|
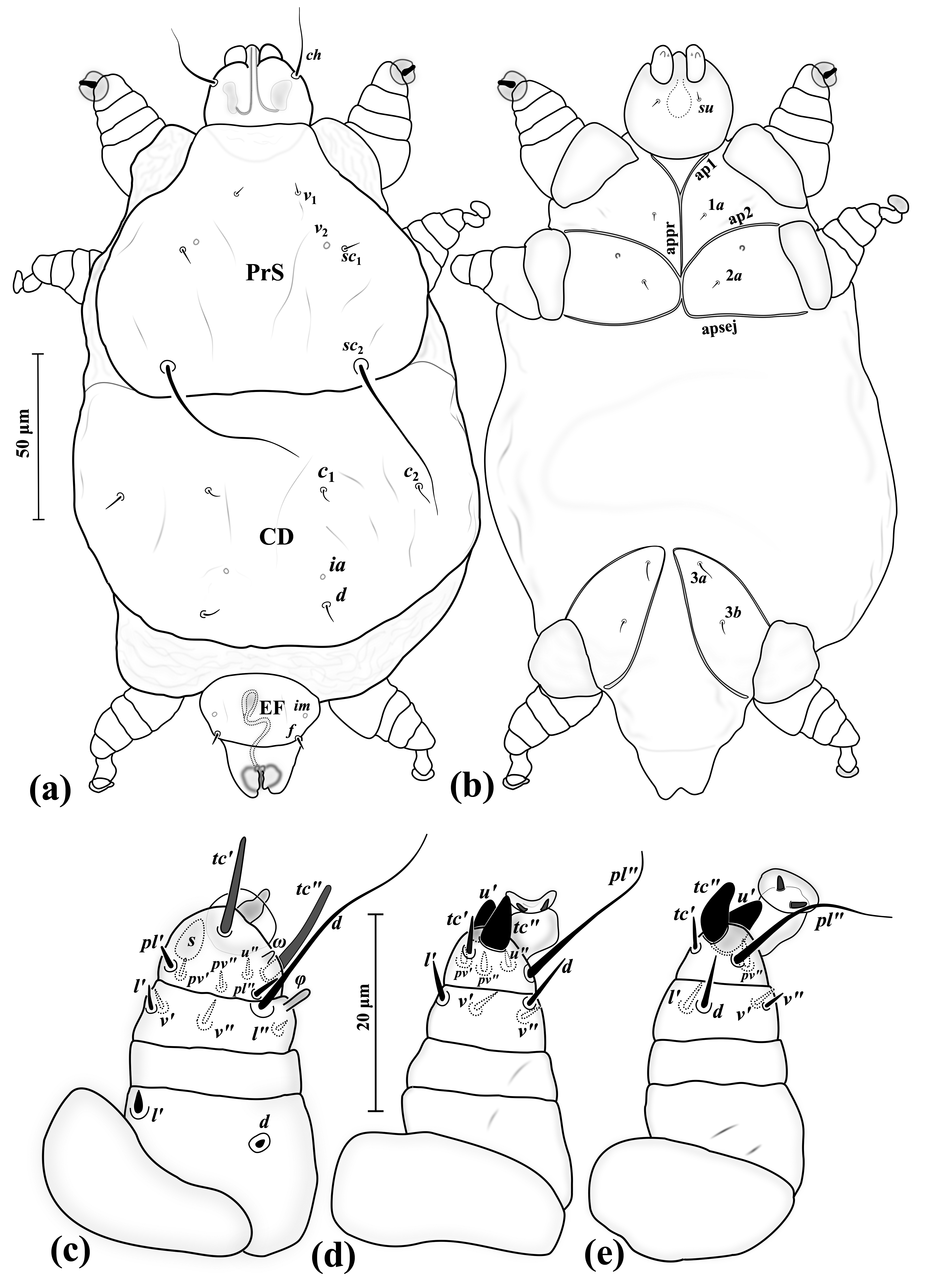
Cochlodispus Minimus
''Cochlodispus minimus'' is a species of mite from the family Microdispidae, formally described by Sándor Mahunka in 1976. One adult individual was measured with a body length of 79 μm (0.079 mm), making it the smallest known mite species. It was originally described from Ethiopia, along with cogeners ''C. africanus'' and ''C. fimbrisetus'', and inhabits soil and litter. Taxonomy The Microdispidae are the least diverse family of pygmephoroid mites, with 20 described genera and about 120 species. Most members of this family are fungivores, although some may be parasitoids of insects. ''Cochlodispus minimus'' is one of 11 species currently described from the genus '' Cochlodispus''. It can be distinguished within its genus by the absence of barbs on setae ''ps2'' (a characteristic shared only with ''C. zanzibariensis'') and by the absence of barbs on setae ''f'' and on the setae of the anterior sternal plate (both distinctly barbed in ''C. zanzibariensis)''. See also * Small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of arachnids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, north, Djibouti to the Djibouti–Ethiopia border, northeast, Somalia to the Ethiopia–Somalia border, east and northeast, Kenya to the Ethiopia–Kenya border, south, South Sudan to the Ethiopia–South Sudan border, west, and Sudan to the Ethiopia–Sudan border, northwest. Ethiopia has a total area of . As of 2022, it is home to around 113.5 million inhabitants, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, 13th-most populous country in the world and the List of African countries by population, 2nd-most populous in Africa after Nigeria. The national capital and largest city, Addis Ababa, lies several kilometres west of the East African Rift that splits the country into the African Plate, Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungivore
Fungivory or mycophagy is the process of organisms consuming fungi. Many different organisms have been recorded to gain their energy from consuming fungi, including birds, mammals, insects, plants, amoebas, gastropods, nematodes, bacteria and other fungi. Some of these, which only eat fungi, are called fungivores whereas others eat fungi as only part of their diet, being omnivores. Animals Mammals Many mammals eat fungi, but only a few feed exclusively on fungi; most are opportunistic feeders and fungi only make up part of their diet. At least 22 species of primate, including humans, bonobos, colobines, gorillas, lemurs, macaques, mangabeys, marmosets and vervet monkeys are known to feed on fungi. Most of these species spend less than 5% of the time they spend feeding eating fungi, and fungi therefore form only a small part of their diet. Some species spend longer foraging for fungi, and fungi account for a greater part of their diet; buffy-tufted marmosets spend up to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlodispus
''Cochlodispus'' is a genus of mites from the family Microdispidae. One member of the genus, ''Cochlodispus minimus'', is considered the smallest known mite species with a recorded adult body length of 79 μm (0.079 mm). Characteristics The Microdispidae are the least diverse family of pygmephoroid mites, with 20 described genera and about 120 species. Most members of the family are fungivores, although some may be parasitoids of insects. All 11 described species of ''Cochlodispus'' inhabit soil and litter. The type species, ''Cochlodispus cochleatus'', was originally designated ''Microdispus cochleatus'' by Sándor Mahunka in 1969. Three years later, Mahunka formally described ''Cochlodispus'' as a distinct genus. Species The genus ''Cochlodispus'' currently contains 11 species: * ''Cochlodispus africanus'' Mahunka, 1975 – described from Ethiopia * ''Cochlodispus chilensis'' Mahunka, 1972 – described from Chile * ''Cochlodispus cochleatus'' Mahunka, 1969 – describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms. Animal setae Protostomes Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. They help, for example, earthworms to attach to the surface and prevent backsliding during peristaltic motion. These hairs make it difficult to pull a worm straight from the ground. Setae in oligochaetes (a group including earthworms) are largely composed of chitin. They are classified according to the limb to which they are attached; for instance, notosetae are attached to notopodia; neurosetae to neuropodia. Crustaceans have mechano- and chemosensory setae. Setae are especially present on the mouthparts of crustaceans and can also be found on grooming limbs. In some cases, setae are modified into scale like structures. Setae on the legs of krill and other small crustaceans help them to gather phytoplankton. It captures them and allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallest Organisms
The smallest organisms found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of organism size, including volume, mass, height, length, or genome size. Given the incomplete nature of scientific knowledge, it is possible that the smallest organism is undiscovered. Furthermore, there is some debate over the definition of life, and what entities qualify as organisms; consequently the smallest known organism (microorganism) is debatable. Microorganisms Obligate endosymbiotic bacteria The genome of ''Nasuia deltocephalinicola'', a symbiont of the European pest leafhopper, '' Macrosteles quadripunctulatus'', consists of a circular chromosome of 112,031 base pairs. The genome of '' Nanoarchaeum equitans'' is 490,885 nucleotides long. ''Pelagibacter ubique'' '' Pelagibacter ubique'' is one of the smallest known free-living bacteria, with a length of and an average cell diameter of . They also have the smallest free-living bacterium genome: 1.3 Mbp, 1354 protein gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trombidiformes
The Trombidiformes are a large, diverse order of mites. Taxonomy In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of acariform mites, Sarcoptiformes. Its members include medically important mites (such as '' Demodex'', the chiggers, and scrub-itch mites) and many agriculturally important species, including the spider mites (Tetranychidae). The superfamily Eriophyoidea, traditionally considered members of the Trombidiformes, have been found to be basal mites in genomic analyses, sister to the clade containing Sarcoptiformes and Trombidiformes. The 2004 classification retained the two suborders, comprising around 125 families and more than 22,000 described species. In the 2011 revised classification, the order now contains 151 families, 2235 genera Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)