|
Christiansborg (slave Ship)
''Christiansborg'' was the first of six ships acquired by the Danish Guinea Company for use in the Triangle Trade. She was named for Fort Christiansborg on the Danish Gold Coast. History 1766–1767 ''Christiansborg'' sailed from Copenhagen on 6 July 1766, bound for the Danish Gold Coast. She sailed from the Danish Gold Coast on 21 February 1767, bound for Saint Croix in the Danish West Indies. 235 of the enslaved Africans were still alive when the ship reached her destination approximately three months later. They were sold for 30,755 Danish rigsdaler 1774–1776 ''Christiansborg'' was captained by Johan Frandsen Ferentz on her second enslaving voyage. The ship saluted Kronborg Castle on 23 March 1774 to mark the beginning of her voyage. The West African coast was first sighted on 1 August. A cargo of 393 enslaved Africans were was acquired from local slave traders at Fort Christiansborg, Fort Fredensborg and Quitta. Ferentz set sail from Christiansborg on 25 February 1776, bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Trade
Triangular trade or triangle trade is trade between three ports or regions. Triangular trade usually evolves when a region has export commodities that are not required in the region from which its major imports come. It has been used to offset trade imbalances between different regions. The most commonly cited example of a triangular trade is the Atlantic slave trade, but other examples existed. These include the seventeenth-century carriage of manufactured goods from England to History of New England, New England and History of Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland, then dried cod from Newfoundland and New England to the Mediterranean and Iberian peninsula, followed by cargoes of gold, silver, olive oil, tobacco, dried fruit, and "sacks" of wine back to England. Maritime carriers referred to this Atlantic trade as the "sack trade." Another example was general cargo from Britain to Australia, Australian coal to China, then tea and silk back to Britain. The Atlantic slave trade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
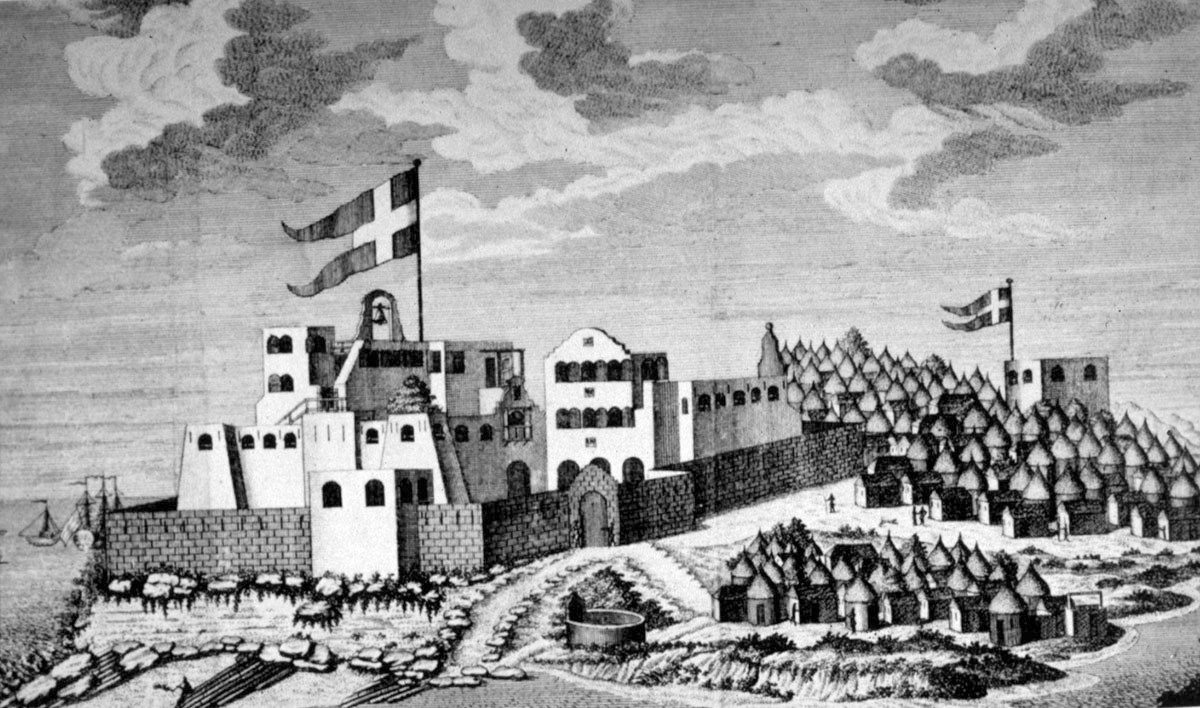
Fort Christiansborg
Osu Castle (also known as Fort Christiansborg or the Castle) is a castle located in Osu, Accra, Osu, Ghana, on the coast of the Gulf of Guinea in Africa. A substantial fort was built by Denmark-Norway in the 1660s; thereafter, the fort changed ownership between Denmark-Norway, Portugal, the Akwamu, United Kingdom, Britain, and finally post-Independence Ghana. Under Denmark–Norway control it was the capital of the Danish Gold Coast, and held and dispatched enslaved people overseas. In 1902, Osu Castle became the seat of government in Ghana but this has now moved to Jubilee House. Because of its testimony to European colonial influence in West Africa and the Atlantic slave trade, the castle was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979 along with several List of castles in Ghana, other castles and forts in Ghana. History The area was first occupied in 1550 by the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese, though in the 17th century Portuguese influence diminished. The are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Gold Coast
The Danish Gold Coast ( or ''Dansk Guinea'') comprised the colonies that Denmark–Norway controlled in Africa as a part of the Gold Coast (region), Gold Coast (roughly present-day southeast Ghana), which is on the Gulf of Guinea. It was colonized by the Dano-Norwegian fleet, first under indirect rule by the Danish West India Company (a chartered company), later as a crown colony of the kingdom of Denmark-Norway. The area under Danish influence was over 10,000 square kilometres. The five Danish Gold Coast Territorial Settlements and forts of the Kingdom of Denmark were sold to the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom in 1850. Denmark had wanted to sell these colonies for some time as the expenses required to run the colonies had increased following the abolition of slavery. Although Britain was also struggling with rising costs, it sought to purchase them to reduce French colonial empire, French and Belgian colonial empire, Belgian influence in the region, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the Øresund strait. The Øresund Bridge connects the two cities by rail and road. Originally a Vikings, Viking fishing village established in the 10th century in the vicinity of what is now Gammel Strand, Copenhagen became the capital of Denmark in the early 15th century. During the 16th century, the city served as the ''de facto'' capital of the Kalmar Union and the seat of the Union's monarchy, which governed most of the modern-day Nordic countries, Nordic region as part of a Danish confederation with Sweden and Norway. The city flourished as the cultural and economic centre of Scandinavia during the Renaissance. By the 17th century, it had become a regional centre of power, serving as the heart of the Danish government and Military history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
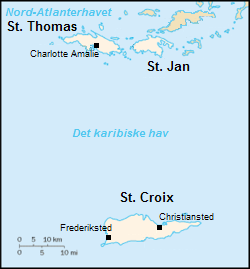
Saint Croix
Saint Croix ( ; ; ; ; Danish language, Danish and ; ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent Districts and sub-districts of the United States Virgin Islands, district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an Unincorporated territories of the United States, unincorporated territory of the United States. St. Croix is the largest of the territory's islands. As of the 2020 U.S. census, its population was 41,004. The island's highest point is Mount Eagle (U.S. Virgin Islands), Mount Eagle, at . St. Croix's nickname is "Twin City", for its two towns, Frederiksted on the western end and Christiansted on the northeast part of the island. Name The island's indigenous Taíno, Taino name is List of indigenous names of Eastern Caribbean islands#Leeward Islands, ''Ay Ay'' ("the river"). Its indigenous Kalinago, Carib name is ''Cibuquiera'' ("the stony land"). Its modern name, ''Saint Croix'', is derived from the French language, French ''Sainte-Croix'', itsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies () or Danish Virgin Islands () or Danish Antilles were a Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas with , Saint John () with , Saint Croix with , and Water Island. The islands of St Thomas, St John, and St Croix were purchased by United States in 1917 and became known as the United States Virgin Islands. Water Island was sold in 1905 to the Danish East Asiatic Company and bought by the U.S. Government in 1944. In 1996, it also became part of the U.S. Virgin Islands. Historical overview Acquisition The Danish West India-Guinea Company annexed uninhabited St. Thomas in 1672. It annexed St. John in 1718 and bought St. Croix from France (King Louis XV) on 28 June 1733. When the Danish West India-Guinea Company went bankrupt in 1754, King Frederik V of Denmark–Norway assumed direct control of the three islands. Although, during the Napoleonic Wars, Britain twice occupied the Danish West Indies, first in 1801� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Rigsdaler
The rigsdaler was the name of several currencies used in Denmark until 1875. The similarly named Reichsthaler, riksdaler and rijksdaalder were used in Germany and Austria-Hungary, Sweden and the Netherlands, respectively. These currencies were often anglicized as rix-dollar or rixdollar. History Several different currency systems have been used by Denmark from the 16th to 19th centuries. The ''krone'' (lit. "crown") first emerged in 1513 as a unit of account worth 8 marks. The more generally used currency system until 1813, however, was the Danish ''rigsdaler'' worth 1 ''krone'' (or ''schlecht daler''), 6 marks, or 96 '' skilling''. The Danish ''rigsdaler'' used in the 18th century was a common system shared with the silver reichsthalers of Norway, Hamburg and Schleswig-Holstein. The currency system consisted of the Reichsthaler specie (''Rigsdaler specie'') worth 120 ''skillings'' in Denmark and Norway, and the lower-valued ''Rigsdaler courant'' worth th of specie or 96 ''ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kronborg Castle
Kronborg is a castle and historical stronghold in the town of Helsingør, Denmark. Immortalised as Elsinore in William Shakespeare's play ''Hamlet'', Kronborg is one of the most important Renaissance castles in Northern Europe. It was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 2000. The castle is situated on the extreme northeastern tip of the island of Zealand (Denmark), Zealand at the narrowest point of the Øresund, the sound between present Denmark and the provinces of present Sweden. The latter were under Danish control at the time the castle was built. In this part, the sound is only wide, hence the strategic importance of maintaining a Coastal defence and fortification, coastal fortification at this location commanding one of the few outlets of the Baltic Sea. The castle's story dates back to a stronghold, ''Krogen'', built by Eric of Pomerania, King Eric VII in the 1420s. Along with the fortress Kärnan in Helsingborg, on the opposite coast of Øresund, it controll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Fredensborg
Fort Fredensborg is situated along the Gulf of Guinea, in the Greater Accra Region in Old Ningo and was built in 1734. Because of its testimony to the Atlantic slave trade and the European colonial influence on West Africa, the fort was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1979, along with several castles and forts in Ghana. History The Danish-Norwegian fort was once used as a slave trading station. However, with the abolition of the slave trade, it soon decayed such that by 1835 only one man was stationed in the fort ‘to maintain the flag’. Fredensborg was already in a state of ruin when it was handed over to the British on 8 March 1850, along with other Danish possessions. See also *Fredensborg (slave ship) *Fredensborg References {{Authority control Danish Gold Coast Castles in Ghana Fredensborg Fredensborg () is a railway town located in Fredensborg Municipality, North Zealand, some 30 kilometres north of Copenhagen, Denmark. It is most known for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiansted
Christiansted ( , ; ) is the largest town on Saint Croix, one of the main islands of the United States Virgin Islands, a territory of the United States of America. The town is named after King Christian VI of Denmark. History The town was founded by Captain Frederik Moth after he was made governor of St. Croix in 1733. Departing from St. Thomas, Moth's party had cleared a space for Fort Christianswærn by 5 September. In a ceremony next to this fort on 8 January 1734, the French formally handed the island over to the Danes in the form of the Danish West India and Guinea Company. St. Croix was to be allotted 300 plantations, 215 for sugar and the rest for cotton. The plantations surveyed were 3,000 by 2,000 feet. In addition, the company established a sugar refinery and distillery. The fort was completed by 1740. The 1742 census listed 120 sugar plantations, 122 cotton plantations, 1,906 slaves, about 300 Englishmen, and 60 Danes. By 1743, St. Croix had a hospital. In 1745, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Sea in the north. It is more than long and wide, covering . It hosts key north European shipping lanes and is a major fishery. The coast is a popular destination for recreation and tourism in bordering countries, and a rich source of energy resources, including wind energy, wind and wave power. The North Sea has featured prominently in geopolitical and military affairs, particularly in Northern Europe, from the Middle Ages to the modern era. It was also important globally through the power northern Europeans projected worldwide during much of the Middle Ages and into the modern era. The North Sea was the centre of the Viking Age, Vikings' rise. The Hanseatic League, the Dutch Golden Age, Dutch Republic, and Kingdom of Great Britain, Brita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |