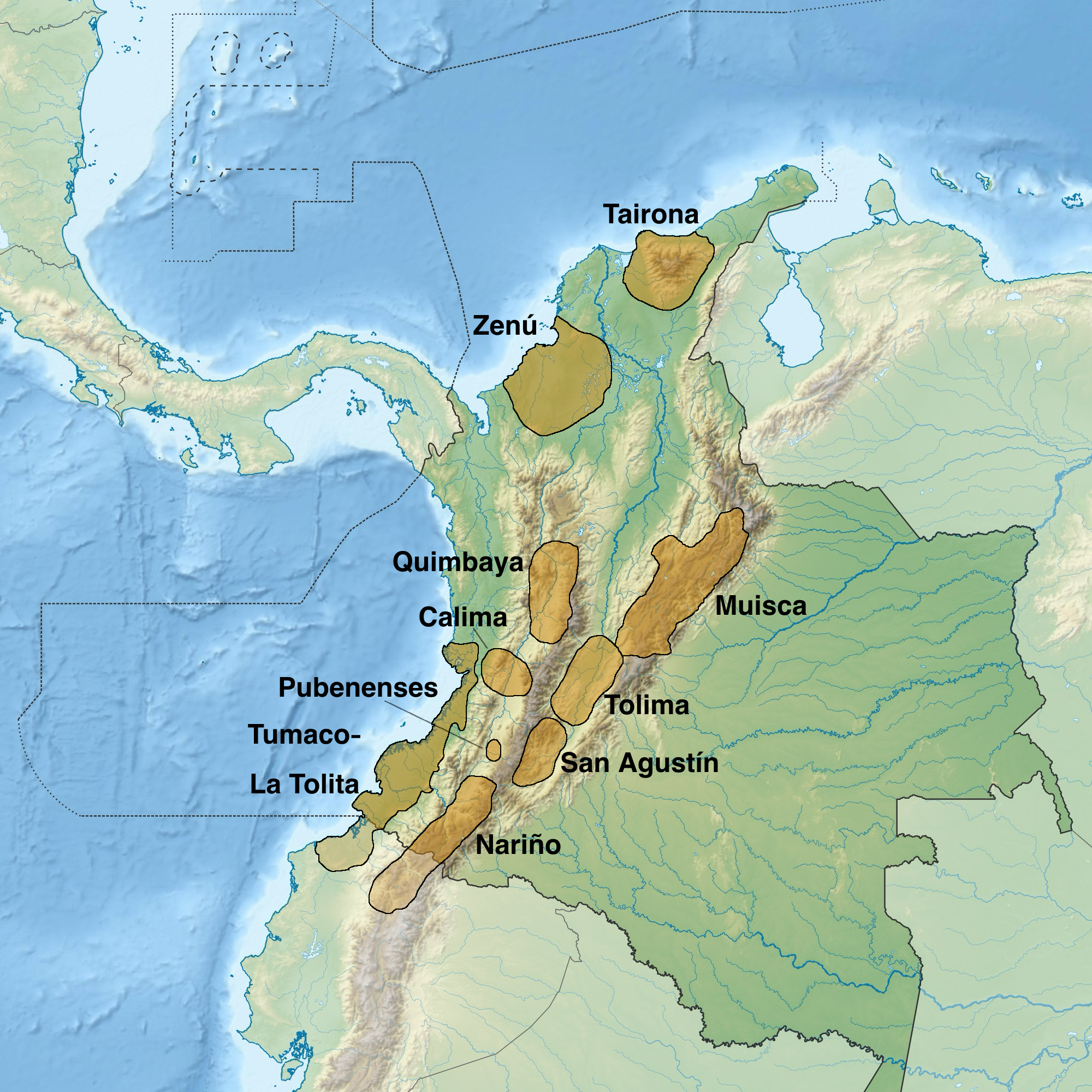
The history of Colombia includes its settlement by indigenous peoples and the establishment of agrarian societies, notably the Muisca Confederation, Quimbaya Civilization, and Tairona Chiefdoms. The Spanish arrived in 1499 and initiated a period of annexation and colonization, ultimately creating the Viceroyalty of New Granada, with its capital at Bogotá. Independence from Spain was won in 1819, but by 1830 the resulting "Gran Colombia" Federation was dissolved. What is now Colombia and Panama emerged as the Republic of New Granada. The new nation experimented with federalism as the Granadine Confederation (1858) and then the United States of Colombia (1863) before the Republic of Colombia was finally declared in 1886. A period of constant political violence ensued, and Panama seceded in 1903. Since the 1960s, the country has suffered from an asymmetric low-intensity armed conflict which escalated in the 1990s but decreased from 2005 onward. The legacy of Colombia's histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombian Armed Conflict (1964–present)
The Colombian conflict () began on May 27, 1964, and is a low-intensity asymmetric war between the government of Colombia, far-right paramilitary groups, crime syndicates and far-left guerrilla groups fighting each other to increase their influence in Colombian territory. Some of the most important international contributors to the Colombian conflict include multinational corporations, the United States, Cuba, and the drug trafficking industry. The conflict is historically rooted in the conflict known as '' La Violencia'', which was triggered by the 1948 assassination of liberal political leader Jorge Eliécer Gaitán and in the aftermath of the anti-communist repression in rural Colombia in the 1960s that led Liberal and Communist militants to re-organize into the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC). The reasons for fighting vary from group to group. The FARC and other guerrilla movements claim to be fighting for the rights of the impoverished in Colombia t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibitó
Tibitó is the second-oldest dated archaeological site on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Colombia.Caracterización de los sitios arqueológicos Sabana de Bogotá - ICANH The is located in the Tocancipá, Cundinamarca, |
Paleoindian
Paleo-Indians were the first peoples who entered and subsequently inhabited the Americas towards the end of the Late Pleistocene period. The prefix ''paleo-'' comes from . The term ''Paleo-Indians'' applies specifically to the lithic period in the Western Hemisphere and is distinct from the term ''Paleolithic''.''Paleolithic'' specifically refers to the period between million years ago and the end of the Pleistocene in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is not used in New World archaeology. Traditional theories suggest that big-animal hunters crossed the Bering Strait from North Asia into the Americas over a land bridge (Beringia). This bridge existed from 45,000 to 12,000 BCE (47,000–14,000 BP). Small isolated groups of hunter-gatherers migrated alongside herds of large herbivores far into Alaska. From BCE ( BP), ice-free corridors developed along the Pacific coast and valleys of North America. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
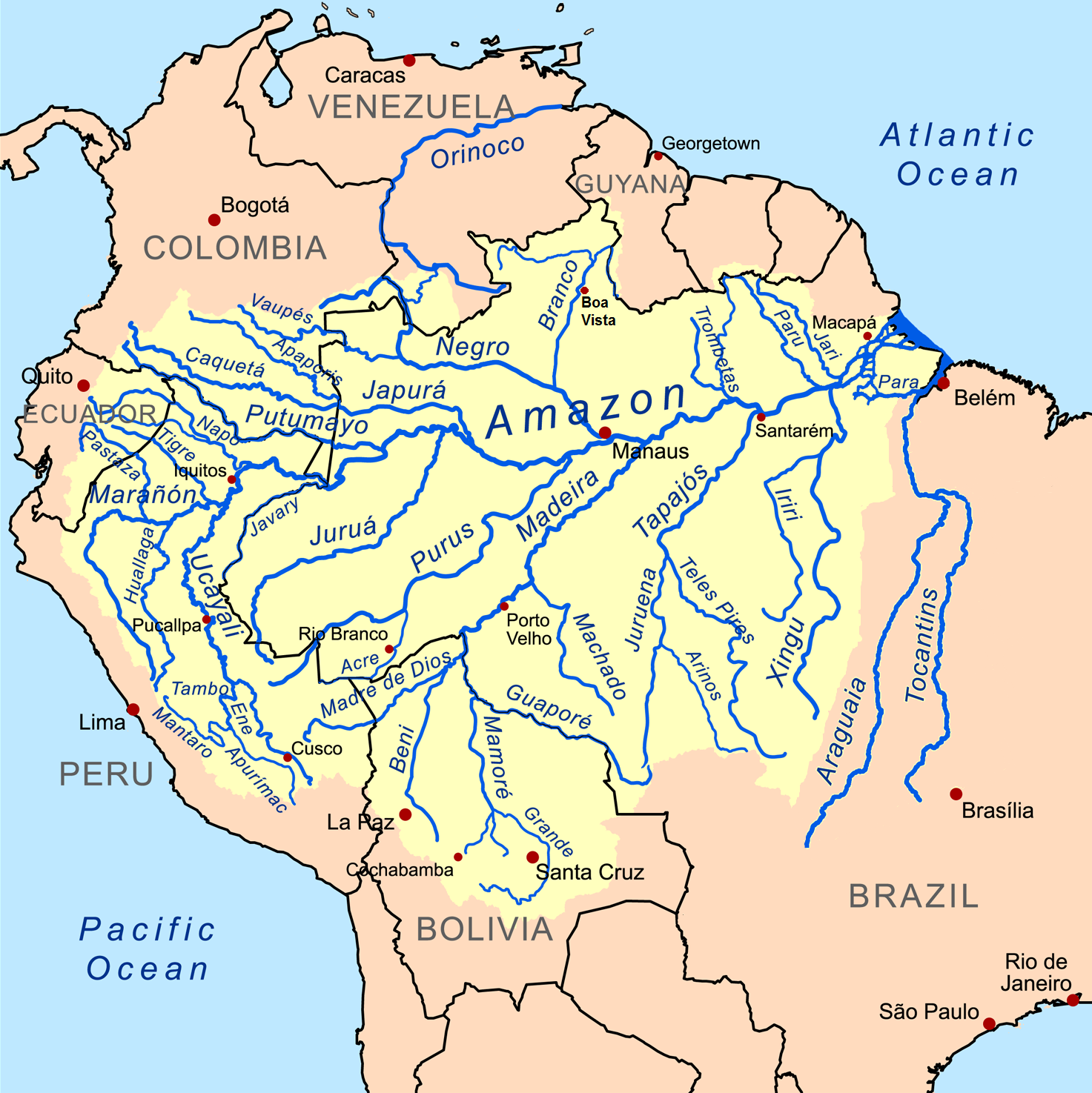
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous List of Caribbean islands, islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo Municipalities of Quintana Roo#Municipalities, islands and Districts of Belize#List, Belizean List of islands of Belize, islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands Department#Islands, Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the Mainland, continental mainland of the Americas bordering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to the Pacific coast of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central and southern Mexico, all of Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, and parts of Honduras, Nicaragua and northwestern part of Costa Rica. As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures. In the pre-Columbian era, many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous societies flourished in Mesoamerica for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas began on Hispaniola in 1493. In world history, Mesoamerica was the site of two historical transformations: (i) primary urban generation, and (ii) the formation of New World cultures from the mixtures of the indigenous Mesoamerican peoples with the European, African, and Asian peoples who were introduced by the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalena River
The Magdalena River (, ; less commonly ) is the main river of Colombia, flowing northward about through the western half of the country. It takes its name from the biblical figure Mary Magdalene. It is navigable through much of its lower reaches, in spite of the shifting sand bars at the mouth of its delta, as far as Honda, at the downstream base of its rapids. It flows through the Magdalena River Valley. Its drainage basin covers a surface of , which is 24% of the country's area and where 66% of its population lives. Course The Magdalena River is the largest river system of the northern Andes, with a length of 1,612 km. Its headwaters are in the south of Colombia, where the Andean subranges Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental separate, in Huila Department. The river runs east then north in a great valley between the two cordilleras. It reaches the coastal plain at about nine degrees north, then runs west for about , then north again, reaching the Caribbean Sea at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tequendama
Tequendama is a preceramic and ceramic archaeological site located southeast of Soacha, Cundinamarca, Colombia, a couple of kilometers east of Tequendama Falls. It consists of multiple evidences of late Pleistocene to middle Holocene population of the Bogotá savanna, the high plateau in the Colombian Andes. Tequendama was inhabited from around 11,000 years BP, and continuing into the prehistorical, Herrera and Muisca periods, making it the oldest site of Colombia, together with El Abra, located north of Zipaquirá.Nivel Paleoindio. Abrigos rocosos del Tequendama Younger evidences also from the Herrera Period have been found close to the site of Tequendama in Soacha, at the construction site of a new electrical plant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Abra
El Abra is the name given to an extensive archeological site, located in the valley of the same name. El Abra is situated in the east of the municipality Zipaquirá extending to the westernmost part of Tocancipá in the department of Cundinamarca, Colombia. The several hundred metres long series of rock shelters is in the north of the Bogotá savanna on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense, Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes at an altitude of . The rock shelter and cave system is one of the first evidences of human settlement in the Americas, dated at 12,400 ± 160 years BP. The site was used by the hunter-gatherers of the Late Pleistocene epoch. Etymology The name El Abra is taken from a large hacienda of that name at the foot of the western portion of the rock formation. The eastern side of the outcropping sandstones is accessible. Climbing activities at these ''Rocas de Sevilla'' are organised. Stratigraphy The first research in the place was conducted in 1967, and the str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
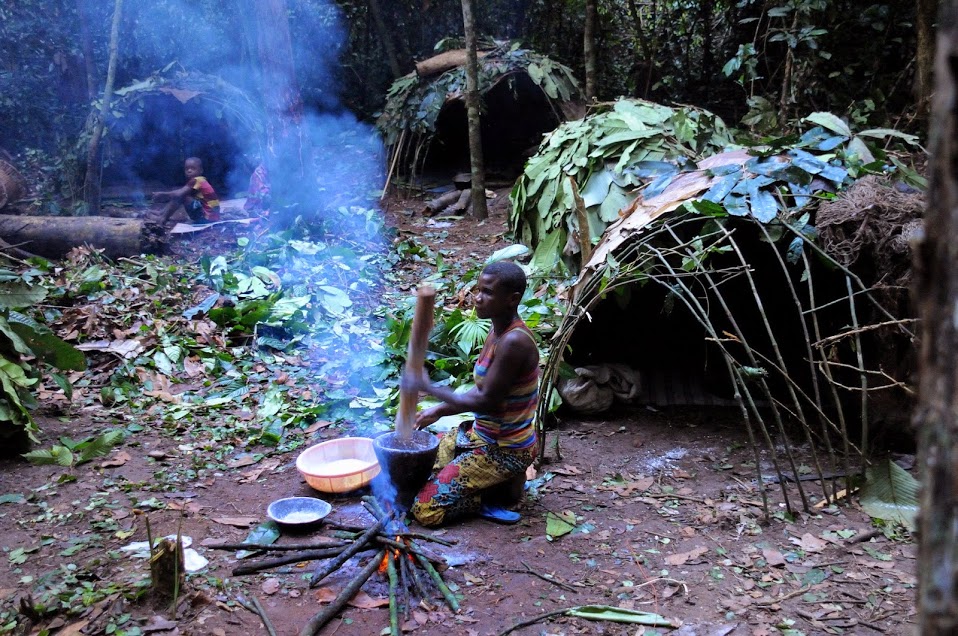
Hunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, especially wild edible plants but also insects, Fungus, fungi, Honey hunting, honey, Eggs as food, bird eggs, or anything safe to eat, or by hunting game (pursuing or trapping and killing Wildlife, wild animals, including Fishing, catching fish). This is a common practice among most vertebrates that are omnivores. Hunter-gatherer Society, societies stand in contrast to the more Sedentism, sedentary Agrarian society, agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful Competition (biology), competitive adaptation in the nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |