|
Chourre-class Aircraft Repair Ship
The ''Chourre''-class aircraft repair ship was a class of repair ships that were operated by the United States Navy during World War II. Design ''Chourre''-class was the first ship class to be designated as aircraft repair ships in the Navy. The class consists of two ships converted from the EC2-S-C1, also known as Liberty ships. The ships were long overall ( between perpendiculars, with a beam of . She had a depth of and a draft of . She was assessed at , , . She was powered by a triple expansion steam engine, which had cylinders of , and diameter by stroke. The engine was built by the Babcock & Wilcox. It drove a single screw propeller, which could propel the ship at . They served well throughout the war without a ship being lost to enemy action. After the war, they were decommissioned but only ''Chourre'' was reactive to take part in the Korean War , date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethlehem Fairfield Shipyard
The Bethlehem-Fairfield Shipyard of Baltimore, Maryland, was a shipyard in the United States from 1941 until 1945. Located on the south shore of the Middle Branch of the Patapsco River which serves as the Baltimore Harbor, it was owned by the Bethlehem Shipbuilding Company, created by the Bethlehem Steel Corporation of Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, which had operated a major waterfront steel mill outside Baltimore to the southeast at Sparrows Point, Maryland in rural Baltimore County since the 1880s. The yard is now the location to the west of several heavy industrial firms with a focus on petro-chemicals, a later Maryland Shipbuilding and Drydock Company, which endured into the 1990s, and the underground south entrance of the Baltimore Harbor Tunnel, built in 1956–1957, carrying Interstate 895 and the Baltimore Harbor Tunnel Thruway through and under the city in the major East Coast thoroughfare. Bethlehem-Fairfield was one of two new emergency shipyards, established by the Maritim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Repair Ship
Aircraft repair ship is a naval auxiliary ship designed to provide maintenance support to aircraft. Aircraft repair ships provide similar services to seaplane tenders, that also cared for the crew. Aircraft repair ships had their own stores of spare parts, like a depot ship. Aircraft repair ships had repair personnel and equipment to repair failures or battle damage on aircraft. Aircraft repair ship also did regular aircraft maintenance.Lenton & Colledge, p.333 United States Navy During World War II there was a great demand for aircraft repair ships. The United States Navy aircraft repair ship were manned by repair units, called Carrier Aircraft Service Units. If needed a Carrier Aircraft Service Unit could be redesignated into a Combat Aircraft Service Unit, Scout Observation Service unit or Patrol Service units. These units could also be land-based or on an aircraft repair ship. Some cargo ships were converted into aircraft repair ships to aid in the repair needs of the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean War Auxiliary Ships Of The United States
Korean may refer to: People and culture * Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula * Korean cuisine * Korean culture * Korean language **Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl **Korean dialects and the Jeju language **See also: North–South differences in the Korean language Places * Korean Peninsula, a peninsula in East Asia * Korea, a region of East Asia * North Korea, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea * South Korea, the Republic of Korea Other uses * Korean Air, flag carrier and the largest airline of South Korea See also *Korean War, 1950–1953 war between North Korea and South Korea * Names of Korea, various country names used in international contexts *History of Korea The Lower Paleolithic era in the Korean Peninsula and Manchuria began roughly half a million years ago. Christopher J. Norton, "The Current State of Korean Paleoanthropology", (2000), ''Journal of Human Evolution'', 38: 803–825. The earlies ..., the history of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II Auxiliary Ships Of The United States
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In '' scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Reef
An artificial reef is a human-created underwater structure, typically built to promote marine life in areas with a generally featureless bottom, to control erosion, block ship passage, block the use of trawling nets, or improve surfing Surfing is a surface water sport in which an individual, a surfer (or two in tandem surfing), uses a board to ride on the forward section, or face, of a moving wave of water, which usually carries the surfer towards the shore. Waves suitabl .... Many reefs are built using objects that were built for other purposes, such as by sinking oil rigs (through the Rigs-to-Reefs program), Sinking ships for wreck diving sites, scuttling ships, or by deploying rubble or construction debris. Other artificial reefs are purpose-built (e.g. the The Reef Ball Foundation, reef balls) from Polyvinyl chloride, PVC or concrete. Shipwrecks may become artificial reefs when preserved on the seafloor. Regardless of construction method, artificial reefs generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Webster (ARV-2)
USS ''Webster'' (ARV-2) was a Chourre class aircraft repair ship that saw service in the United States Navy during World War II. On 30 March 1944, prior to the beginning of work on her construction, ''Masbate'' (ARG-1) was renamed ''Webster'' and reclassified ARV-2. The ship's keel was laid down under a Maritime Commission contract (MCE hull 2666) on 1 July 1944 at Baltimore, MD, by the Bethlehem Fairfield Shipyard, Inc. Sponsored by Mrs. Walter W. Webster, the widow of the ship's namesake, the ship was launched on 5 August 1944 and commissioned at Baltimore on 17 March 1945. After fitting out, ''Webster'' departed Baltimore on 22 March 1945 and arrived at Norfolk Naval Base later that day. There, the aircraft repair ship loaded supplies and provisions into the second week of April, when she got underway for shakedown and training in Chesapeake Bay. After subsequent minor repairs and alterations at the Norfolk Navy Yard from 21 April to 8 May, ''Webster'' joined Convoy No. 50 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Chourre (ARV-1)
USS ''Chourre'' (ARV-1) was a that saw service in the United States Navy during World War II and the Korean War. Originally authorized as USS ''Dumaran'' (ARG-14), an internal combustion engine repair ship, she was renamed and reclassified as an aircraft repair ship 22 February 1944; launched 22 May 1944 by Bethlehem Fairfield Shipyard, Inc., Baltimore, MD, under a Maritime Commission contract; sponsored by Mrs. E. A. Forde, Jr., and commissioned 7 December 1944. Sailing from Norfolk 2 March 1945 ''Chourre'' arrived at Pearl Harbor 12 April to embark aviation personnel for Espiritu Santo, where she arrived 29 April. She transferred an aviation repair unit to Saipan, then sailed to San Pedro Bay, Leyte, for duty as station supply ship replenishing carriers from 26 May to 17 July. Except for one trip to Guam to replenish stores (17 July-7 August) she remained at San Pedro Bay until 24 October when she sailed for Tokyo Bay to serve ships taking part in the occupation. On 1 Janua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Korean War , partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict , image = Korean War Montage 2.png , image_size = 300px , caption = Clockwise from top:{{Flatlist, * A column of the U.S. 1st Marine Division's infantry and armor moves through Chinese lines during their breakout from the Chosin Reservoir * UN landing at Incheon harbor, starting point of the Battle of Incheon * Korean refugees in front of a U.S. M46 Patton tank * U.S. Marines, led by First Lieutenant Baldomero Lopez, landing at Incheon * F-86 Sabre fighter aircraft , date = {{Ubl, 25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953 (''de facto'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950, month2=7, day2=27, year2=1953), 25 June 1950 – present (''de jure'')({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=6, day1=25, year1=1950) , place = Korean Peninsula, Yellow Sea, Sea of Japan, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propeller
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis. History Early developments The principle employed in using a screw propeller is derived from sculling. In sculling, a single blade is moved through an arc, from side to side taking care to keep presenting the blade to the water at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
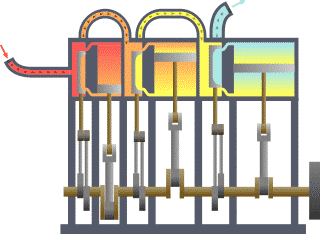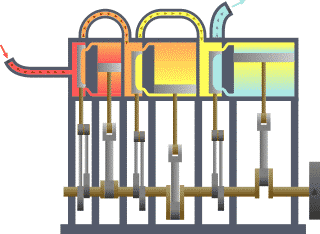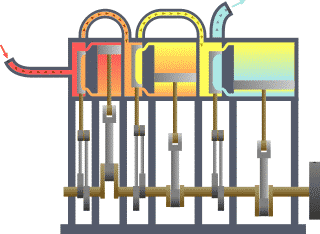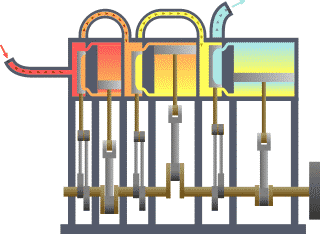
Triple Expansion Steam Engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam. Invented in 1781, this technique was first employed on a Cornish beam engine in 1804. Around 1850, compound engines were first introduced into Lancashire textile mills. Compound systems There are many compound systems and configurations, but there are two basic types, according to how HP and LP piston strokes are phased and hence whether the HP exhaust is able to pass directly from HP to LP ( Woolf compounds) or whether pressure fluctuation necessitates an intermediate "buffer" space in the form of a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Length Between Perpendiculars
Length between perpendiculars (often abbreviated as p/p, p.p., pp, LPP, LBP or Length BPP) is the length of a ship along the summer load line from the forward surface of the stem, or main bow perpendicular member, to the after surface of the sternpost A sternpost is the upright structural member or post at the stern of a (generally wooden) ship or a boat, to which are attached the transoms and the rearmost left corner part of the stern. The sternpost may either be completely vertical or m ..., or main stern perpendicular member. When there is no sternpost, the centerline axis of the rudder stock is used as the aft end of the length between perpendiculars. Measuring to the stern post or rudder stock was believed to give a reasonable idea of the ship's carrying capacity, as it excluded the small, often unusable volume contained in her overhanging ends. On some types of vessels this is, for all practical purposes, a waterline measurement. In a ship with raked stems, natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberty Ship
Liberty ships were a ship class, class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Though British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost construction. Mass-produced on an unprecedented scale, the Liberty ship came to symbolize U.S. wartime industrial output. The class was developed to meet British orders for transports to replace ships that had been lost. Eighteen American shipyards built 2,710 Liberty ships between 1941 and 1945 (an average of three ships every two days), easily the largest number of ships ever produced to a single design. Their production mirrored (albeit on a much larger scale) the manufacture of "Hog Islander" and similar standardized ship types during World War I. The immensity of the effort, the number of ships built, the role of Rosie the Riveter, female workers in their construction, and the survival of some far longer than their original five-year desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)