|
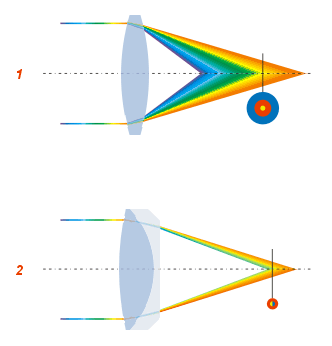
Chromatic Aberration
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Since the focal length of the lens varies with the color of the light different colors of light are brought to focus at different distances from the lens or with different levels of magnification. Chromatic aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image. Types There are two types of chromatic aberration: ''axial'' (''longitudinal''), and ''transverse'' (''lateral''). Axial aberration occurs when different wavelengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Aberration (comparison)
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion, color aberration, color fringing, or purple fringing, is a failure of a lens (optics), lens to Focus (optics), focus all colors to the same point. It is caused by Dispersion (optics), dispersion: the refractive index of the lens elements varies with the wavelength of light. The refractive index of most transparent materials decreases with increasing wavelength. Since the focal length of a lens depends on the refractive index, this variation in refractive index affects focusing. Since the focal length of the lens varies with the color of the light different colors of light are brought to focus at different distances from the lens or with different levels of magnification. Chromatic Aberration in optical systems, aberration manifests itself as "fringes" of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image. Types There are two types of chromatic aberration: ''axial'' (''longitudinal''), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberration In Optical Systems
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as Lens (optics), lenses and mirrors, that causes the ''image'' created by the optical system to not be a faithful reproduction of the ''object'' being observed. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred, distorted in shape or have color fringing or other effects not seen in the object, with the nature of the distortion depending on the type of aberration. Aberration can be defined as a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements. An image-forming optical system with aberration will produce an image which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatic Aberration Lens Diagram
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize Scale (music), scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, Musical note, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the Common practice period, common practice music of the period 1600–1900. These terms may mean different things in different contexts. Very often, ''diatonic'' refers to musical elements derived from the modes and transpositions of the "white note scale" C–D–E–F–G–A–B. In some usages it includes all forms of heptatonic scale that are in common use in Western music (the major, and all forms of the minor). ''Chromatic'' most often refers to structures derived from the chromatic scale in 12-tone equal temperament, which consists of all semitones. Historically, however, it had other senses, referring in Ancient Greek mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublet (lens)
In optics, a doublet is a type of lens made up of two simple lenses paired together. Such an arrangement allows more optical surfaces, thicknesses, and formulations, especially as the space between lenses may be considered an "element". With additional degrees of freedom, optical designers have more latitude to correct more optical aberrations more thoroughly. Types Doublets can come in many forms, though most commercial doublets are achromats, which are optimized to reduce chromatic aberration while also reducing spherical aberration and other optical aberrations. The lenses are made from glasses with different refractive indices and different amounts of dispersion. Often one element is a positive lens made of crown glass and the other is a negative lens made of flint glass. This combination produces a better image than a simple lens. Some Trilobites, which are now extinct, had natural doublet lenses in their eyes. Apochromats can also be made as doublets. Doublet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatic Lens
An achromatic lens or achromat is a lens (optics), lens that is designed to limit the effects of chromatic aberration, chromatic and spherical aberration. Achromatic lenses are corrected to bring two wavelengths (typically red and blue) into focus on the same plane. Wavelengths in between these two then have better focus error than could be obtained with a simple lens. The most common type of achromat is the achromatic doublet, which is composed of two individual lenses made from glasses with different amounts of Dispersion (optics), dispersion. Typically, one element is a negative (Lens (optics)#Types of simple lenses, concave) element made out of flint glass such as F2, which has relatively high dispersion, and the other is a positive (Lens (optics)#Types of simple lenses, convex) element made of Crown glass (optics), crown glass such as BK7, which has lower dispersion. The lens elements are mounted next to each other, often cemented together, and shaped so that the chromati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Least Confusion
In optics, a circle of confusion (CoC) is an optical spot caused by a cone of light rays from a lens not coming to a perfect focus when imaging a point source. It is also known as disk of confusion, circle of indistinctness, blur circle, or blur spot. In photography, the circle of confusion is used to determine the depth of field, the part of an image that is acceptably sharp. A standard value of CoC is often associated with each image format, but the most appropriate value depends on visual acuity, viewing conditions, and the amount of enlargement. Usages in context include ''maximum permissible circle of confusion'', ''circle of confusion diameter limit'', and the ''circle of confusion criterion''. Real lenses do not focus all rays perfectly, so that even at best focus, a point is imaged as a spot rather than a point. The smallest such spot that a lens can produce is often referred to as the circle of least confusion. Two uses Two important uses of this term and concep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catadioptric System
A catadioptric optical system is one where refraction and Reflection (physics), reflection are combined in an optical system, usually via lens (optics), lenses (dioptrics) and curved mirrors (catoptrics). Catadioptric combinations are used in focusing systems such as searchlights, headlamps, early lighthouse focusing systems, optical telescopes, microscopes, and telephoto photographic lens, lenses. Other optical systems that use lenses and mirrors are also referred to as "catadioptric", such as surveillance catadioptric sensors. Early catadioptric systems Catadioptric combinations have been used for many early optical systems. In the 1820s, Augustin-Jean Fresnel developed several catadioptric lighthouse reflector versions of his Fresnel lens. Léon Foucault developed a catadioptric microscope in 1859 to counteract aberrations of using a lens to image objects at high power. In 1876 a French engineer, A. Mangin, invented what has come to be called the Mangin mirror, a concave glas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catoptric
Catoptrics (from ''katoptrikós'', "specular", from ''katoptron'' "mirror") deals with the phenomena of reflected light and image-forming optical systems using mirrors. A catoptric system is also called a ''catopter'' (''catoptre''). History Ancient Texts ''Catoptrics'' is the title of two texts from ancient Greece: *The Pseudo-Euclidean ''Catoptrics''. This book is attributed to Euclid, although the contents are a mixture of work dating from Euclid's time together with work which dates to the Roman period., accessed 31 January 2013 It has been argued that the book may have been compiled by the 4th century mathematician Theon of Alexandria. The book covers the mathematical theory of mirrors, particularly the images formed by plane and spherical concave mirrors. *Hero's ''Catoptrics''. Written by Hero of Alexandria, this work concerns the practical application of mirrors for visual effects. In the Middle Ages, this work was falsely ascribed to Ptolemy. It only survives in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newtonian Telescope
The Newtonian telescope, also called the Newtonian reflector or just a Newtonian, is a type of reflecting telescope invented by the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton, using a concave primary mirror and a flat diagonal secondary mirror. Newton's first reflecting telescope was completed in 1668 and is the earliest known functional reflecting telescope. The Newtonian telescope's simple design has made it very popular with amateur telescope makers. Description |
Reflecting Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter Objective (optics), objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptrics, catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metalusually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. In the optical spectrum, light wavelength is viewed as continuous, and spectral colors are seen to blend into one another smoothly when organized in order of their corresponding wavelengths. As scientific understanding of light advanced, the term came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including radiation not visible to the human eye. ''Spectrum'' has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. Radio waves, at the low-frequency end of the spectrum, have the lowest photon energy and the longest wavelengths—thousands of kilometers, or more. They can be emitted and received by antenna (radio), antennas, and pass through the atmosphere, foliage, and most building materials. Gamma rays, at the high-frequency end of the spectrum, have the highest photon energies and the shortest wavelengths—much smaller than an atomic nucleus. Gamma rays, X-rays, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |