|
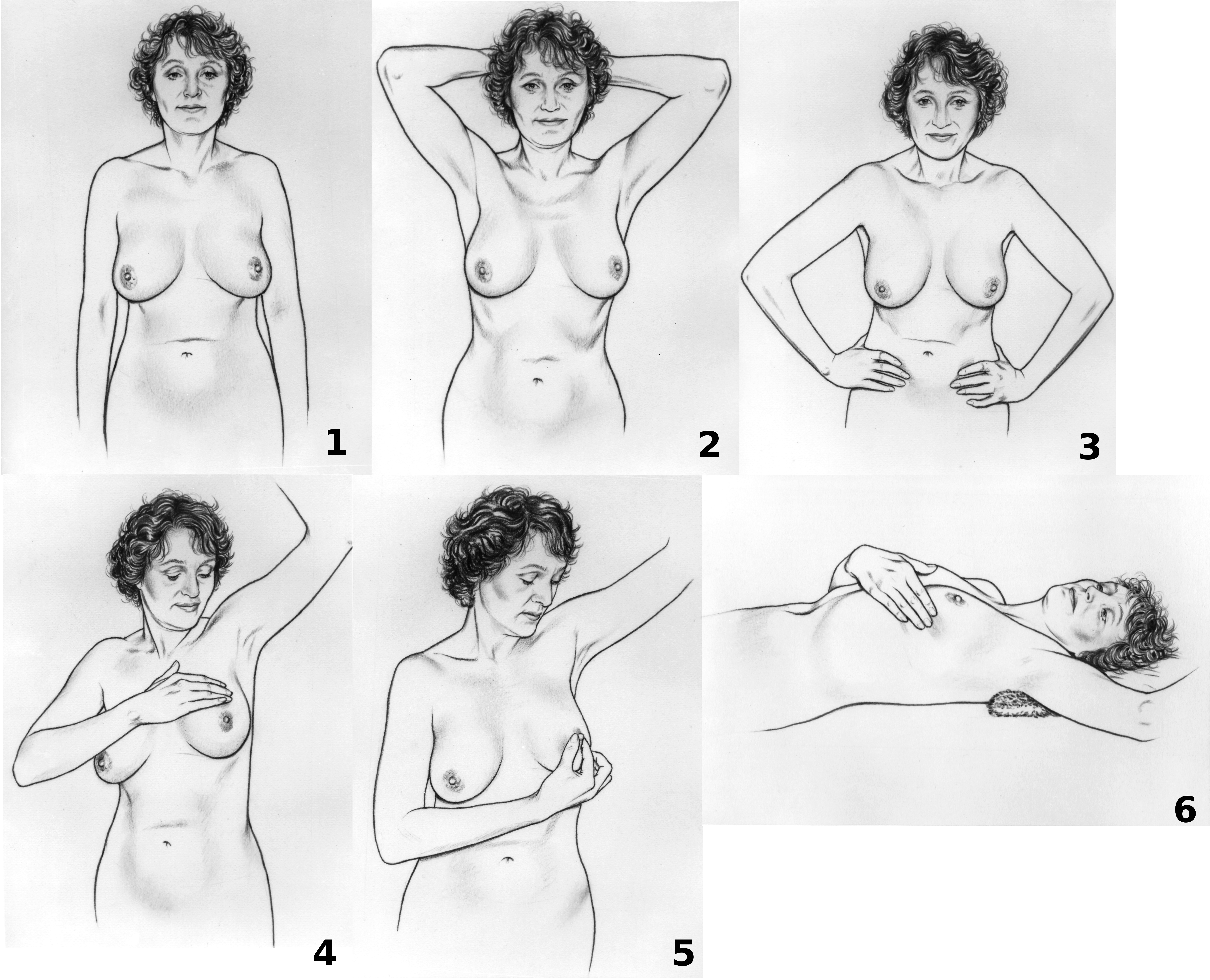
Clinical Breast Examination
Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. A clinical or self breast exam involves feeling the breast for lumps or other abnormalities. Medical evidence, however, does not support its use in women with a typical risk for breast cancer. Universal screening with mammography is controversial as it may not reduce all-cause mortality and may cause harms through unnecessary treatments and medical procedures. Many national organizations recommend it for most older women. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends screening mammography in women at normal risk for breast cancer, every two years between the ages of 50 and 74. Other po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
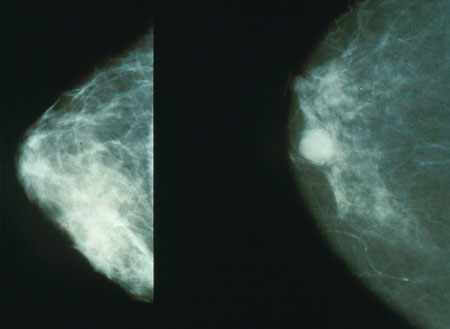
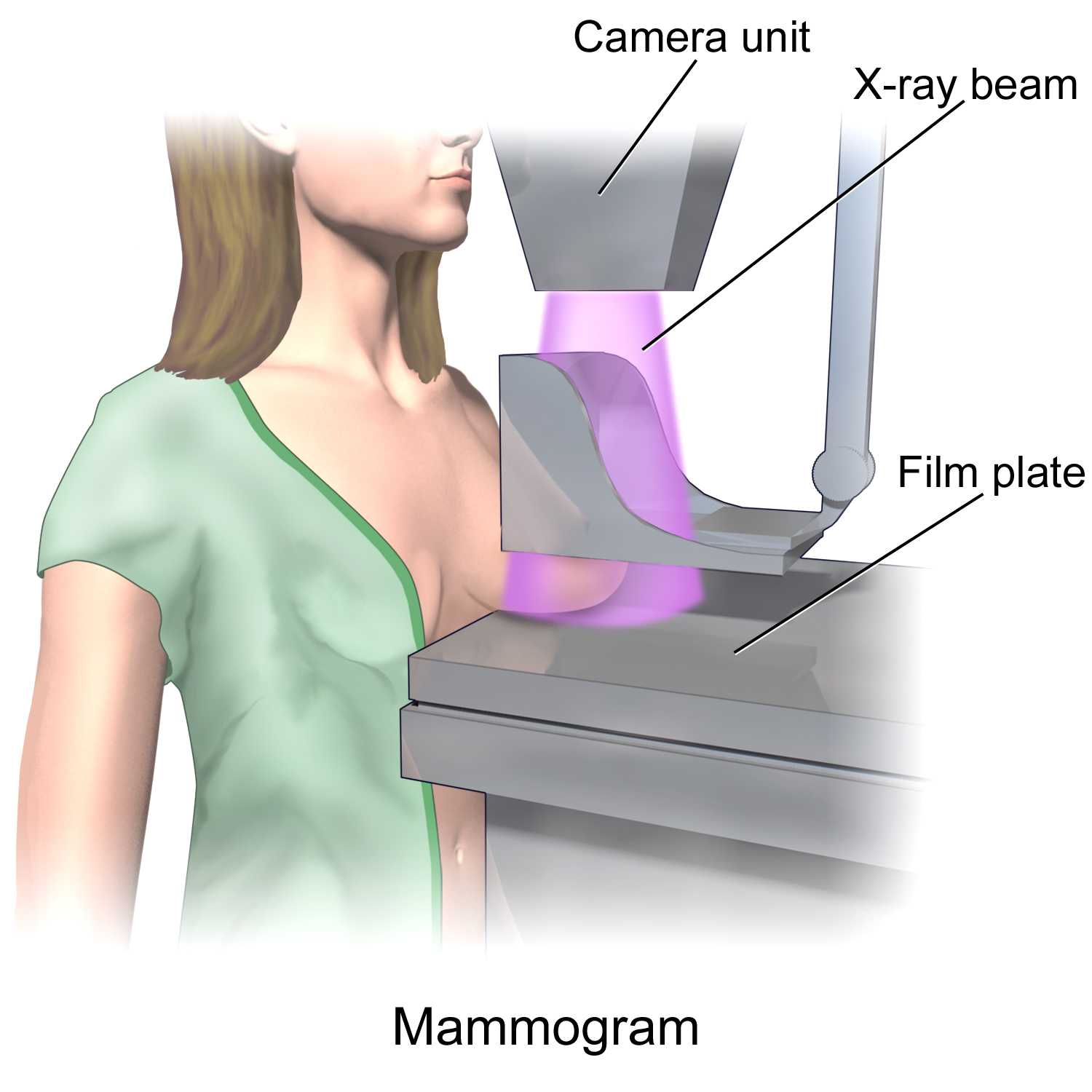
Mammogram
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses, microcalcifications, asymmetries, and distortions. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D ( tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiography
Radiography is an imaging technology, imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical ("diagnostic" radiography and "therapeutic radiography") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security, (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and it is projected towards the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation are absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a X-ray detector, detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two-dimensional images by this technique is called Projection radiography, projectional radiography. In computed tomography (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diana Miglioretti
Diana Lynn Miglioretti is an American biostatistician specializing in the availability and effectiveness of breast cancer screening and in radiation hazards from medical imaging; she has also studied connections between Down syndrome and leukemia. She is Dean's Professor of Public Health Sciences and head of the biostatistics division in the UC Davis School of Medicine. She co-leads the U.SBreast Cancer Surveillance Consortium Education and career Miglioretti graduated from the University of Maryland, College Park in 1992. She went to the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health for graduate study in biostatistics, earning a master's degree in 1996 and completing her Ph.D. in 2000. Her dissertation, ''Template Mixture Models for Functional Brain Mapping'', was jointly supervised by Scott L. Zeger and Colin Craig McCulloch. After completing her Ph.D., she became a researcher in the Group Health Cooperative in Seattle, also holding an affiliate faculty position in bios ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response to a present threat, whereas anxiety is the anticipation of a future one. It is often accompanied by nervous behavior such as pacing back and forth, Somatic anxiety, somatic complaints, and Rumination (psychology), rumination. Anxiety is a feeling of uneasiness and worry, usually generalized and unfocused as an overreaction to a situation that is only subjectively seen as menacing. It is often accompanied by muscular tension, restlessness, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, inability to catch one's breath, tightness in the abdominal region, nausea, and problems in concentration. Anxiety is closely related to fear, which is a response to a real or perceived immediate threat (fight-or-flight response); anxiety involves the expectation of a future t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Positive
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result incorrectly indicates the absence of a condition when it is actually present. These are the two kinds of errors in a binary test, in contrast to the two kinds of correct result (a and a ). They are also known in medicine as a false positive (or false negative) diagnosis, and in statistical classification as a false positive (or false negative) error. In statistical hypothesis testing, the analogous concepts are known as type I and type II errors, where a positive result corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. The terms are often used interchangeably, but there are differences in detail and interpretation due to the differences between medical testing and sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-aided Diagnosis
Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical imaging, medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, endoscopy, and Medical ultrasound, ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the Radiology, radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional. CAD also has potential future applications in digital pathology with the advent of whole-slide imaging and machine learning algorithms. So far its application has been limited to quantifying immunostaining but is also being investigated for the standard H&E stain. CAD is an interdisciplinary technology combining elements of artificial intelligence and computer visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Mammography
Mammography (also called mastography; DICOM modality: MG) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses, microcalcifications, asymmetries, and distortions. As with all X-rays, mammograms use doses of ionizing radiation to create images. These images are then analyzed for abnormal findings. It is usual to employ lower-energy X-rays, typically Mo (K-shell X-ray energies of 17.5 and 19.6 keV) and Rh (20.2 and 22.7 keV) than those used for radiography of bones. Mammography may be 2D or 3D (tomosynthesis), depending on the available equipment or purpose of the examination. Ultrasound, ductography, positron emission mammography (PEM), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are adjuncts to mammography. Ultrasound is typically used for further evaluation of masses found on mammography or palpable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Film
Photographic film is a strip or sheet of transparent film base coated on one side with a gelatin photographic emulsion, emulsion containing microscopically small light-sensitive silver halide crystals. The sizes and other characteristics of the crystals determine the sensitivity, contrast, and image resolution, resolution of the film. Film is typically segmented in ''frames'', that give rise to separate photographs. The emulsion will gradually darken if left exposed to light, but the process is too slow and incomplete to be of any practical use. Instead, a very short exposure (photography), exposure to the image formed by a camera lens is used to produce only a very slight chemical change, proportional to the amount of light absorbed by each crystal. This creates an invisible latent image in the emulsion, which can be chemically photographic processing, developed into a visible photograph. In addition to visible light, all films are sensitive to ultraviolet light, X-rays, gamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide treatment within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiation), but today it includes all imaging modalities. This includes technologies that use no ionizing electromagnetic radiation, such as ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), as well as others that do use radiation, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above. The modern practice of radiology involves a team of several different healthcare professionals. A radiologist, who is a medical doctor with specialized post-graduate training, interprets medical images, communicates these findings to other physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionizing Radiation
Ionizing (ionising) radiation, including Radioactive decay, nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have enough energy per individual photon or particle to ionization, ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel up to 99% of the speed of light, and the electromagnetic waves are on the high-energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Gamma rays, X-rays, and the higher energy vacuum ultraviolet, ultraviolet part of the electromagnetic spectrum are ionizing radiation; whereas the lower energy ultraviolet, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves are non-ionizing radiation. Nearly all types of laser light are non-ionizing radiation. The boundary between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation in the ultraviolet area cannot be sharply defined, as different molecules and atoms ionize at Ionization energies of the elements (data page), different energies. The energy of ionizing radiation starts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frailty Syndrome
Frailty or frailty syndrome refers to a state of health in which older adults gradually lose their bodies' in-built reserves and functioning. This makes them more vulnerable, less able to recover and even apparently minor events (infections, environmental changes) can have drastic impacts on their physical and mental health. Frailty can have various symptoms including muscle weakness (reduced grip strength), slower walking speed, exhaustion, unintentional weight loss, and frequent falls. Older people with certain medical conditions such as diabetes, heart disease and dementia, are also more likely to have frailty. In addition, adults living with frailty face more symptoms of anxiety and depression than those who do not. Frailty is not an inevitable part of aging. Its development can be prevented, delayed and its progress slowed. The most effective ways of preventing or improving frailty are regular physical activity and a healthy diet. The prevalence of frailty varies based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammo Breast Cancer
''Mammo'' is a 1994 Indian Hindi-language film by Shyam Benegal. It stars Farida Jalal, Surekha Sikri, Amit Phalke and Rajit Kapur. The film won the National Film Award for Best Feature Film in Hindi in 1995. Farida Jalal won Filmfare Critics Award for Best Performance, while Surekha Sikri won the National Film Award for Best Supporting Actress. It was the first film of Benegal’s Muslim trilogy, which included '' Sardari Begum'' (1996) and '' Zubeidaa'' (2001). The film was critically acclaimed and is regarded among his best works. The film’s writer, Khalid Muhammad, mentioned that he wrote the role for Waheeda Rehman who was hesitant to do the role, thus casting Farida Jalal. Plot 13-year-old Riyaz (Amit Phalke) lives a poor lifestyle in Bombay, India, with his grandmother, Fayyuzi ( Surekha Sikri), and her sister, Mehmooda Begum, nicknamed Mammo (Farida Jalal). Quite outspoken and embittered over his dad abandoning him, Riyaz does not have many friends, save Roha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |