|
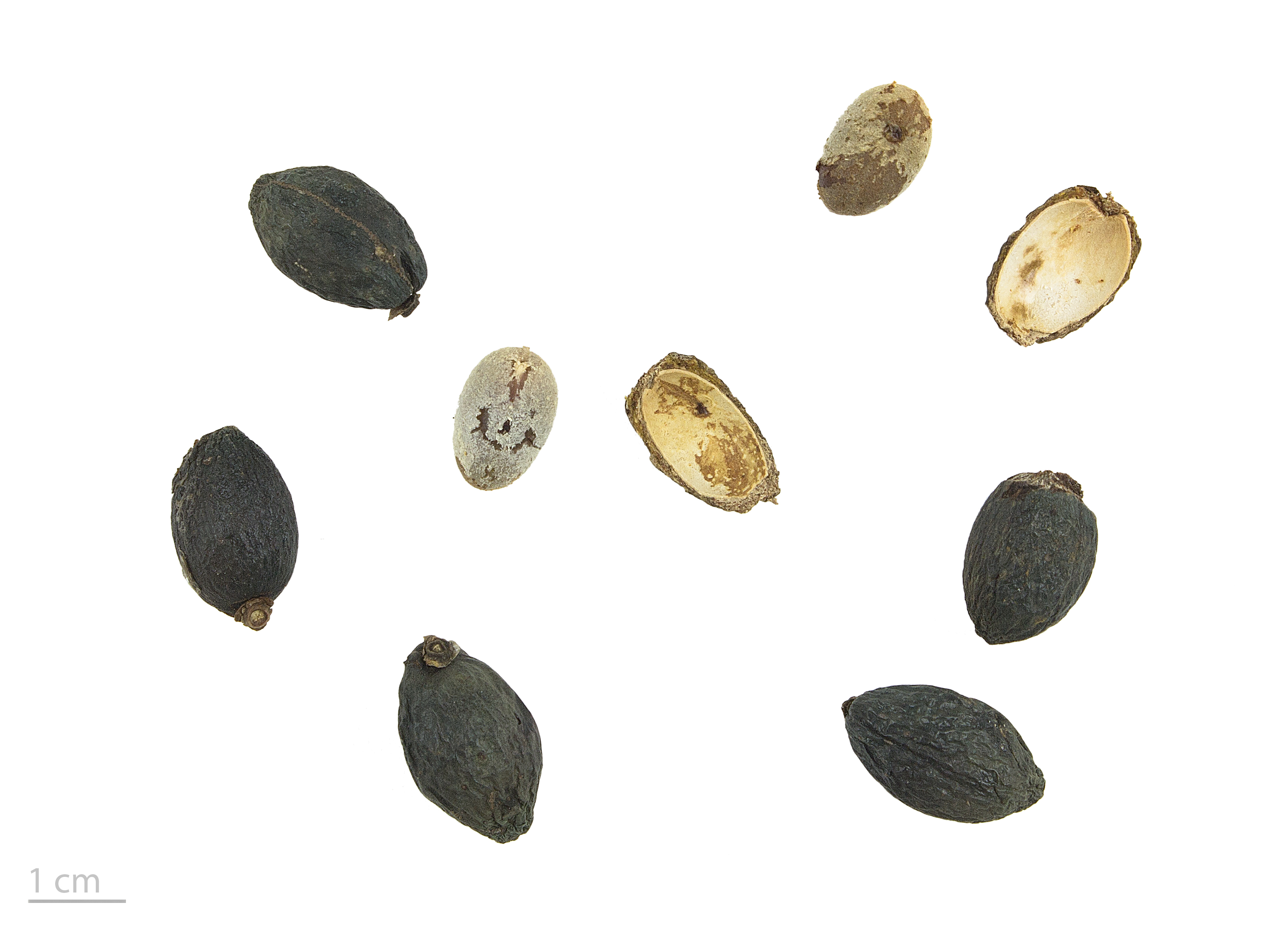
Chinese Fan Palm
''Livistona chinensis'', the Chinese fan palm or fountain palm, is a species of subtropical palm tree of east Asia. It is native to southern Japan, Taiwan, the Ryukyu Islands, southeastern China and Hainan. In Japan, two notable populations occupy islands near the coast of Miyazaki Prefecture, Aoshima and Tsuki Shima. It is also reportedly naturalized in South Africa, Mauritius, Réunion, the Andaman Islands, Java, New Caledonia, Micronesia, Hawaii, Florida, Bermuda, Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic. Description Vegetative characteristics ''Livistona chinensis'' can attain heights of about and a spread of . The leaves are fan shaped. Cultivation The palm is cultivated as an ornamental tree in gardens and conservatories. It is hardy in USDA zones 9-11, tolerating temperatures down to about . They are often grown as a landscape palm in hot and wet tropical and subtropical climates like eastern Australia, Southeast Asia, and the southeast United States. This plant can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolaus Joseph Von Jacquin
Nikolaus Joseph Freiherr von Jacquin (16 February 172726 October 1817) was a scientist who studied medicine, chemistry and botany. Biography Born in Leiden in the Netherlands, he studied medicine at Leiden University, then moved first to Paris and afterward to Vienna. In 1752, he studied under Gerard van Swieten in Vienna. Between 1755 and 1759, Jacquin was sent to the West Indies, Central America, Venezuela and New Granada by Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis I to collect plants for the Schönbrunn Palace, and amassed a large collection of animal, plant and mineral samples. In 1797, Alexander von Humboldt profited from studying these collections and conversing with Jacquin in preparation of his own journey to the Americas. In 1763, Jacquin became professor of chemistry and mineralogy at the Mining Academy (Banská Štiavnica), Bergakademie Schemnitz (now Banská Štiavnica in Slovakia). In 1768, he was appointed Professor of Botany and Chemistry and became director of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Straits of Florida to the south, and The Bahamas to the southeast. About two-thirds of Florida occupies a peninsula between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. It has the List of U.S. states by coastline, longest coastline in the contiguous United States, spanning approximately , not including its many barrier islands. It is the only state that borders both the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of over 23 million, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, third-most populous state in the United States and ranks List of states and territories of the United States by population density, seventh in population density as of 2020. Florida spans , ranking List of U.S. states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of China
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated Plant stem, stem, or trunk (botany), trunk, usually supporting Branch, branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only Bark (botany), woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller Arecaceae, palms, Cyatheales, tree ferns, Musa (genus), bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a Monophyletic group, monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that Convergent evolution, have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trees Of Japan
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only plants that are usable as lumber, or only plants above a specified height. But wider definitions include taller palms, tree ferns, bananas, and bamboos. Trees are not a monophyletic taxonomic group but consist of a wide variety of plant species that have independently evolved a trunk and branches as a way to tower above other plants to compete for sunlight. The majority of tree species are angiosperms or hardwoods; of the rest, many are gymnosperms or softwoods. Trees tend to be long-lived, some trees reaching several thousand years old. Trees evolved around 400 million years ago, and it is estimated that there are around three trillion mature trees in the world currently. A tree typically has many secondary branches supported clear of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livistona
''Livistona'' is a genus of palms, the botanical family Arecaceae, native to southeastern and eastern Asia, Australasia, and the Horn of Africa. They are fan palms, the leaves with an armed petiole terminating in a rounded, costapalmate fan of numerous leaflets. '' L. speciosa'', locally called ''kho'', gives its name to Khao Kho District in Thailand. Taxonomy The genus was established by Robert Brown in his ''Prodromus Florae Novae Hollandiae'' (1810) to accommodate his descriptions of two species collected during an expedition to Australia. The names published by Brown were '' Livistona humilis'' and '' L. inermis'', describing material he had collected in the north of Australia, a partial taxonomic revision in 1963 nominated the first of these as the lectotype. His collaborator Ferdinand Bauer, the botanist and master illustrator, produced artworks to accompany Brown's descriptions, but these were not published until 1838. In 1983 a species of palm from Somalia was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Islands
Most of the Caribbean countries are islands in the Caribbean Sea, with only a few in inland lakes. The largest islands include Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica and Puerto Rico. Some of the smaller islands are referred to as a ''rock'' or ''reef.'' ''Islands are listed in alphabetical order by sovereign state. Islands with coordinates can be seen on the map linked to the right.'' Antigua and Barbuda There are 54 islands in Antigua and Barbuda. There are three main islands, the two populated islands (Antigua and Barbuda) and Redonda. There are 51 off-shore islands. The islands of the country of Antigua and Barbuda include: *Antigua, , Northeast Marine Management Area * Jenny Island, Antigua, Jenny Island * Exchange Island * Rabbit Island, Antigua, Rabbit Island * Lobster Island * Long Island, Antigua, Long Island * Maiden Island, Antigua (North West), Maiden Island * Rat Island, Antigua and Barbuda, Rat Island * Little Bird Island, Antigua, Little Bird Island * Hell's Gate Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially in the soils. Wetlands form a transitional zone between waterbodies and dry lands, and are different from other terrestrial or aquatic ecosystems due to their vegetation's roots having adapted to oxygen-poor waterlogged soils. They are considered among the most biologically diverse of all ecosystems, serving as habitats to a wide range of aquatic and semi-aquatic plants and animals, with often improved water quality due to plant removal of excess nutrients such as nitrates and phosphorus. Wetlands exist on every continent, except Antarctica. The water in wetlands is either freshwater, brackish or saltwater. The main types of wetland are defined based on the dominant plants and the source of the water. For example, ''marshes'' ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native species that become harmful to their native environment after human alterations to its food web. Since the 20th century, invasive species have become serious economic, social, and environmental threats worldwide. Invasion of long-established ecosystems by organisms is a natural phenomenon, but human-facilitated introductions have greatly increased the rate, scale, and geographic range of invasion. For millennia, humans have served as both accidental and deliberate dispersal agents, beginning with their earliest migrations, accelerating in the Age of Discovery, and accelerating again with the spread of international trade. Notable invasive plant species include the kudzu vine, giant hogweed (''Heracleum mantegazzianum''), Japanese knotw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal Environmental factor, factors. External factors—including climate—control the ecosystem's structure, but are not influenced by it. By contrast, internal factors control and are controlled by ecosystem processes; these include decomposition, the types of species present, root competition, shading, disturbance, and succession. While external factors generally determine which Resource (biology), resource inputs an ecosystem has, their availability within the ecosystem is controlled by internal factors. Ecosystems are wikt:dynamic, dynamic, subject to periodic disturbances and always in the process of recovering from past disturbances. The tendency of an ecosystem to remain clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, growing where it conflicts with human preferences, needs, or goals.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. Plants with characteristics that make them hazardous, aesthetically unappealing, difficult to control in managed environments, or otherwise unwanted in agriculture, farm land, Orchard, orchards, gardens, lawns, Park, parks, recreational spaces, residential and industrial areas, may all be considered weeds.Holzner, W., & Numata, M. (Eds.). (2013). ''Biology and ecology of weeds'' (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media. The concept of weeds is particularly significant in agriculture, where the presence of weeds in fields used to grow crops may cause major losses in yields. Invasive species, plants introduced to an environment where their presence negatively impacts the overall functioning and biodiversity of the ecosystem, may also sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
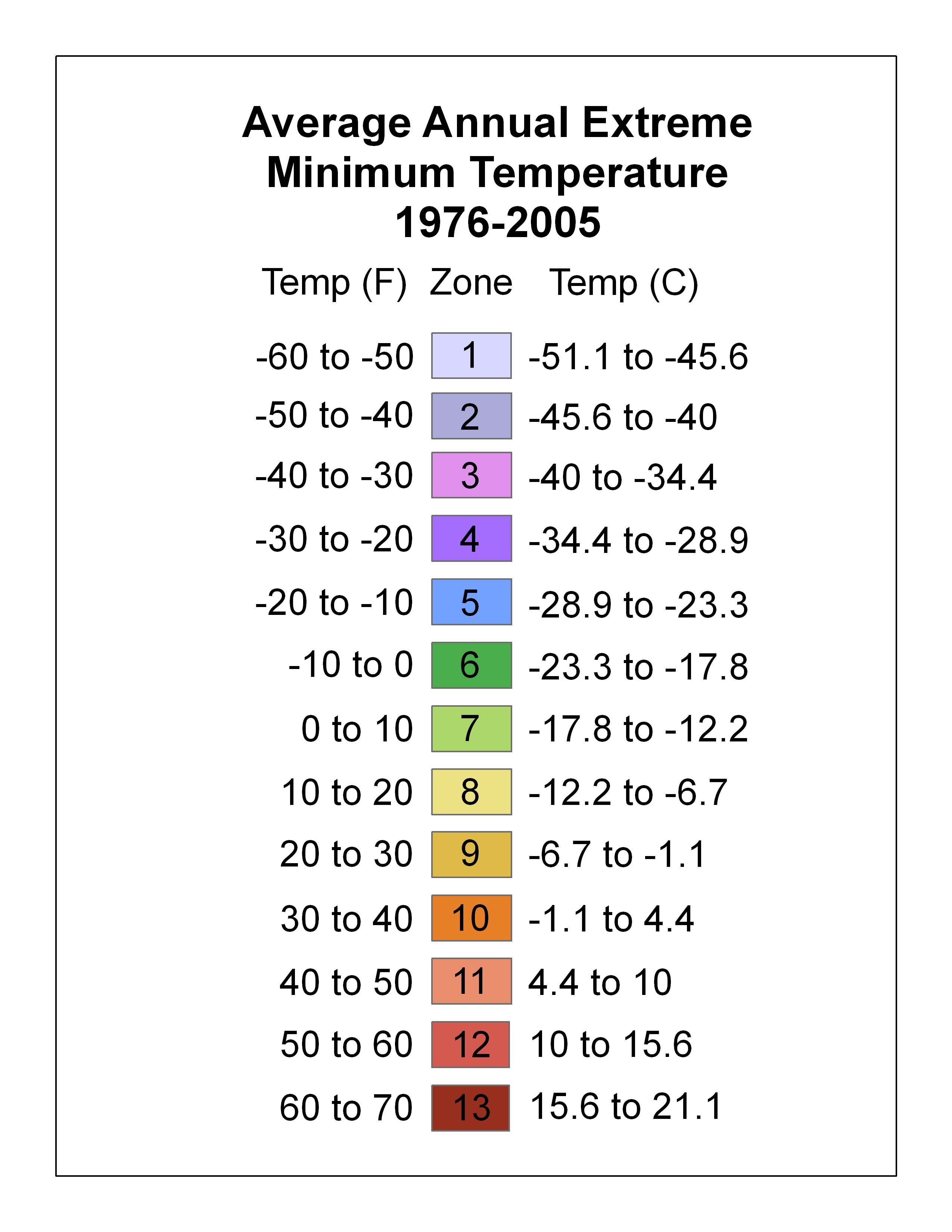
USDA Hardiness Zones
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. A plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of . Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. However, some confusion can exist in discussing buildings and HVAC, where "climate zone" can refer to the International Energy Conservation Code zones, where Zone 1 is warm and Zone 8 is cold. Other hardiness rating schemes have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornamental Tree
Ornamental plants or ''garden plants'' are plants that are primarily grown for their beauty but also for qualities such as scent or how they shape physical space. Many flowering plants and garden varieties tend to be specially bred cultivars that improve on the original species in qualities such as color, shape, scent, and long-lasting blooms. There are many examples of fine ornamental plants that can provide height, privacy, and beauty for any garden. These ornamental perennial plants have seeds that allow them to reproduce. One of the beauties of ornamental grasses is that they are very versatile and low maintenance. Almost all types of plant have ornamental varieties: trees, shrubs, climbers, grasses, succulents, aquatic plants, herbaceous perennials and annual plants. Non-botanical classifications include houseplants, bedding plants, hedges, plants for cut flowers and ''foliage plants''. The cultivation of ornamental plants comes under floriculture and tree nurseries, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |