|
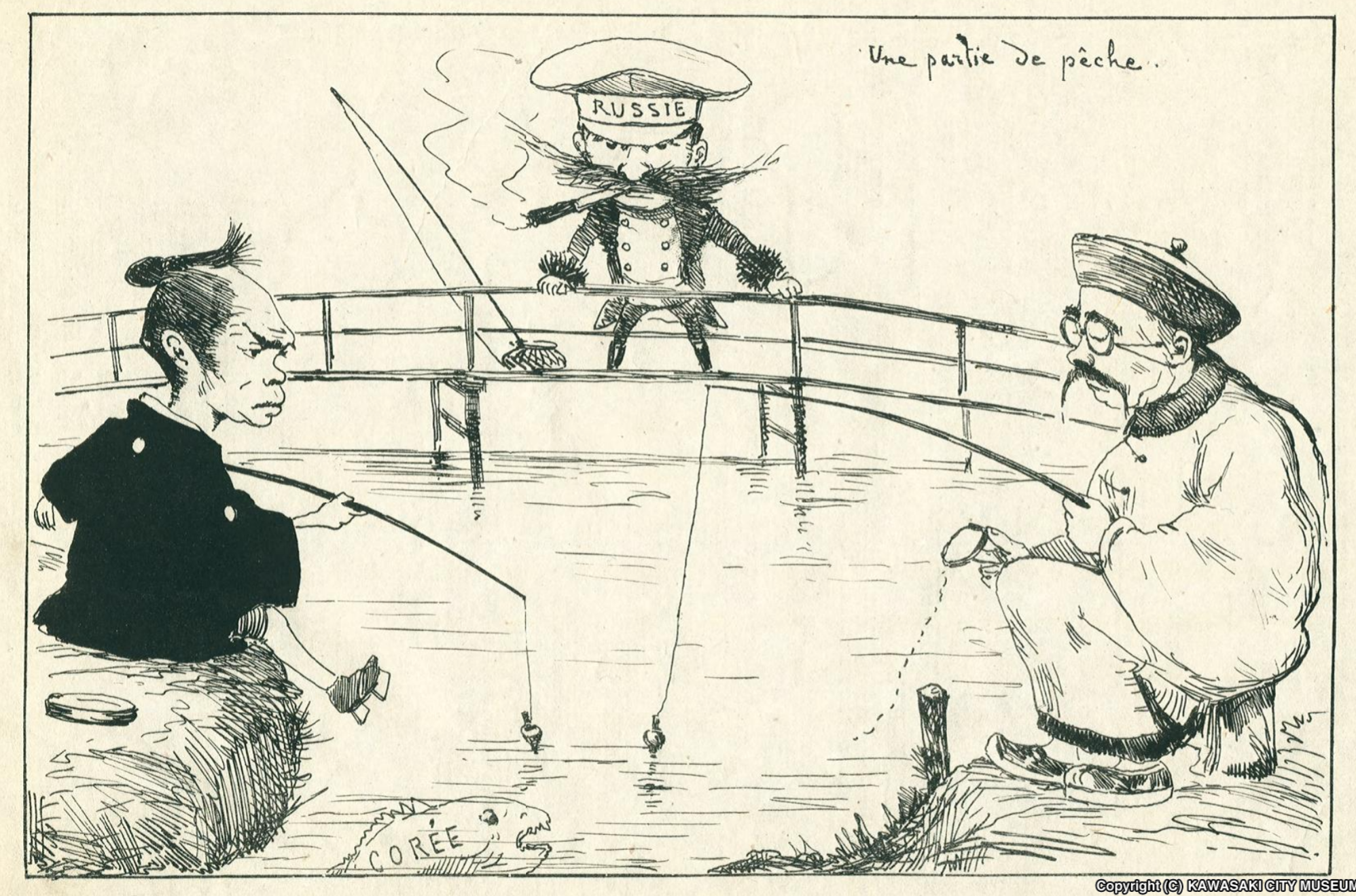
Chinese Ironclad Zhenyuan
''Zhenyuan'' () was an ironclad warship, ironclad battleship built for the Qing Dynasty, Chinese Beiyang Fleet. She was the second and final member of the , which included one other vessel, , both of which were built in German Empire, Germany in the early 1880s. Delivery of the two ironclads was delayed by the Sino-French War of 1884–1885. The ships were armed with a main battery of four guns in a pair of gun turrets, making them the most powerful warships in East Asian waters at the time. In the 1880s and early 1890s, the Beiyang Fleet conducted a routine of training exercises and cruises abroad, with emphasis placed on visits to Empire of Japan, Japan to intimidate the country. The latter resulted in the Nagasaki Incident in 1886 and contributed to a rise in hostility between the two countries that culminated in the First Sino-Japanese War in 1894. She saw action at the Battle of the Yalu River (1894), Battle of the Yalu River on 17 September, where the Japanese Combined Fle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after India, representing 17.4% of the world population. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and Borders of China, borders fourteen countries by land across an area of nearly , making it the list of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by land area. The country is divided into 33 Province-level divisions of China, province-level divisions: 22 provinces of China, provinces, 5 autonomous regions of China, autonomous regions, 4 direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities, and 2 semi-autonomous special administrative regions. Beijing is the country's capital, while Shanghai is List of cities in China by population, its most populous city by urban area and largest financial center. Considered one of six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conning Tower
A conning tower is a raised platform on a ship or submarine, often armoured, from which an officer in charge can conn (nautical), conn (conduct or control) the vessel, controlling movements of the ship by giving orders to those responsible for the ship's engine, rudder, lines, and ground tackle. It is usually located as high on the ship as is practical, to give the conning team good visibility of the entirety of the ship, ocean conditions, and other vessels. The naval term "conn" may derive from the Middle English ''conne'' (study, become acquainted with) or French ''conduire'' from Latin ''conducere'' (conduct). Surface ships On surface ships, the conning tower was a feature of all battleships and armored cruiser, armoured cruisers from about 1860 to the early years of World War II. Located at the front end of the superstructure, the conning tower was a heavily armored cylinder, with tiny slit windows on three sides providing a reasonable field of view. Designed to shield j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combined Fleet
The was the main sea-going component of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Until 1933, the Combined Fleet was not a permanent organization, but a temporary force formed for the duration of a conflict or major naval maneuvers from various units normally under separate commands in peacetime. History Sino-Japanese War (1894–95) The Combined Fleet was formally created for the first time on 18 July 1894 by the merger of the Standing Fleet and the Western Fleet. The Standing Fleet (also known as the Readiness Fleet) contained the navy's most modern and combat-capable warships. The Western Fleet was a reserve force consisting primarily of obsolete ships deemed unsuitable for front-line combat operations, but still suitable for commerce protection and coastal defense. Vice-admiral Itō Sukeyuki was appointed the first Commander-in-Chief of the Combined Fleet for the duration of the first Sino-Japanese War against China. Russo-Japanese War (1904–05) The Combined Fleet was re-formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Yalu River (1894)
The Battle of the Yalu River ( zh, t=黃海海戰, s=黄海海战, p=Huáng Hǎi Hǎizhàn; ; ) was the largest naval engagement of the First Sino-Japanese War, and took place on 17 September 1894, the day after the Japanese victory at the land Battle of Pyongyang. It involved ships from the Imperial Japanese Navy and the Chinese Beiyang Fleet. The battle is also known by a variety of names: Battle of Haiyang Island, Battle of Dadonggou, Battle of the Yellow Sea and Battle of Yalu, after the geographic location of the battle, which was in the Yellow Sea off the mouth of the Yalu River and not in the river itself. There is no agreement among contemporary sources on the exact numbers and composition of each fleet, but both were of a similar size, and the battle is considered to be one of the Imperial Japanese Navy's greatest victories. Background Japan's strategy Japan's initial strategy was to gain command of the sea, which was critical to its operations in Korea. Command of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First China–Japan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as the Jiawu War. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the ports of Lüshunkou (Port Arthur) and Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895 and signed the Unequal treaties, unequal Treaty of Shimonoseki two months later, ending the war. In the late 19th century, Korea remained one of China's tributary states, while Japan viewed it as a target of imperial expansion. In June 1894, the Qing government, at the request of the Korean emperor Gojong of Korea, Gojong, sent 2,800 troops to aid in suppressing the Donghak Peasant Revolution. The Japanese considered this a violation of the 1885 Convention of Tientsin, and sent an expeditionary force of 8,000 troops, which la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagasaki Incident
The , also known as the Nagasaki―Qing Navy Incident (長崎清国水兵事件) was an incident took place on August 13, 1886 (the twelfth year of the reign of Emperor Guangxu Emperor, Guangxu of the Qing Dynasty) during the Beiyang Fleet visit to Nagasaki, Japan. Some Chinese sailors violated military discipline when they went ashore for shopping, went to local brothels and drank and made troubles. As a result, they clashed with the Japanese police. A Japanese policeman was stabbed and seriously injured, and a Chinese sailor was slightly injured. In February 1887, the two sides reached an agreement under the mediation of the British Empire, British and German Empire, German ministers. Both parties compensated the dead and injured persons of the other party. Outline On 1 August 1886 (Meiji period, Meiji 19), the Qing dynasty's Beiyang Fleet, consisting of four warships, the Chinese turret ship Dingyuan, ''Dingyuan'', the Chinese turret ship Zhenyuan, ''Zhenyuan'', the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gun Turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanism of a projectile-firing weapon and at the same time lets the weapon be aimed and fired in some degree of azimuth and elevation (cone of fire). Description Rotating gun turrets protect the weapon and its crew as they rotate. When this meaning of the word "turret" started being used at the beginning of the 1860s, turrets were normally cylindrical. Barbettes were an alternative to turrets; with a barbette the protection was fixed, and the weapon and crew were on a rotating platform inside the barbette. In the 1890s, armoured hoods (also known as "gun houses") were added to barbettes; these rotated with the platform (hence the term "hooded barbette"). By the early 20th century, these hoods were known as turrets. Modern warships have gun-m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a naval gun or group of guns used in volleys, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted groups of similar large-caliber naval rifles. With the evolution of technology the term has come to encompass guided missiles and torpedoes as a warship's principal offensive weaponry, deployed both on surface ships and submarines. A main battery features common parts, munition and fire control system across the weapons which it comprises. Description In the age of cannon at sea, the main battery was the principal group of weapons around which a ship was designed, usually its heavies. With the coming of naval rifles and subsequent revolving gun turrets, the main battery became the principal group of heaviest guns, regardless of how many turrets they were placed in. As missiles displaced guns both above and belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sino-French War
The Sino-French or Franco-Chinese War, also known as the Tonkin War, was a limited conflict fought from August 1884 to April 1885 between the French Third Republic and Qing China for influence in Vietnam. There was no declaration of war. The Chinese armies performed better than in their other nineteenth-century wars. Although French forces emerged victorious from most engagements, the Chinese scored noteworthy successes on land, notably forcing the French to hastily withdraw from occupied Lạng Sơn in the late stages of the war, thus gaining control of the town and its surroundings. However, a lack of foreign support, French naval supremacy, and northern threats posed by Russia and Japan forced China to enter negotiations. China ceded to France its sphere of influence over Northern and Central Vietnam, which respectively became the protectorates of Tonkin and Annam. Both sides ratified the Treaty of Tientsin and no diplomatic gain was reaped by either nation. On another ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Empire
The German Empire (),; ; World Book, Inc. ''The World Book dictionary, Volume 1''. World Book, Inc., 2003. p. 572. States that Deutsches Reich translates as "German Realm" and was a former official name of Germany. also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich or simply Germany, was the period of the German Reich; . from the unification of Germany in 1871 until the German revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution in 1918, when the German Reich changed its form of government from a monarchy to a Weimar Republic, republic. The German Empire consisted of States of the German Empire, 25 states, each with its own nobility: four constituent Monarchy, kingdoms, six Grand duchy, grand duchies, five Duchy, duchies (six before 1876), seven Principality, principalities, three Free imperial city, free Hanseatic League, Hanseatic City-state, cities, and Alsace–Lorraine, one imperial territory. While Prussia was one of four kingdoms in the realm, it contained about two-thirds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiyang Fleet
The Beiyang Fleet (Pei-yang Fleet; , alternatively Northern Seas Fleet) was one of the Imperial Chinese Navy#Fleets, four modernized Chinese navies in the late Qing dynasty. Among the four, the Beiyang Fleet was particularly sponsored by Li Hongzhang, one of the most trusted vassals of Empress Dowager Cixi and the principal patron of the "self-strengthening movement" in northern China in his capacity as the Viceroy of Zhili and the Minister of Beiyang Commerce (北洋通商大臣). Due to Li's influence in the imperial court, the Beiyang Fleet garnered much greater resources than the other Chinese fleets and soon became the dominant navy in Asia before the onset of the 1894–1895 First Sino-Japanese War. It was the largest fleet in Asia and the 8th in the world during the late 1880s in terms of tonnage. Creation The creation of the Beiyang Fleet dated back to 1871, when four ships from the southern provinces were shifted north to patrol the northern waters. The Beiyang fleet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |