|
Cloquet's Node
Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the groin. They are situated in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region. They are subdivided into two groups: the superficial inguinal lymph nodes and deep inguinal lymph nodes. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes The superficial inguinal lymph nodes are the inguinal lymph nodes that form a chain immediately inferior to the inguinal ligament. They lie deep to the fascia of Camper that overlies the femoral vessels at the medial aspect of the thigh. They are bounded superiorly by the inguinal ligament in the femoral triangle, laterally by the border of the sartorius muscle, and medially by the adductor longus muscle. There are approximately 10 superficial lymph nodes. They normally measure up to 2 cm in diameter. Last updated: Last updated: Feb 16, 2017 They are divided into three groups: * inferior – inferior of the saphenous opening of the leg, receive drainage from lower legs * superolateral – on the side of the saphenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that include B and T cells. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cells, but have no detoxification function. In the lymphatic system, a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Lymph nodes become inflamed or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancers. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttock
The buttocks (: buttock) are two rounded portions of the exterior anatomy of most mammals, located on the posterior of the pelvic region. In humans, the buttocks are located between the lower back and the perineum. They are composed of a layer of exterior skin and underlying subcutaneous fat superimposed on a left and right gluteus maximus and gluteus medius muscles. The two gluteus maximus muscles are the largest muscles in the human body. They are responsible for movements such as straightening the body into the upright (standing) posture when it is bent at the waist; maintaining the body in the upright posture by keeping the hip joints extended; and propelling the body forward via further leg (hip) extension when walking or running. In many cultures, the buttocks play a role in sexual attraction. Many cultures have also used the buttocks as a primary target for corporal punishment, as the buttocks' layer of subcutaneous fat offers protection against injury while still ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
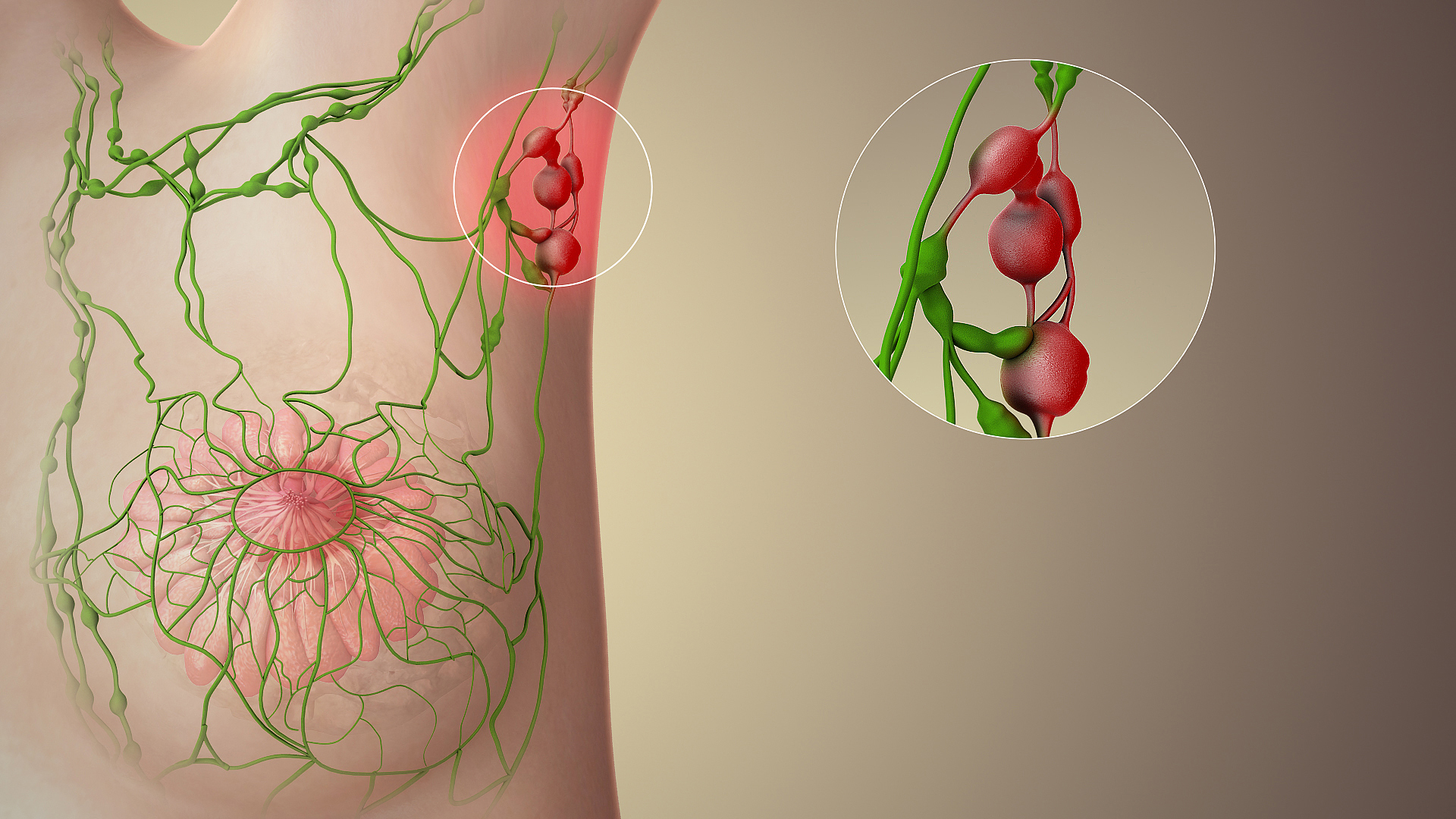
Sentinel Lymph Node
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer cells from the tumor. The sentinel node procedure (also termed sentinel lymph node biopsy or SLNB) is the identification, removal and analysis of the sentinel lymph nodes of a particular tumour. Physiology The spread of some forms of cancer usually follows an orderly progression, spreading first to regional lymph nodes, then the next echelon of lymph nodes, and so on, since the flow of lymph is directional, meaning that some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to determine if the cancer has spre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Iliac Lymph Nodes
The external iliac lymph nodes are lymph nodes, from eight to ten in number, that lie along the external iliac vessels. They are arranged in three groups, one on the lateral, another on the medial, and a third on the anterior aspect of the vessels; the third group is, however, sometimes absent. Their principal afferents are derived from the inguinal lymph nodes, the deep lymphatics of the abdominal wall below the umbilicus and of the adductor region of the thigh, and the lymphatics from the glans penis, glans clitoridis, the membranous urethra, the prostate, the fundus of the urinary bladder, the cervix uteri, and upper part of the vagina. Additional images File:Lymph_node_regions.svg, Regional lymph tissue File:Gray611.png , The parietal lymph glands of the pelvis The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Range
In medicine and health-related fields, a reference range or reference interval is the range or the interval of values that is deemed normal for a physiological measurement in healthy persons (for example, the amount of creatinine in the blood, or the partial pressure of oxygen). It is a basis for comparison for a physician or other health professional to interpret a set of test results for a particular patient. Some important reference ranges in medicine are reference ranges for blood tests and reference ranges for urine tests. The standard definition of a reference range (usually referred to if not otherwise specified) originates in what is most prevalent in a reference group taken from the general (i.e. total) population. This is the general reference range. However, there are also ''optimal health ranges'' (ranges that appear to have the optimal health impact) and ranges for particular conditions or statuses (such as pregnancy reference ranges for hormone levels). Value ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation of the values of a variable about its Expected value, mean. A low standard Deviation (statistics), deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while a high standard deviation indicates that the values are spread out over a wider range. The standard deviation is commonly used in the determination of what constitutes an outlier and what does not. Standard deviation may be abbreviated SD or std dev, and is most commonly represented in mathematical texts and equations by the lowercase Greek alphabet, Greek letter Sigma, σ (sigma), for the population standard deviation, or the Latin script, Latin letter ''s'', for the sample standard deviation. The standard deviation of a random variable, Sample (statistics), sample, statistical population, data set, or probability distribution is the square root of its variance. (For a finite population, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cribriform Fascia
The cribriform fascia (also known as the fascia cribrosa, or Hesselbach's fascia) is the portion of the superficial layer of the deep fascia of leg which extends between the sartorius muscle, adductor longus muscle, and inguinal ligament to form the anterior portion of the femoral canal. The cribriform fascia forms numerous openings to allow the passage of vessels and nerves, the most prominent of these being the saphenous opening (saphenous hiatus) (which gives passage to the great saphenous vein). Anatomy Structure An inferior aponeurotic thickening of the cribriform fascia - the falciform margin of sphenous opening - forms the inferior margin of the sapnenous opening, embracing the arch of the great saphenous vein. Clinical significance The cribriform fascia has been proposed for use in preventing new vascularization when surgery is performed at the join between the great saphenous vein The great saphenous vein (GSV; ) or long saphenous vein is a large, subcutaneo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Vein
In the human body, the femoral vein is the vein that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It is a deep vein that begins at the adductor hiatus (an opening in the adductor magnus muscle) as the continuation of the popliteal vein. The great saphenous vein (a superficial vein), and the deep femoral vein drain into the femoral vein in the femoral triangle when it becomes known as the common femoral vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament where it becomes the external iliac vein. Its major tributaries are the deep femoral vein, and the great saphenous vein. The femoral vein contains valves. Structure The femoral vein bears valves which are mostly bicuspid and whose number is variable between individuals and often between left and right leg. Course The femoral vein continues into the thigh as the continuation from the popliteal vein at the back of the knee. It drains blood from the deep thigh muscles and thigh bone. Proximal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pectinate Line
The pectinate line (dentate line) is a line which divides the upper two-thirds and lower third of the anal canal. Developmentally, this line represents the hindgut- proctodeum junction. It is an important anatomical landmark in humans, and forms the boundary between the anal canal and the rectum according to the anatomic definition. Colorectal surgeons instead define the anal canal as the zone from the anal verge to the anorectal ring (palpable structure formed by the external anal sphincter and the puborectalis muscle The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis. It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the ...). Several distinctions can be made based upon the location of a structure relative to the pectinate line: Additional images File:Rectoanal jxn.JPG, Microscopic cross section of the anorectal junction File:A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anus
In humans, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin ''ānus'', "ring", "circle") is the external opening of the rectum located inside the intergluteal cleft. Two sphincters control the exit of Human feces, feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relax as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. Above the anus is the perineum, which is also located beneath the vulva or scrotum. In part owing to its exposure to feces, a number of medical conditions may affect the anus, such as hemorrhoids. The anus is the site of potential infections and other conditions, including cancer (see anal cancer). With anal sex, the anus can play a role in Human sexuality, sexuality. Attitudes toward anal sex vary, and it is illeg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vulval vestibule, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands (Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's). The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina (which leads to the uterus). Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Lymphatic vessel#Afferent vessels, Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliac Crest
The crest of the ilium (or iliac crest) is the superior border of the wing of ilium and the superolateral margin of the greater pelvis. Structure The iliac crest stretches posteriorly from the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) to the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS). Behind the ASIS, it divides into an outer and inner lip separated by the intermediate zone. The outer lip bulges laterally into the iliac tubercle.Platzer (2004), p 186 Palpation, Palpable in its entire length, the crest is convex superiorly but is sinuously curved, being concave inward in front, concave outward behind.Palastanga (2006), p 243 It is thinner at the center than at the extremities. Development The iliac crest is derived from endochondral bone. Function To the external lip are attached the ''Tensor fasciae latae'', ''abdominal external oblique muscle, Obliquus externus abdominis'', and ''Latissimus dorsi muscle, Latissimus dorsi'', and along its whole length the ''fascia lata''; to the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |