|
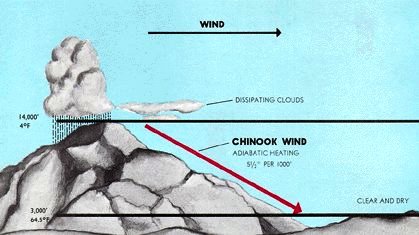
Chinook Winds
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from the ocean. The interior Chinooks are occasional warm, dry föhn winds blowing down the eastern sides of interior mountain ranges. The coastal Chinooks were the original term, used along the northwest coast, and the term in the interior of North America is later and derives from the coastal term. * Along the Pacific Northwest coast, where the name is pronounced ('chin'+'uk'), the name refers to wet, warm winds off the ocean from the southwest; this is the original use of the term. The coastal Chinook winds deliver tremendous amounts of moisture both as rain along the coast and snow in the coastal mountains, that sustain the characteristic temperate rainforests and climate of the Pacific Northwest. * In North American western interior, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westerly Wind
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes (about 30 degrees) and trend towards the Geographical pole, poles and steer extratropical cyclones in this general manner. Tropical cyclones which cross the subtropical ridge axis into the westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The winds are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. The westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere (called also 'Brave West winds' at striking Chile, Argentina, Tasmania and New Zealand), in areas where land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and Navigation, marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to Calibration, calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead a long-term average of tide gauge readings at a particular reference location. The term ''above sea level'' generally refers to the height above mean sea level (AMSL). The term APSL means above present sea level, comparing sea levels in the past with the level today. Earth's radius at sea level is 6,378.137 km (3,963.191 mi) at the equator. It is 6,356.752 km (3,94 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the namesake Hudson's Bay (department store), Hudson's Bay department stores (colloquially The Bay), and also owns or manages approximately of gross leasable real estate through its HBC Properties and Investments business unit. HBC previously owned the full-line Saks Fifth Avenue and off-price Saks Off 5th in the United States, which were spun-off into the Saks Global holding company in 2024. After incorporation by royal charter issued in 1670 by Charles II of England, King Charles II, the company was granted a right of "sole trade and commerce" over an expansive area of land known as Rupert's Land, comprising much of the Hudson Bay drainage basin. This right gave the company a monopoly, commercial monopoly over that area. The HBC functioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Métis In Canada
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They have a shared history and culture, deriving from specific mixed European (primarily French, Scottish, and English) and Indigenous ancestry (primarily Cree with strong kinship to Cree people and communities), which became distinct through ethnogenesis by the mid-18th century, during the early years of the North American fur trade. In Canada, the Métis, with a population of 624,220 as of 2021, are one of three legally recognized Indigenous peoples in the ''Constitution Act, 1982'', along with the First Nations and Inuit. The term ''Métis'' (uppercase 'M') typically refers to the specific community of people defined as the Métis Nation, which originated largely in the Red River Valley and organized politically in the 19th century, radiating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ; ) is a complex estuary, estuarine system of interconnected Marine habitat, marine waterways and basins located on the northwest coast of the U.S. state of Washington (state), Washington. As a part of the Salish Sea, the sound (geography), sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel. Puget Sound extends approximately from Deception Pass in the north to Olympia, Washington, Olympia in the south. Its average depth is and its maximum depth, off Jefferson Point between Indianola, Washington, Indianola and Kingston, Washington, Kingston, is . The depth of the main basin, between the southern tip of Whidbey Island and Tacoma, Washington, Tacoma, is approximately . In 2009, the term Salish Sea was established by the United States Board on Geographic Names as the collective wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. The 42nd parallel north, 42° north parallel delineates the southern boundary with California and Nevada. The western boundary is formed by the Pacific Ocean. Oregon has been home to many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous nations for thousands of years. The first European traders, explorers, and settlers began exploring what is now Oregon's Pacific coast in the early to mid-16th century. As early as 1564, the Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, Spanish began sending vessels northeast from the Philippines, riding the Kuroshio Current in a sweeping circular route across the northern part of the Pacific. In 1592, Juan de Fuca undertook detailed mapping a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington (state)
Washington, officially the State of Washington, is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is often referred to as Washington State to distinguish it from Washington, D.C., the national capital, both named after George Washington (the first President of the United States, U.S. president). Washington borders the Pacific Ocean to the west, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and shares Canada–United States border, an international border with the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. Olympia, Washington, Olympia is the List of capitals in the United States, state capital, and the most populous city is Seattle. Washington is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 18th-largest state, with an area of , and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 13th-most populous state, with a population of just less than 8 million. The majority of Washington's residents live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Coast
The British Columbia Coast, popularly referred to as the BC Coast or simply the Coast, is a geographic region of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia. As the entire western continental coastline of Canada along the Pacific Ocean is in the province, it is synonymous with being the West Coast of Canada. While the exact boundaries are variously defined, the region is generally defined to include the 15 regional districts that have coastline along the Pacific Ocean or Salish Sea, or are part of the Lower Mainland, a subregion of the British Columbia Coast. Other boundaries may exclude parts of or even entire regional districts, such as those of the aforementioned ''Lower Mainland''. Boundaries While the term ''British Columbia Coast'' has been recorded from the earliest period of non-native settlement in British Columbia, it has never been officially defined in legal terms. The term has historically been in popular usage for over a century to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calgary
Calgary () is a major city in the Canadian province of Alberta. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806 making it the third-largest city and fifth-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Calgary is at the confluence of the Bow River and the Elbow River in the southwest of the province, in the transitional area between the Rocky Mountain Foothills and the Canadian Prairies, about east of the front ranges of the Canadian Rockies, roughly south of the provincial capital of Edmonton and approximately north of the Canada–United States border. The city anchors the south end of the Statistics Canada-defined urban area, the Calgary–Edmonton Corridor. Calgary's economy includes activity in many sectors: energy; financial services; film and television; transportation and logistics; technology; manufacturing; aerospace; health and wellness; retail; and tourism. The Calgary Metropolitan Region is home to Canada' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelowna
Kelowna ( ) is a city on Okanagan Lake in the Okanagan, Okanagan Valley in the British Columbia Interior, southern interior of British Columbia, Canada. It serves as the head office of the Regional District of Central Okanagan. The name Kelowna derives from the Okanagan language, Okanagan word ', referring to a grizzly bear. Kelowna is the province's third-largest Greater Kelowna, metropolitan area (after Greater Vancouver, Vancouver and Greater Victoria, Victoria). It is the List of municipalities in British Columbia, seventh-largest municipality in BC and the largest in the Interior. It is the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, 20th-largest metropolitan area in Canada. The city proper encompasses , and the Census geographic units of Canada#Census metropolitan area, census metropolitan area . Kelowna's population in 2025 is 165,907 in the city proper. Nearby communities include the City of West Kelowna (also referred to as Westbank and Westside) to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provinces are partially covered by grasslands, plains, and lowlands, mostly in the southern regions. The northernmost reaches of the Canadian Prairies are less dense in population, marked by forests and more variable topography. If the region is defined to include areas only covered by prairie land, the corresponding region is known as the Interior Plains. Physical or ecological aspects of the Canadian Prairies extend to northeastern British Columbia, but that area is not included in political use of the term. The prairies in Canada are a biome of temperate grassland and shrubland within the prairie ecoregion of Canada that consists of northern mixed grasslands in Alberta, Saskatchewan, southern Manitoba, as well as northern short grasslands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Okanagan
The Okanagan ( ), also called the Okanagan Valley and sometimes the Okanagan Country, is a region in the Canadian province of British Columbia defined by the basin of Okanagan Lake and the Canadian portion of the Okanagan River. It is part of the Okanagan Country, extending into the United States as Okanogan County in north-central Washington. According to the 2016 Canadian census, the region's population is 362,258. The largest populated cities are Kelowna, Penticton, Vernon, and West Kelowna. The region is known for its sunny climate, dry landscapes, lakeshore communities, and particular lifestyle. The economy is retirement- and commercial-recreation-based, with outdoor activities such as boating and watersports, skiing, and hiking. Agriculture has been focused primarily on fruit orchards, with a recent shift in focus to vineyards and wine. The region stretches northwards via the Spallumcheen Valley to Sicamous in the Shuswap Country, and reaches south of the Canada� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |