|
Collybiopsis Confluens
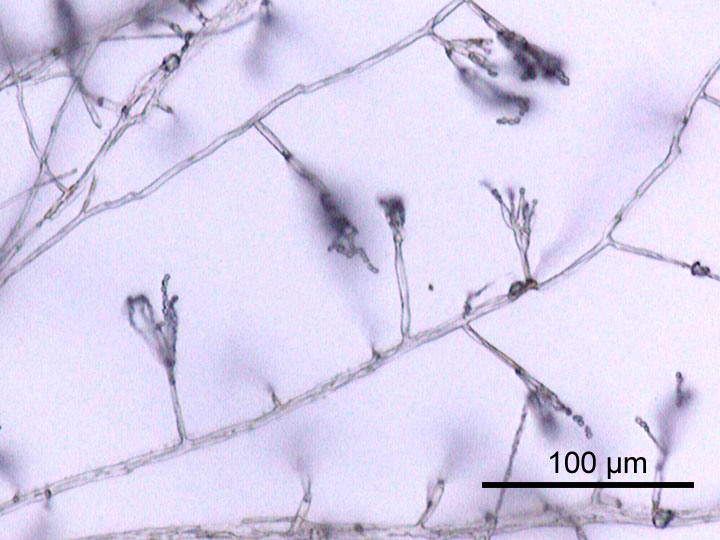
''Collybiopsis confluens'', commonly known as the clustered toughshank, is a type of mushroom from the Omphalotaceae family. The fruiting body appears from summer until autumn in deciduous and coniferous forests. ''Collybiopsis confluens'' is not an edible mushroom. Taxonomy The mushroom was first classified as ''Agaricus confluens'' by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1796. In 1828, Persoon re-classified this species under the name of ''Agaricus archyropus''. In 1828, Elias Magnus Fries gave the mushroom the name ''Maramius archyropus'' and so put it in the genus ''Marasmius''. Indeed, he used also the younger epithet ''archyropus'', although the older epithet ''confluens'' through the designation took precedence. This was corrected in 1898 by P. Karsten, who gave the species the name ''Marasmius confluens'' and so used the older epithet for the classification into the genus ''Marasmius''. In 1871, Paul Kummer placed the mushroom as ''Collybia confluens'' in the genus ''Collybi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon
Christiaan Hendrik Persoon (31 December 1761 – 16 November 1836) was a Cape Colony mycologist who is recognized as one of the founders of mycology, mycological Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. Early life Persoon was born in Cape Colony at the Cape of Good Hope, the third child of an immigrant Pomeranian father, Christiaan Daniel Persoon, and Netherlands, Dutch mother, Wilhelmina Elizabeth Groenwald. His mother died soon after he was born. In 1775, at the age of thirteen, he was sent to Europe for his education. His father died a year later in 1776. Education Initially a student of theology at University of Halle-Wittenberg, Halle, Persoon switched his studies to medicine, which he pursued in Leiden and then Göttingen. He received a doctorate from the German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina, Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher in Erlangen 1799. Later years He moved to Paris by 1803, where he spent the rest of his life, renting the upper floor of a house in a poor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stipe (mycology)
In mycology, a stipe () is the stem or stalk-like feature supporting the cap of a mushroom. Like all tissues of the mushroom other than the hymenium, the stipe is composed of sterile hyphal tissue. In many instances, however, the fertile hymenium extends down the stipe some distance. Fungi that have stipes are said to be stipitate. The evolutionary benefit of a stipe is generally considered to be in mediating spore dispersal. An elevated mushroom will more easily release its spores into wind currents or onto passing animals. Nevertheless, many mushrooms do not have stipes, including cup fungi, puffballs, earthstars, some polypores, jelly fungi, ergots, and smuts. It is often the case that features of the stipe are required to make a positive identification of a mushroom. Such distinguishing characters include: # the texture of the stipe (fibrous, brittle, chalky, leathery, firm, etc.) # whether it has remains of a partial veil (such as an annulus (ring) or cortina) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
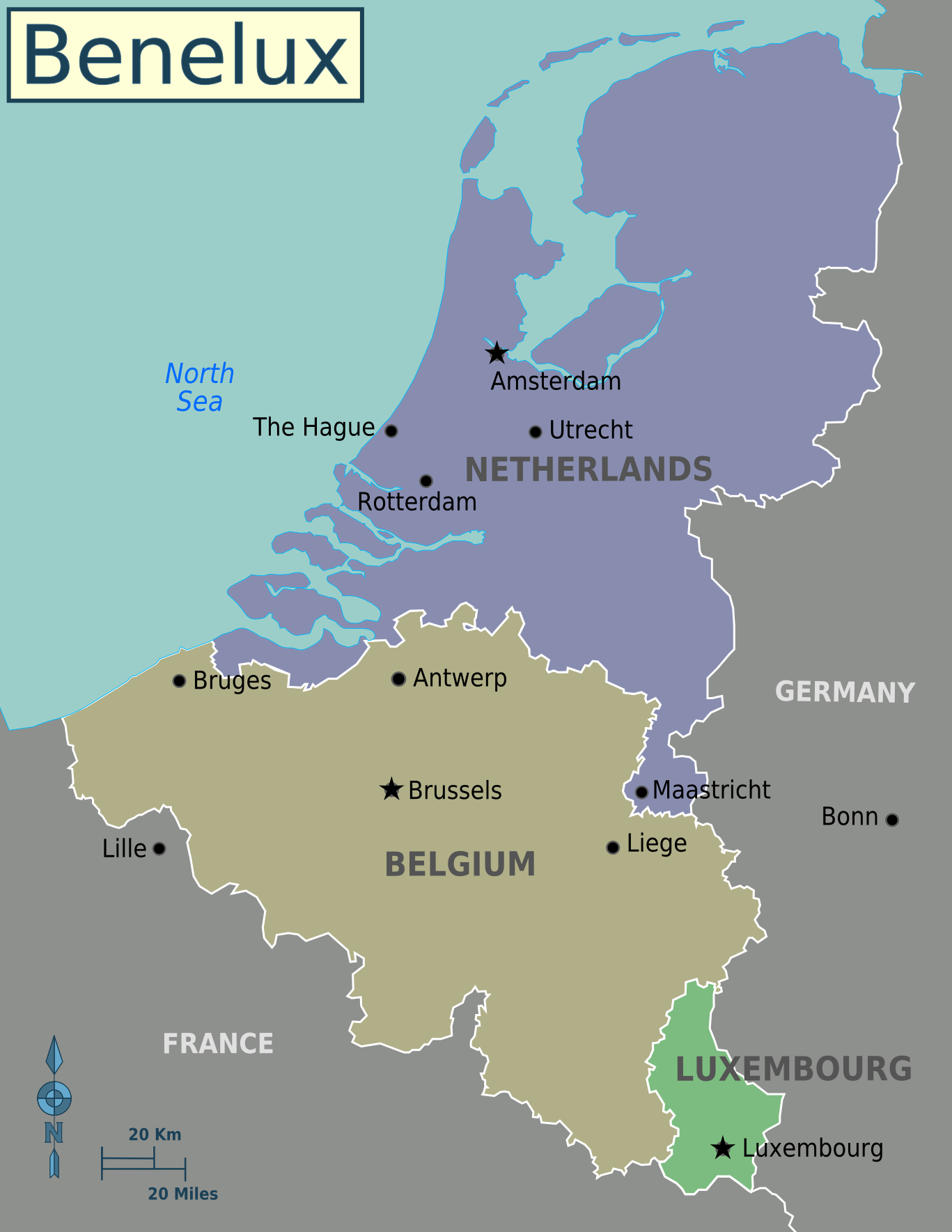
Benelux
The Benelux Union (; ; ; ) or Benelux is a politico-economic union, alliance and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighbouring states in Western Europe: Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The name is a portmanteau formed from joining the first few letters of each country's name and was first used to name the customs agreement that initiated the union (signed in 1944). It is now used more generally to refer to the geographic, economic, and cultural grouping of the three countries. The Benelux is an economically dynamic and densely populated region, with 5.6% of the European population (29.55 million residents) and 7.9% of the joint EU GDP (€36,000/resident) on 1.7% of the whole surface of the EU. In 2015, 37% of the total number of EU cross-border workers worked in the Benelux; 35,000 Belgian residents work in Luxembourg, while 37,000 others cross the border to work in the Netherlands each day. In addition, 12,000 Dutch and close to a thous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holarctic Realm
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region (which covers most of North America), and Alfred Wallace's Palearctic zoogeographical region (which covers North Africa, and all of Eurasia except for Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the southern Arabian Peninsula). These regions are further subdivided into a variety of ecoregions. Many ecosystems and the animal and plant communities that depend on them extend across a number of continents and cover large portions of the Holarctic realm. This continuity is the result of those regions’ shared glacial history. Major ecosystems Within the Holarctic realm, there are a variety of ecosystems. The type of ecosystem found in a given area depends on its latitude and the local geography. In the far north, a band of Arctic tundra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnopus Peronatus
''Collybiopsis peronata'', also known as wood woolly-foot, is a species of gilled mushroom which is common in European woods. Naming This species was originally described by James Bolton in his 1788 book "An history of fungusses, growing about Halifax" as ''Agaricus peronatus'' at a time when all gilled mushrooms were assigned to genus ''Agaricus''. Then in 1821 another Englishman, Samuel Frederick Gray published his "Natural Arrangement of British Plants" (including fungi) in which he allocated the species to the already existing genus ''Gymnopus''. In 1791 Bulliard described the same species as ''Agaricus urens'', the epithet "urens" ("burning") referring to the acrid taste, and in 1836 Fries put it genus ''Marasmius''. Also in 1871 Paul Kummer put this mushroom in genus '' Collybia'', giving it the name ''Collybia peronata''. For many years it was known either as ''Marasmius urens'' or ''Collybia peronata'' (or sometimes ''Marasmius peronatus'' or ''Collybia urens''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clamp Connections
A clamp connection is a hook-like structure formed by growing hyphal cells of certain fungi. It is a characteristic feature of basidiomycete fungi. It is created to ensure that each cell, or segment of hypha separated by septa (cross walls), receives a set of differing nuclei, which are obtained through mating of hyphae of differing sexual types. It is used to maintain genetic variation within the hypha much like the mechanisms found in croziers (hooks) during the sexual reproduction of ascomycetes. Formation Clamp connections are formed by the terminal hypha during elongation. Before the clamp connection is formed this terminal segment contains two nuclei. Once the terminal segment is long enough it begins to form the clamp connection. At the same time, each nucleus undergoes mitotic division to produce two daughter nuclei. As the clamp continues to develop it uptakes one of the daughter (green circle) nuclei and separates it from its sister nucleus. While this is occurring the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pileipellis
The pileipellis is the uppermost layer of hyphae in the pileus of a fungal fruit body. It covers the trama, the fleshy tissue of the fruit body. The pileipellis is more or less synonymous with the cuticle, but the cuticle generally describes this layer as a macroscopic feature, while pileipellis refers to this structure as a microscopic layer. Pileipellis type is an important character in the identification of fungi. Pileipellis types include the cutis, trichoderm, epithelium, and hymeniderm types. Types Cutis A cutis is a type of pileipellis characterized by hyphae that are repent, that is, that run parallel to the pileus surface. In an ixocutis, the hyphae are gelatinous. Trichoderm In a trichoderm, the outermost hyphae emerge roughly parallel, like hairs, perpendicular to the cap surface. The prefix "tricho-" comes from a Greek word for "hair". In an ixotrichodermium, the outermost hyphae are gelatinous. Epithelium An epithelium is a pileipellis consisting of rounded ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypha
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium. Structure A hypha consists of one or more cells surrounded by a tubular cell wall. In most fungi, hyphae are divided into cells by internal cross-walls called "septa" (singular septum). Septa are usually perforated by pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and sometimes nuclei to flow between cells. The major structural polymer in fungal cell walls is typically chitin, in contrast to plants and oomycetes that have cellulosic cell walls. Some fungi have aseptate hyphae, meaning their hyphae are not partitioned by septa. Hyphae have an average diameter of 4–6 μm. Growth Hyphae grow at their tips. During tip growth, cell walls are extended by the external assembly and polymerization of cell wall components, and the internal production of new cell membrane. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheilocystidia
A cystidium (: cystidia) is a relatively large cell found on the sporocarp of a basidiomycete (for example, on the surface of a mushroom gill), often between clusters of basidia. Since cystidia have highly varied and distinct shapes that are often unique to a particular species or genus, they are a useful micromorphological characteristic in the identification of basidiomycetes. In general, the adaptive significance of cystidia is not well understood. Classification By position Cystidia may occur on the edge of a lamella (or analogous hymenophoral structure) (cheilocystidia), on the face of a lamella (pleurocystidia), on the surface of the cap (dermatocystidia or pileocystidia), on the margin of the cap (circumcystidia) or on the stipe (caulocystidia). Especially the pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia are important for identification within many genera. Sometimes the cheilocystidia give the gill edge a distinct colour which is visible to the naked eye or with a hand lens. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidia
A basidium (: basidia) is a microscopic spore-producing structure found on the hymenophore of reproductive bodies of basidiomycete fungi. The presence of basidia is one of the main characteristic features of the group. These bodies are also called tertiary mycelia, which are highly coiled versions of secondary mycelia. A basidium usually bears four sexual spores called basidiospores. Occasionally the number may be two or even eight. Each reproductive spore is produced at the tip of a narrow prong or horn called a sterigma (), and is forcefully expelled at full growth. The word ''basidium'' literally means "little pedestal". This is the way the basidium supports the spores. However, some biologists suggest that the structure looks more like a club. A partially grown basidium is known as a basidiole. Structure Most basidiomycota have single celled basidia (holobasidia), but some have ones with many cells (a phragmobasidia). For instance, rust fungi in the order ''Puccinal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Blue
Methyl blue is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C37H27N3Na2O9S3. It is used as a stain in histology, and stains collagen blue in tissue sections. It can be used in some differential staining techniques such as Mallory's trichrome stain and Gömöri trichrome stain, and can be used to mediate electron transfer in microbial fuel cells. Fungal cell walls are also stained by methyl blue. Methyl blue is also available in mixture with water blue, under name Aniline Blue WS, Aniline blue, China blue, or Soluble blue; and in a solution of phenol, glycerol, and lactic acid under the name Lactophenol cotton blue (LPCB), which is used for microscopic visualization of fungi. Chemistry Methyl blue ( is[4-[(sulfophenyl)amino.html" ;"title="4-[Bis[4-[(sulfophenyl)amino">4-[Bis[4-[(sulfophenyl)aminohenylethylene]-2,5-cyclohexadien-1-ylidene]amino]-benzenesulfonic acid disodium salt) is distinctly different to methylene blue ([7-(dimethylamino)phenothiazin-3-ylidene]-dimethy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |