|
Civil Administration Area Of Luxembourg
The Civil Administration Area of Luxembourg was a German civil administration in German-occupied Luxembourg that existed from 29 July 1940 to 30 August 1942, when Luxembourg was annexed into Gau Moselland. History Gustav Simon was appointed '' Chef der Zivilverwaltung'' (''CdZ''; "Chief of the Civil Administration") by the Oberkommando des Heeres on 21 July 1940. Luxembourg was then included into the ''CdZ-Gebiet Luxemburg'' on 29 July. While initially subordinate to the military commands in Belgium and northern France, Simon was confirmed in his appointment on 2 August by Adolf Hitler himself, indicating that he reported directly to the ''Führer ''and no one else. This granted him a wide degree of autonomy with regards to the military and civil authorities of Nazi Germany. Simon, who was also the ''Gauleiter'' of the neighbouring ''Gau Trier-Koblenz,'' later '' Moselland ''(''Gauleiter ''being a title denoting the leader of a regional branch of the Nazi party), led a propagand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Administration
Civil authority or civil government is the practical implementation of a state on behalf of its citizens, other than through military units (martial law), that enforces law and order and that is distinguished from religious authority (for example, canon law) and secular authority. The enforcement of law and order is typically the role of the police in modern states. History Among the first modern experiments in civil government took place in 1636 when Roger Williams, a Christian minister, founded the colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations. He sought to create a " wall of separation" between church and state to prevent corruption of the church and maintain civil order as expounded upon in his 1644 book, '' Bloudy Tenent of Persecution''.James Emanuel Ernst, Roger Williams, ''New England Firebrand'' (Macmillan Co., Rhode Island, 1932), pg. 24/ref> Types of authority Thus four forms of authority may be seen: *Civil authority * Military government, Military authority *Rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
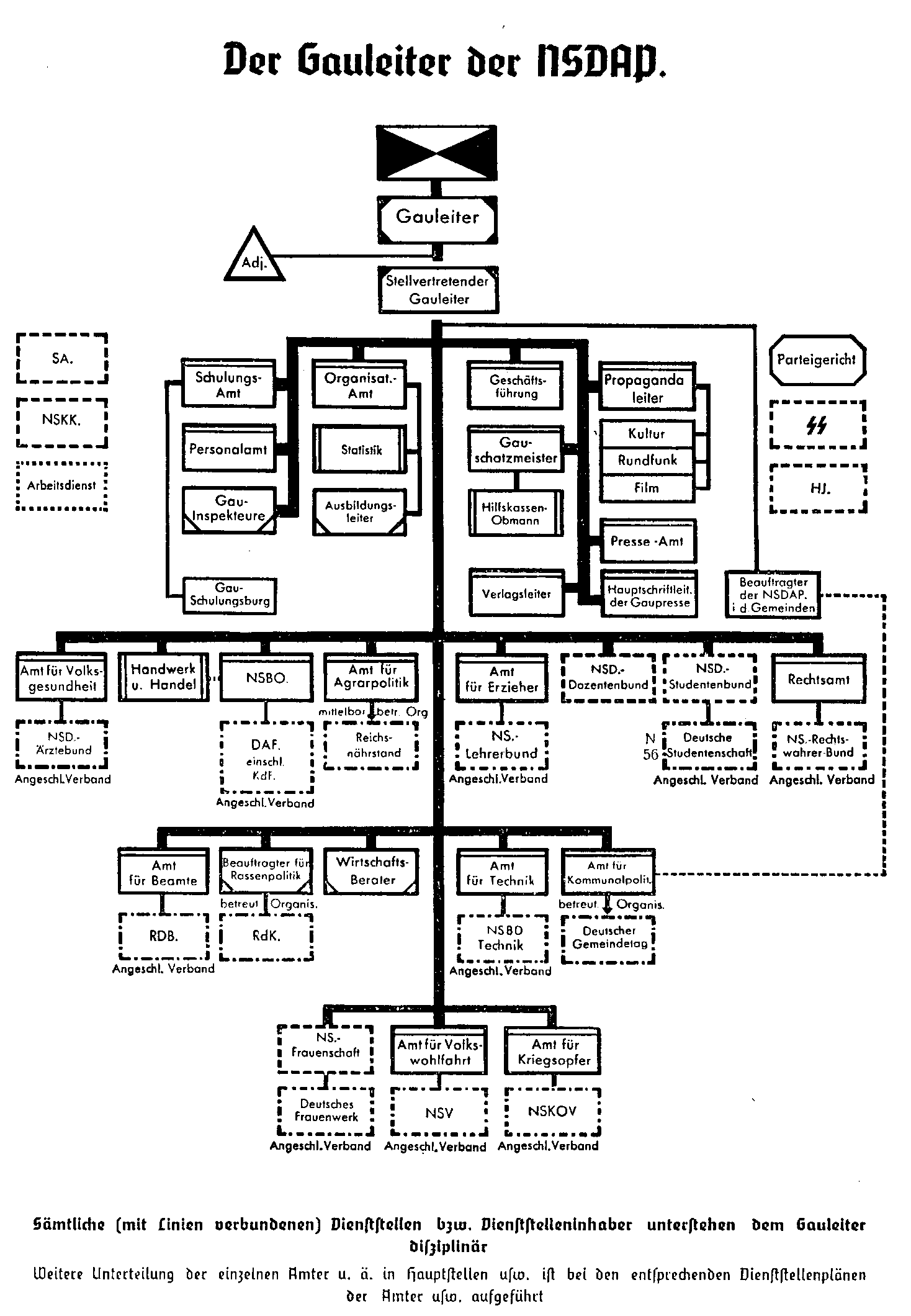
Gauleiter
A ''Gauleiter'' () was a regional leader of the Nazi Party (NSDAP) who served as the head of a ''Administrative divisions of Nazi Germany, Gau'' or ''Reichsgau''. ''Gauleiter'' was the third-highest Ranks and insignia of the Nazi Party, rank in the Nazi political leadership, subordinate only to ''Reichsleiter'' and to the ''Führer'' himself. The position was effectively abolished with the fall of the Nazi regime on 8 May 1945. History and development Origin and early years The first use of the term ''Gauleiter'' by the Nazi Party was in 1925 around the time Adolf Hitler re-founded the Party on 27 February, after the lifting of the ban that had been imposed on it in the aftermath of the Beer Hall Putsch of 9 November 1923. The word can be singular or plural in German usage, depending on its context, and derives from the German words ''Gau (territory), Gau'' and ''leiter'' (''leader''). The word ''Gau'' is an old term for a region of the German ''Reich'' (Empire). The Frankis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of Germany During World War II
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalitarianism, totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies of World War II, Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, End of World War II in Europe, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole ''Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxembourg In World War II
The involvement of the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg in World War II began with its invasion by German forces on 10 May 1940 and lasted beyond its liberation by Allied forces in late 1944 and early 1945. Luxembourg was placed under occupation in 1940 and was annexed into Germany in 1942. During the occupation, the German authorities orchestrated a programme of "Germanisation" of the country, suppressing non-German languages and customs and conscripting Luxembourgers into the ''Wehrmacht'', which led to extensive resistance, culminating in a general strike in August 1942 against conscription. The Germanisation was facilitated by a collaborationist political group, the '' Volksdeutsche Bewegung'', founded shortly after the occupation. Shortly before the surrender, the government had fled the country along with Grand Duchess Charlotte, eventually arriving in London, where a Government-in-exile was formed. Luxembourgish soldiers also fought in Allied units until liberation. Background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reichsarbeitsdienst
The Reich Labour Service (''Reichsarbeitsdienst''; RAD) was a major paramilitary organization established in Nazi Germany as an agency to help mitigate the effects of unemployment on the Economy of Nazi Germany, German economy, militarise the workforce and indoctrinate it with Nazism, Nazi ideology. It was the official state labour service, divided into separate sections for men and women. From June 1935 onward, men aged between 18 and 25 may have served six months before their military service. During World War II, compulsory service also included young women, and the RAD developed to an Auxiliaries, auxiliary Military organization#Formation, formation which provided support for the Wehrmacht armed forces. Foundation In the course of the Great Depression, the German government of the Weimar Republic under Chancellor Heinrich Brüning by Article 48 (Weimar Constitution), emergency decree established the ''Freiwilliger Arbeitsdienst'' ('Voluntary Labour Service', FAD), on 5 Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Basque Country
The French Basque Country (; ; ), or Northern Basque Country (, or , ), is a region lying on the west of the French department of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques. Since 1 January 2017, it constitutes the Basque Municipal Community (; ) presided over by . It includes three former historic French provinces in the north-east of the traditional Basque Country (historical territory), Basque Country totalling : Lower Navarre (; ), until 1789 nominally Kingdom of Navarre, with ; Labourd (), with ; Soule (), with . The population included in the Basque Municipal Community amounts to 309,723 inhabitants distributed in 158 municipalities. It is delimited in the north by the department of Landes (département), Landes, in the west by the Bay of Biscay, in the south by the Southern Basque Country and in the east by Béarn (although in the Béarnese village of Esquiule, Basque is spoken), which is the eastern part of the department. Bayonne and Biarritz (BAB) are its chief towns, included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beret
A beret ( , ; ; ; ) is a soft, round, flat-crowned cap made of hand-knitted wool, crocheted cotton, wool felt, or acrylic fibre. Mass production of berets began in the 19th century in Southern France and the north of History of Spain (1808–1874), Spain, specifically in the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country, where they were already common headwear, and the beret remains associated with these countries. Berets are worn as part of the uniform of many military and police units worldwide, as well as by other organizations. History Archaeology and art history indicate that headwear similar to the modern beret has been worn since the Bronze Age across Northern Europe and as far south as ancient Crete and Italy, where it was worn by the Minoan civilization, Minoans, Etruscans and Ancient Rome, Romans. Such headgear has been popular among the nobility and artists across Europe throughout modern history. Dutch artist, Rembrandt, 15 July 1606 - 4 October 1669, was w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of the Nazi Party. The two laws were the Law for the Protection of German Blood and German Honour, which forbade marriages and extramarital intercourse between Jews and Germans and the employment of German females under 45 in Jewish households; and the Reich Citizenship Law, which declared that only those of German or related blood were eligible to be Reich citizens. The remainder were classed as state subjects without any citizenship rights. A supplementary decree outlining the definition of who was Jewish was passed on 14 November, and the Reich Citizenship Law officially came into force on that date. The laws were expanded on 26 November 1935 to include Romani and Black people. This supplementary decree defined Romani people as "enemies of the race-based state", the same category ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sondergerichte
A ''Sondergericht'' (plural: ''Sondergerichte'') was a German "special court". After taking power in 1933, the Nazis quickly moved to remove internal opposition to the Nazi regime in Germany. The legal system became one of many tools for this aim and the Nazis gradually supplanted the normal justice system with political courts with wide-ranging powers. The function of the special courts was to intimidate the German public, but as they expanded their scope and took over roles previously done by ordinary courts such as '' Amtsgerichte'' this function became diluted. Function in Germany Special courts had existed in Germany as far back as the nineteenth century. They had generally been set up temporarily in response to some major but localised civil disturbance and then quickly dissolved once they had served their purpose. A more permanent national network of Special Courts came into being during 1933, soon after the passage of the Reichstag Fire Decree, which all but eliminat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of State Of Luxembourg
The Council of State (, , ) is an institution in Luxembourg that advises the national legislature, the Chamber of Deputies of Luxembourg, Chamber of Deputies as well as the Government of Luxembourg, Government. Until 1 January 1997, it was also the country's supreme administrative court, but this function was ceded to the newly created Administrative Tribunal and Administrative Court. The Council of State was created by King-Grand Duke William III of the Netherlands, William III in the Luxembourg Coup of 1856, Coup of 1856. It was originally entirely appointed by the Grand Duke, but this was changed in 1866, and, despite the roll-back of many changes brought about by the coup, the Council of State has otherwise remained. Composition The Council of State is composed of twenty-one councillors, who are appointed by the Grand Duke of Luxembourg, Grand Duke on the proposal, in order, of the government, the parliament as well as the Council of State. Of these, at least eleven must ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In linguistics, Germanisation of non-German languages also occurs when they adopt many German words. Under the policies of states such as the Teutonic Order, Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the German Empire, non-German minorities were often discouraged or even prohibited from using their native language, and had their traditions and culture suppressed in the name of linguistic imperialism. In addition, the Government also encouraged immigration from the Germanosphere to further upset the linguistic balance, but with varying degrees of success. In Nazi Germany, linguistic Germanisation was replaced by a policy of genocide against certain ethnic groups like Poles, Baltic natives, and Czechoslovaks, even when they were already German-spea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Reich
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a totalitarian dictatorship. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", referred to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945, after 12 years, when the Allies defeated Germany and entered the capital, Berlin, ending World War II in Europe. After Hitler was appointed Chancellor of Germany in 1933, the Nazi Party began to eliminate political opposition and consolidate power. A 1934 German referendum confirmed Hitler as sole '' Führer'' (leader). Power was centralised in Hitler's person, and his word became the highest law. The government was not a coordinated, coopera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |