|
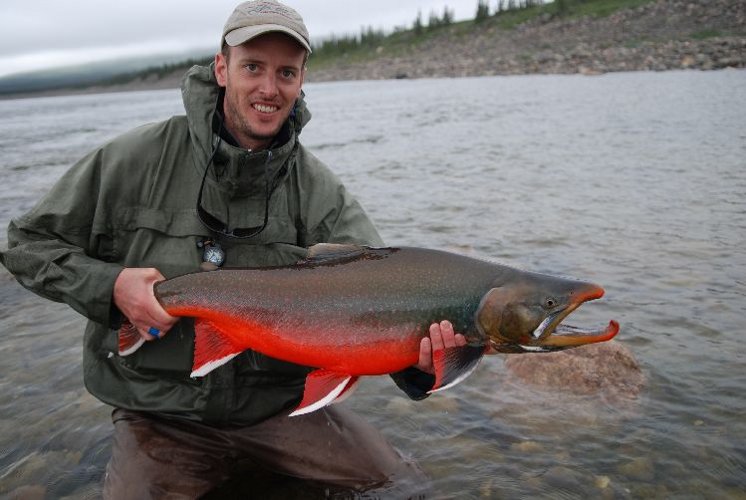
Chum Salmon
The chum salmon (''Oncorhynchus keta''), also known as dog salmon or keta salmon, is a species of anadromous salmonid fish from the genus ''Oncorhynchus'' (Pacific salmon) native to the coastal rivers of the North Pacific and the Beringian Arctic, and is often marketed under the trade name silverbrite salmon in North America. The English name "chum salmon" comes from the Chinook Jargon term ''tsəm'', meaning "spotted" or "marked"; while ''keta'' in the scientific name comes from Russian language, Russian, which in turn comes from the Evenki language of Eastern Siberia. The term 'Dog Salmon' is most commonly used in Alaska and refers to the Salmon whose flesh Alaskans use to feed their dogs. In Japan, chum salmon is also known as the , or simply , while historically it was known in ''kun'yomi'' as up until the Meiji period. In Greater China, it is known academically as the "kype, hook-snout salmon" ( zh, 钩吻鲑), but is more often called the ''damaha'' fish (), which is loanw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Julius Walbaum
Johann Julius Walbaum (30 June 1724 – 21 August 1799) was a German physician, natural history, naturalist and fauna taxonomist. Works Walbaum was from Greifswald. As an ichthyologist, he was the first to describe many previously unknown fish species from remote parts of the globe, such as the Barracuda, Great Barracuda (''Sphyraena barracuda''), the Chum salmon (''Oncorhynchus keta'') from the Kamchatka River in Siberia, and the curimatá-pacú (''Prochilodus marggravii'') from the São Francisco River in Brazil. Walbaum was one of the first to observe gloves as a preventative against infection in medical surgery. As early as 1767, he used gloves made from sheep intestines for vaginal exams. Legacy The Natural History Museum in Lübeck, opened in 1893, was based on Walbaum's extensive scientific collection. The museum's collection was, however, destroyed during the Bombing of Lübeck in World War II, Bombing of Lübeck. See also * References 18th-century German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
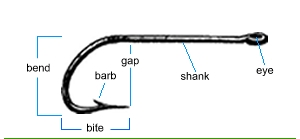
Fishing Tackle
Fishing tackle is the equipment used by fishermen, anglers when fishing. Almost any equipment or gear used in fishing can be called fishing tackle, examples being fishing hook, hooks, fishing line, lines, fishing bait, baits/fishing lure, lures, fishing rod, rods, fishing reel, reels, fishing float, floats, fishing sinker, sinkers/groundbait#Method feeder, feeders, fishing net, nets, spearfishing, spears, fishing gaff, gaffs and fishing trap, traps, as well as wires, snaps, beads, spoons, blades, spinners, clevises and tools that make it easy to tie knots. Tackle attached to the end of a fishing line that gets casting (fishing), cast out along with the bait are referred to as terminal tackle. Terminal tackle can include hooks, leaders, floats, sinkers/feeders, fishing swivel, swivels and attached shackle, snaps and/or circle cotter, split rings. Sometimes the term "rig (fishing), rig" is used for a specific assemblage of terminal tackle. Fishing tackle can be contrasted with fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudal Peduncle
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish (Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish (Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are predominantl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
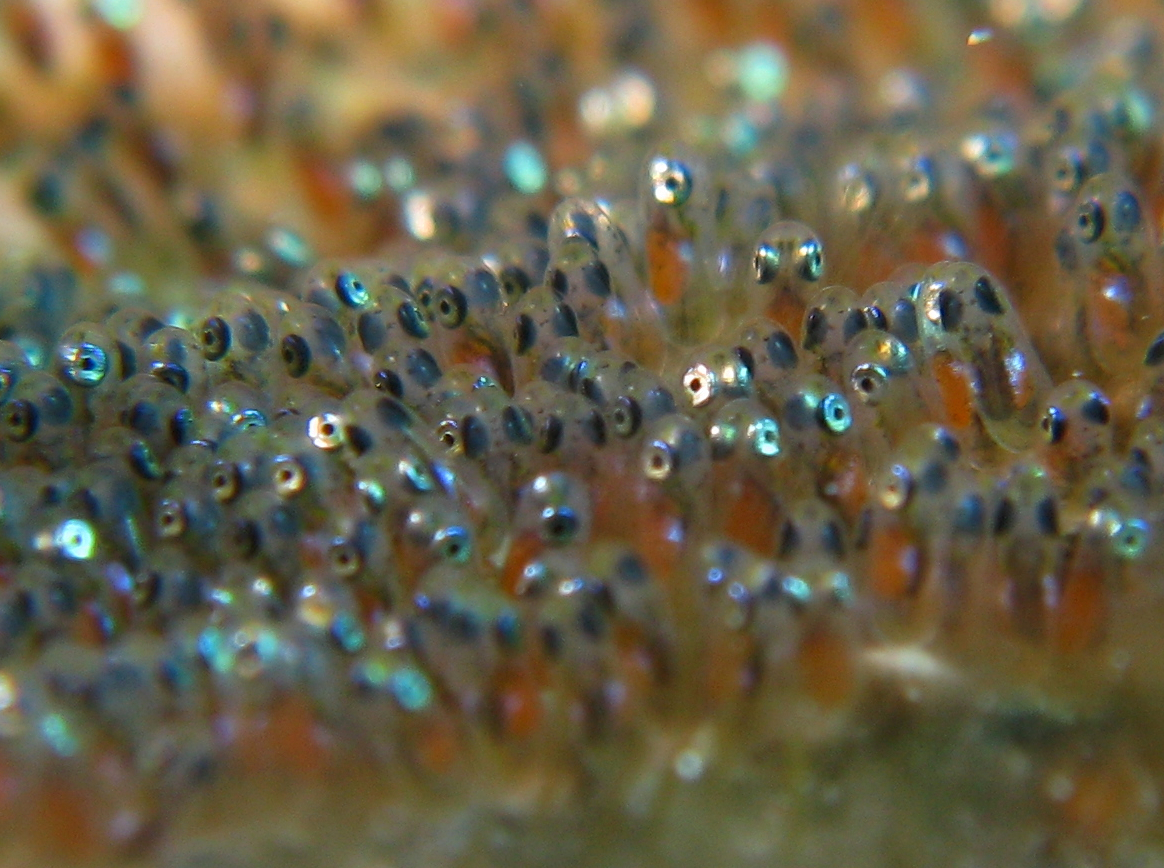
Spawning
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is known as spawning. The vast majority of aquatic and amphibious animals reproduce through spawning. These include the following groups: *Bony fishes *Crustaceans (such as crabs, shrimps, etc.) *Mollusks (such as oysters, octopus, squid) *Echinoderms (such as sea urchins, sea stars, sea cucumbers, etc.) *Amphibians (such as frogs, toads, salamanders, newts) *Aquatic insects (such as dragonflies, mayflies, mosquitoes) *Coral, which are living colonies of tiny, aquatic organisms—not plants, as they are sometimes perceived to be. Corals, while appearing sedentary or botanical by nature, actually spawn by releasing clouds of sperm and egg cells into the water column, where the two mix. As a general rule, aquatic or semiaquatic reptiles, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast China
Northeast China () is a geographical region of China, consisting officially of three provinces Liaoning, Jilin and Heilongjiang. The heartland of the region is the Northeast China Plain, the largest plain in China with an area of over . The region is separated from the Russian Far East to the north and east by the Amur, Argun and Ussuri Rivers; from North Korea to the south by the Yalu and Tumen Rivers; and from the neighboring North China to the west by the Greater Khingan Range and Yan Mountains. It is also bounded by the Bohai Bay and Yellow Sea to the southwest, about away from East China's Jiaodong Peninsula across the Bohai Strait, due to be connected via a proposed undersea tunnel. The four prefectures of Inner Mongolia (which is part of North China) east of the Greater Khingan, i.e. Chifeng, Tongliao, Hinggan and Hulunbuir, are sometimes also considered broader parts of Northeast China, and together with the aforementioned three provinces formed what was h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanai People
The Nanai people () are a Tungusic people of East Asia who have traditionally lived along Heilongjiang (Amur), Songhuajiang (Sunggari) and Wusuli River (Ussuri) on the Middle Amur Basin. The ancestors of the Nanai were the Wild Jurchens of northernmost Manchuria, which is now the region of Outer Manchuria in Russia's Far Eastern Federal District. The Nanai language belongs to the Manchu-Tungusic family. According to the 2010 census there were 12,003 Nanai in Russia. Name Common names for these people include Nanai ( Nanai: , , , ) and Hezhen (, ; ). There are also terms formerly in use: Goldi, Golds, Goldes, and Samagir. Other self names are Qilang (, ; ), and . means 'land, earth, ground, country' or, in this context, 'native, local'; , , or means 'people' in different dialects. The Russian linguist L. I. Sem gives the name ''Hezhe nai'' () or ''Hezheni'' (, ) and explains it as the self-name of the Nanai of the lower Amur, meaning 'people who live along the low ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanai Language
The Nanai language (also called Gold, Goldi, or Hezhen) is spoken by the Nanai people in Siberia, and to a much smaller extent in China's Heilongjiang province, where it is known as Hezhe. The language has about 1,400 speakers out of 17,000 ethnic Nanai, but most (especially the younger generations) are also fluent in Russian or Chinese, and mostly use one of those languages for communication. Nomenclature In China, the language is referred to as ''Hèzhéyǔ'' ( Chinese: ). The Nanai people there variously refer to themselves as /na nio/, , /na nai/ (which all mean "local people"), , and , the last being the source of the Chinese ethnonym ''Hezhe''. Distribution The language is distributed across several distantly-located areas: * Middle/lower Amur dialects (Naykhin, Dzhuen, Bolon, Ekon, etc.): the areas along the Amur River below Khabarovsk (Nanai, Amursk, Solnechny and Komsomolsk districts of Khabarovsk Krai); * Kur-Urmi dialect: the area around the city of Khabarovsk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term that is well established in the linguistic field despite its acknowledged descriptive flaws: nothing is taken away from the donor language and there is no expectation of returning anything (i.e., the loanword). Loanwords may be contrasted with calques, in which a word is borrowed into the recipient language by being directly translated from the donor language rather than being adopted in (an approximation of) its original form. They must also be distinguished from cognates, which are words in two or more related languages that are similar because they share an etymological origin in the ancestral language, rather than because one borrowed the word from the other. Examples and related terms A loanword is distinguished from a calque (or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kype
A kype is a hook-like secondary sex characteristic which develops at the distal tip of the lower jaw in some male salmonids prior to the spawning season. The structure usually develops in the weeks prior to, and during, migration to the spawning grounds. In addition to the development of the kype, a large depression forms in the two halves of the premaxilla in the upper jaw, allowing the kype to fit into the premaxilla when the mouth is closed. The kype functions as a secondary sexual characteristic and influences the formation of dominance hierarchies at the spawning grounds. The size of the kype is believed to determine male spawning frequency. Description The kype grows rapidly from bony needles proliferating from the tip of the dentary (the anterior and largest of the bones making up the lower jaw). The needles form a mesh, but do not interfere with the connective tissues used by bone marrow. At the snout, the needles strengthen into Sharpey's fibres. The speed at which the k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater China
In ethnogeography, "Greater China" is a loosely-defined term that refers to the region sharing cultural and economic ties with the Chinese people, often used by international enterprises or organisations in unofficial usage. The notion contains a "great deal of ambiguity in its geographical coverage and politico-economic implications", because some users use it to refer to "the commercial ties among ethnic Chinese, whereas others are more interested in cultural interactions, and still others in the prospects for political reunification". The term encompass "linkages among regional Chinese communities", but usually refers to an area encompassing the People’s Republic of China (mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau) and the Republic of China (known as Taiwan), places where the majority population is culturally Chinese. The term's usage is contested; some observers in Taiwan characterise the term as harmful or a conflation of distinct polities and markets, while the Chinese government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Period
The was an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868, to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |