|
Chinese Constellation
Traditional Chinese astronomy has a system of dividing the celestial sphere into asterisms or constellations, known as "officials" ( Chinese ''xīng guān''). The Chinese asterisms are generally smaller than the constellations of Hellenistic tradition. The Song dynasty (13th-century) Suzhou planisphere shows a total of 283 asterisms, comprising a total of 1,565 individual stars. The asterisms are divided into four groups, the Twenty-Eight Mansions (, ''Èrshíbā Xiù'') along the ecliptic, and the Three Enclosures of the northern sky. The southern sky was added as a fifth group in the late Ming dynasty based on European star charts, comprising an additional 23 asterisms. The Three Enclosures (, ''Sān Yuán'') include the Purple Forbidden Enclosure, which is centered on the north celestial pole and includes those stars which could be seen year-round,Needham, J.Astronomy in Ancient and Medieval China. ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London''. Ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzhou Star Cartography
Suzhou is a major prefecture-level city in southern Jiangsu province, China. As part of the Yangtze Delta megalopolis, it is a major economic center and focal point of trade and commerce. Founded in 514 BC, Suzhou rapidly grew in size by the Eastern Han dynasty, mostly due to emigration from Northern and southern China, northern China. From the 10th century onwards, it has been an important economic, cultural, and commercial center, as well as the largest non-capital city in the world, until it was overtaken by Shanghai. Since Chinese economic reform, economic reforms began in 1978, Suzhou attained GDP growth rates of about 14% in 35 years. In 2023, Suzhou had 5 million registered residents. Suzhou is listed as the 48th List of cities by scientific output, cities by scientific output according to the Nature Index 2022. The city is home to universities, including Soochow University (Suzhou), Soochow University, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Xi'an Jiaotong–Liverp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Civilisation In China
''Science and Civilisation in China'' (1954–present) is an ongoing series of books about the history of science and technology in China published by Cambridge University Press. It was initiated and edited by British historian Joseph Needham (1900–1995). Needham was a well-respected scientist before undertaking this encyclopedia and was even responsible for the "S" in UNESCO. To date there have been seven volumes in twenty-seven books. The series was on the Modern Library Board's 100 Best Nonfiction books of the 20th century. Needham's work was the first of its kind to praise Chinese scientific contributions and provide their history and connection to global knowledge in contrast to eurocentric historiography. By asking his grand questions: why did modern science not develop in China, and why China was technologically superior to the West prior to the 16th century, Needham’s ''Science and Civilisation in China'' is also recognized as one of the most influential works in stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Xian (astronomer)
Wuxian () was a Chinese shaman, or Wu () who practiced divination, prayer, sacrifice, rainmaking, and healing in Chinese traditions dating back over 3,000 years. Wuxian lived in the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC) of China, and served under king Tai Wu. He is considered one of the main ancient Chinese astronomers alongside more historical figures such as Gan De and Shi Shen, the latter two of whom lived during the Warring States (403–221 BC).Peng, Yoke Ho (2000). Li, Qi and Shu: An Introduction to Science and Civilization in China. Courier Dover Publications. He has also been represented as one of the "Three Astronomical Traditions" on the Dunhuang map which was made during the Tang dynasty (618–907). Whitfield, Susan. 004 004, 0O4, O04, OO4 may refer to: * 004, fictional British 00 Agent * 0O4, Corning Municipal Airport (California) * O04, the Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation * Abdul Haq Wasiq, Guantanamo detainee 004 * Junkers Jumo 004 turbojet engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gan De
Gan De (; fl. 4th century BC), also known as the Lord Gan (Gan Gong), was an ancient Chinese astronomer and astrologer born in the State of Qi. Along with Shi Shen, he is believed to be the first in history known by name to compile a star catalogue, preceded by the anonymous authors of the early Babylonian star catalogues and followed by the Greek Hipparchus who is the first known in the Western tradition of Hellenistic astronomy to have compiled a star catalogue. He also made observations of the planets, particularly Jupiter. His writings are lost, but some of his works' titles and fragments quoted from them are known from later texts. Gan De may have been the first to describe one of the Galilean moons of Jupiter, usually invisible without the aid of telescopes. In the 20th century, a fragment of Gan's work, in a later compilation of astronomical texts, was identified by Xi Zezong as describing a naked-eye observation of either of the two largest and brightest moons, Ganym ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi Shen
Shi Shen (, fl. 4th century BC) was a Chinese astronomer and astrologer. He was a contemporary of Gan De born in the State of Wei, also known as the Shi Shenfu. Observations Shi is credited with positioning the 121 stars found in the preserved texts. Shen also made the earliest surviving deliberate sunspot observation, sometimes erroneously credited to Gan De. He assumed that these spots were eclipses that began at the center of the Sun and spread outward. Although he was wrong, he recognised the spots for what they were – solar phenomena. His works included the 8-volume ''The rocks of Space'', the one-volume ''Celestial Map'' and the one-volume ''Star Catalogue of Shi''. The latter two are now believed to be written by his school followers. Most of his works did not survive intact, but a few of his crucial writings were preserved in the '' Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era''. Books Shi Shen wrote the ''Astronomy'' (石氏天文, ''Shishi Tianwen''), later known as ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunhuang Star Chart
The Dunhuang map or Dunhuang Star map is one of the first known graphical representations of stars from ancient Chinese astronomy, dated to the Tang dynasty (618–907). Before this map, much of the star information mentioned in historical Chinese texts had been questioned.Whitfield, Susan. 004(2004)''The Silk Road: Trade, Travel, War and Faith''. British Library Staff. Serindia Publications. . The map provides a graphical verification of the star observations, and are part of a series of pictures on one of the Dunhuang manuscripts. The astronomy behind the map is explained in an educational resource posted on the website of the International Dunhuang Project, where much of the research on the map has been done. The Dunhuang Star map is to date the world's oldest complete preserved star atlas. History Early in 1900s (decade), a walled-up cave containing a cache of manuscripts was discovered by Chinese Taoist Wang Yuan-lu in the Mogao Caves. The scroll with the star c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatise On Astrology Of The Kaiyuan Era
The ''Great Tang Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era'', also called the ''Kaiyuan Star Observations''Deng, Yinke. 005(2005). Chinese Ancient Inventions. (''Kaiyuan Zhanjing''),Needham, Volume 3, 109. is a Chinese astrology encyclopedia compiled by Gautama Siddha and a team of scholars between 714 and 724 AD during the Kaiyuan era of the Tang dynasty. The book is divided into 120 volumes and consists of about 600,000 words. The ''Kaiyuan Zhanjing'' incorporates many fragments of other works, including the star catalogues of Shi Shen and Gan De and a translated version of Indian ''Navagraha'' calendar at chapter 104. It may have made use of the ''Yisizhan'', compiled by Li Chunfeng around 645. Aryabhata's sine table by the eponymous Indian astronomer, was also translated into the ''Kaiyuan Zhanjing''. The ''Kaiyuan Zhanjing'' ceased to be copied in the 10th century, but was received attention from the scholar Cheng Mingshan in 1616 and was later included in the Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Maps
Chinese star maps ( zh, s=星图, t=星圖, p=xīngtú) are usually directional or graphical representations of Chinese astronomy, Chinese astronomical alignments. Throughout the history of China, numerous star maps have been recorded. This page is intended to list or show the best available version of each star map. Star catalogs are also listed. For academic purposes, related star maps found in East Asia outside China are also listed. List of star maps See also * Chinese constellations * Traditional Chinese star names * Dunhuang Star Chart References External links * *https://web.archive.org/web/20080117162040/http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/StarShine/HKSkyMap/e_starshine_hkskymap.htm *{{cite web, url=http://www.tsm.toyama.toyama.jp/curators/aroom/edo/se-bunrui.htm, title=富山市科学博物館 Toyama Science Museum, publisher=tsm.toyama.toyama.jp, accessdate=October 10, 2015, archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080322033710/http://www.tsm.toyama.toyama.jp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
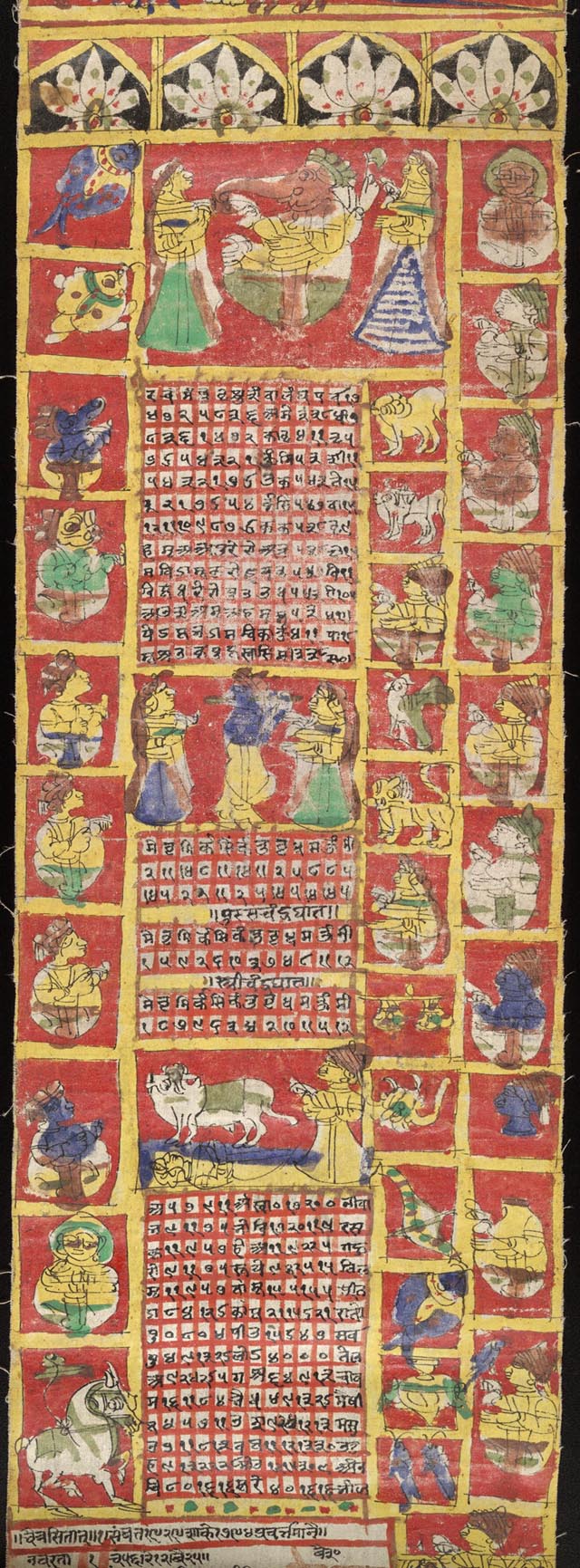
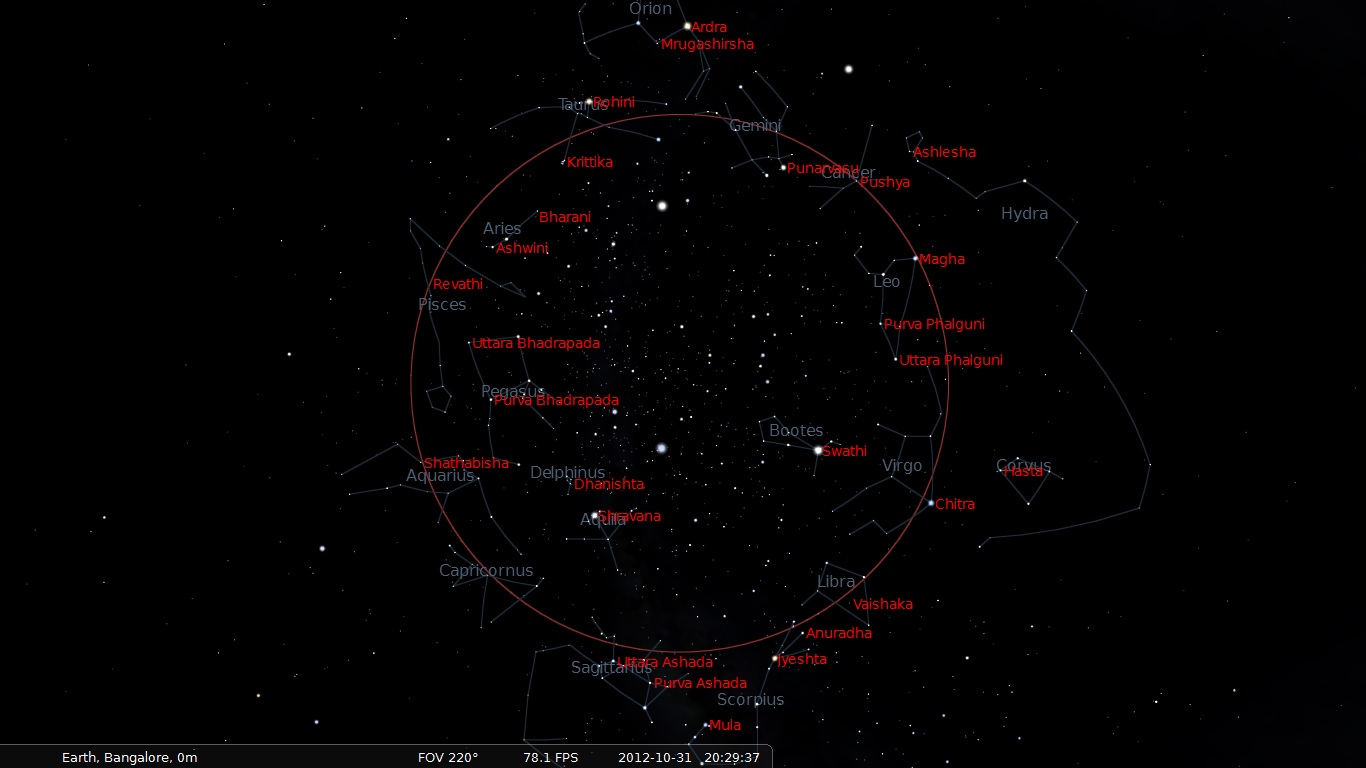
Nakshatra
Nakshatra () is the term for Lunar mansion in Hindu astrology and Buddhist astrology. A nakshatra is one of 27 (sometimes also 28) sectors along the ecliptic. Their names are related to a prominent star or asterisms in or near the respective sectors. In essence (in Western astronomical terms), a nakshatra simply is a constellation. Every nakshatra is divided into four ''padas'' ( "steps"). The starting point for the nakshatras according to the ''Vedas'' is "Krittika" (it has been argued, because the Pleiades may have started the year at the time the ''Vedas'' were compiled, presumably at the vernal equinox), but, in more recent compilations, the start of the nakshatras list is the point on the ecliptic directly opposite the star Spica, called ''Chitrā'' in Sanskrit. This translates to Ashwinī, a part of the modern constellation of Aries. These compilations, therefore, may have been compiled during the centuries when the sun was passing through Aries at the time of the ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Astronomy
Astronomy has a long history in the Indian subcontinent, stretching from History of India, pre-historic to History of India (1947–present), modern times. Some of the earliest roots of Indian astronomy can be dated to the period of Indus Valley civilisation or earlier. Astronomy later developed as a discipline of Vedanga, or one of the "auxiliary disciplines" associated with the study of the Vedas dating 1500 BCE or older. The oldest known text is the ''Vedanga Jyotisha'', dated to 1400–1200 BCE (with the extant form possibly from 700 to 600 BCE). Indian astronomy was influenced by Greek astronomy beginning in the 4th century BCEHighlights of Astronomy, Volume 11B: As presented at the XXIIIrd General Assembly of the IAU, 1997. Johannes Andersen Springer, 31 January 1999 – Science – 616 pages. p. 72/ref>Babylon to Voyager and Beyond: A History of Planetary Astronomy. David Leverington. Cambridge University Press, 29 May 2010 – Science – 568 pages. p. 4/ref>Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sargon Of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; ; died 2279 BC), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly uncertain, depending entirely on the (conflicting) regnal years given in the various copies of the Sumerian King List, specifically the uncertain duration of the Gutian dynasty. The added regnal years of the Sargonic and the Gutian dynasties have to be subtracted from the accession of Ur-Nammu of the Third Dynasty of Ur, which is variously dated to either 2047 BC ( Short Chronology) or 2112 BC ( Middle Chronology). An accession date of Sargon of 2334 BC assumes: (1) a Sargonic dynasty of 180 years (fall of Akkad 2154 BC), (2) a Gutian interregnum of 42 years and (3) the Middle Chronology accession year of Ur-Nammu (2112 BC). He is sometimes identified as the first person in recorded history to rule over an empire. He was the founder of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |