|
Chiriquí Fire Salamander
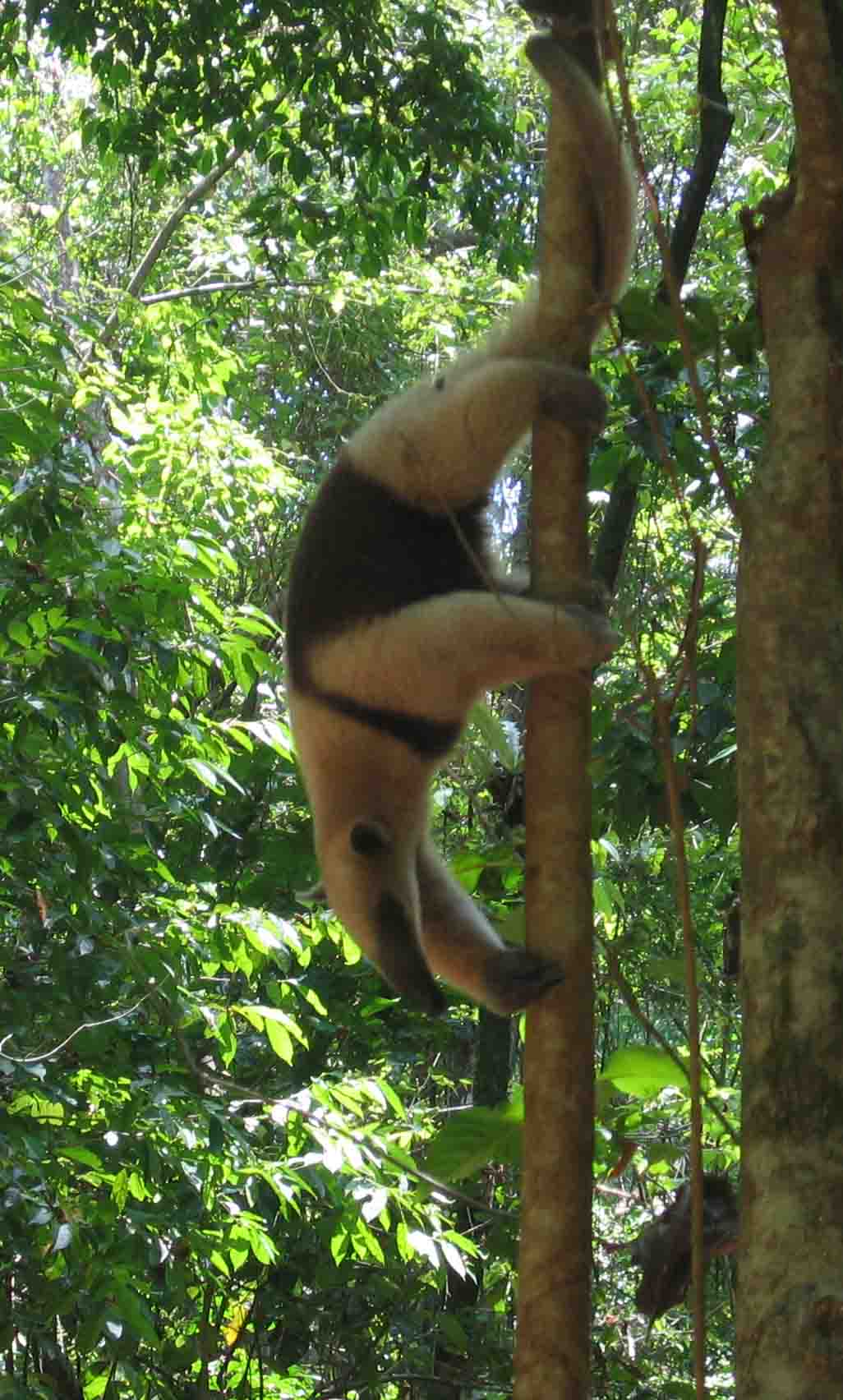
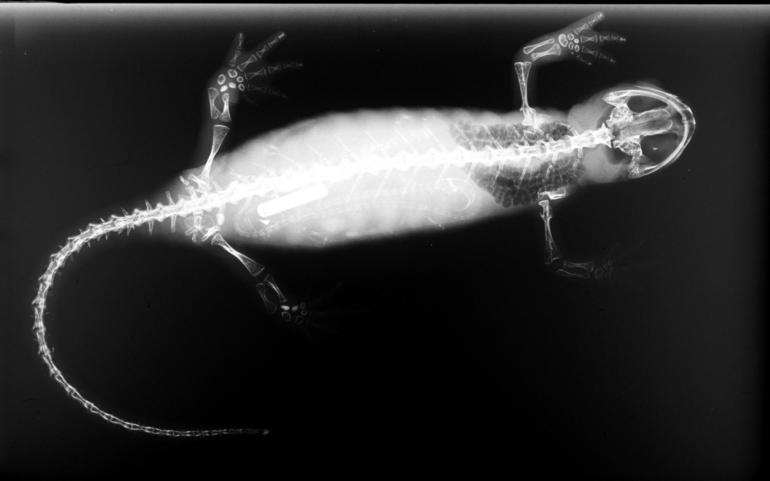
The Chiriquí fire salamander (''Bolitoglossa cathyledecae''), known as "Salamandra de fuego chiricana" in native Spanish, is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is found exclusively in Panama and is endemic to the western highlands of Chiriquí Province. Like many Central American endemic species, it is threatened by habitat loss. Discovery During expeditions through La Amistad International Park, investigators discovered a salamander that was very distinct from other species in the region. Notably the Chiriqui fire salamander has different coloration, foot webbing, and upper maxillary tooth numbers than other known salamanders. The species was formally described to science in 2022 with a specific epithet chosen by the discoverers to honor Cathy Ledec, a conservationist and supporter of Neotropical salamanders. Description The holotype specimen of Chiriquí fire salamander had a head-to-torso length of 46 mm and a tail length of 68.8 mm. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathy Ledec
''Cathy'' is an American gag-a-day comic strip, drawn by Cathy Guisewite from 1976 until 2010. The comic follows Cathy, a woman who struggles through the "four basic guilt groups" of life: food, love, family, and work. The strip gently pokes fun at the lives and foibles of modern women. The strip's debut was on November 22, 1976, and it appeared in over 1,400 newspapers at its peak. The strips have been compiled into more than 20 books. Three television specials were also created. Guisewite received the National Cartoonists Society Reuben Award in 1992 for the strip. History Initially, the strip was based largely on Guisewite's own life as a single woman. "The syndicate felt it would make the strip more relatable if the character's name and my name were the same," Guisewite said in an interview. "They felt it would make it a more personal strip, and would help people know it was a real woman who was going through these things. I hated the idea of calling it 'Cathy'. Guisewite h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibians Described In 2022
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant taxon, extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass (biology), subclass Lissamphibia, with three living order (biology), orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater ecosystem, freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their biological life cycle, life cycle typically starts out as aquatic animal, aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolitoglossa
''Bolitoglossa'' is a genus of lungless salamanders, Common name, commonly called mushroom-tongued salamanders, tropical climbing salamanders, and web-footed salamanders, in the family Plethodontidae. Their combined geographic ranges extend from northern Mexico through Central America to Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, northeastern Brazil, and central Bolivia. Neotropical salamanders of the genus ''Bolitoglossa'' make up the largest genus in the order Caudata, consisting of approximately one-fifth of all known species of salamanders. Adult salamanders of the genus ''Bolitoglossa'' have a Snout–vent length, snout-to-vent length in the range of depending on the particular species. They are known for the ability to project the tongue to seize prey items. They are also known for webbed feet, having significantly more webbing than any other species outside their genus with the exception of the cave-dwelling Mexican Bolitoglossinae, bolitoglossine ''Chiropterotriton magnipes''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critically Endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of the 157,190 species currently on the IUCN Red List, 9,760 of those are listed as critically endangered, with 1,302 being possibly extinct and 67 possibly extinct in the wild. The IUCN Red List provides the public with information regarding the conservation status of animal, fungi, and plant species. It divides various species into seven different categories of conservation that are based on habitat range, population size, habitat, threats, etc. Each category represents a different level of global extinction risk. Species that are considered to be critically endangered are placed within the "Threatened" category. As the IUCN Red List does not consider a species extinct until extensive targeted surveys have been conducted, species that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talamancan Montane Forests
The Talamancan montane forests ecoregion, in the tropical moist broadleaf forest biome, are in montane Costa Rica and western Panama in Central America. Setting The Talamancan montane forests cover a discontinuous area of in Cordilleran mountains, including the Cordillera de Guanacaste, Cordillera de Tilarán, Cordillera Central, and Cordillera de Talamanca, from northwestern Costa Rica to western Panama, with outliers on Cerro Hoya on Panama's Azuero Peninsula. The montane forests lie above 750 to 1500 meters elevation, up to approximately 3000 meters elevation, where they transition to the grasslands and shrublands of the Costa Rican páramo on the highest peaks. The montane forests are surrounded at lower elevations by lowland forests, including the Isthmian–Atlantic moist forests on the Atlantic (Caribbean) slope, the Isthmian–Pacific moist forests to the south on the Pacific slope, and the Costa Rican seasonal moist forests to the northwest. Flora The fores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cordillera De Talamanca
The Cordillera de Talamanca is a mountain range that lies in the southeast half of Costa Rica and the far west of Panama. Much of the range and the area around it is included in La Amistad International Park, which also is shared between the two countries. This range in the south of Costa Rica stretches from southwest of San José to beyond the border with Panama and contains the highest peaks of both Costa Rica and Panama, among them Cerro Chirripó at , and the more accessible high peak of Cerro de la Muerte. Much of the Caribbean areas of the range are still unexplored. Exploration and classification The range is covered by the Talamancan montane forests to elevations of approximately . Much of it is covered by rainforests. Above elevations of these are dominated by huge oak trees ('' Quercus costaricensis''). Above , the forests transition to enclaves of sub-páramo, a sort of shrub and dwarf bamboo '' Chusquea'' dominated scrub, above this becomes Costa Rican páramo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehensile Tail
A prehensile tail is the tail of an animal that has Adaptation (biology), adapted to grasp or hold objects. Fully Prehensility, prehensile tails can be used to hold and manipulate objects, and in particular to aid arboreal creatures in finding and eating food in the trees. If the tail cannot be used for this it is considered only partially prehensile; such tails are often used to anchor an animal's body to dangle from a branch, or as an aid for climbing. The term ''prehensile'' means "able to grasp" (from the Latin ''prehendere'', to take hold of, to grasp). Evolution One point of interest is the distribution of animals with prehensile tails. The prehensile tail is predominantly a New World adaptation, especially among mammals. Many more animals in South America have prehensile tails than in Africa and Southeast Asia. It has been argued that animals with prehensile tails are more common in South America because the forest there is denser than in Africa or Southeast Asia. In contra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany and mycology, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, generally pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same genetic individual. A holotype is not necessarily "ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Epithet
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammar, Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the ''generic name (biology), generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten extant salamander families are grouped together under the order Urodela, the sole surviving order from the group Caudata. ''Urodela'' is a scientific Latin term based on the Ancient Greek : ourà dēlē "conspicuous tail". ''Caudata'' is the Latin for "tailed ones", from : "tail". Salamander diversity is highest in eastern North America, especially in the Appalachian Mountains; most species are found in the Holarctic realm, with some species present in the Neotropical realm. Salamanders never have more than four toes on their front legs and five on their rear legs, but some species have fewer digits and others lack hind limbs. Their permeable skin usually makes them reliant on habitats in or near water or other cool, damp places. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Anatomy Structure The maxilla is a paired bone - the two maxillae unite with each other at the intermaxillary suture. The maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla: pyramid-shaped; has an orbital, a nasal, an infratemporal, and a facial surface; contains the maxillary sinus. * Four processes: ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process It has three surfaces: * the anterior, posterior, medial Features of the maxilla include: * t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |