|
Children Of Muhammad
The common view is that the Prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad had three sons, named Abd Allah ibn Muhammad, Abd Allah, Ibrahim ibn Muhammad, Ibrahim, and Qasim ibn Muhammad, Qasim, and four daughters, named Fatima, Ruqayya bint Muhammad, Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum bint Muhammad, Umm Kulthum, and Zainab bint Muhammad, Zaynab. The children of Muhammad are said to have been born to his first wife Khadija bint Khuwaylid, except his son Ibrahim, who was born to Maria al-Qibtiyya. None of Muhammad's sons reached adulthood, but he had an adult foster son, Zayd ibn Harithah. Daughters of Muhammad all reached adulthood but only Fatima outlived her father. Citing, among others, the advanced age of Khadija, some Twelver Shi'ism, Twelver Shia sources contend that Fatima was the only biological daughter of Muhammad, as she is known to have enjoyed a closer relationship with Muhammad, compared to Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum, and Zaynab. That Fatima was the only biological daughter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qasim Ibn Muhammad
Al-Qāsim ibn Muḥammad () was the eldest of the sons of Muhammad and Khadija bint Khuwaylid. He died in 601 CE (before the declaration of his father's prophethood in 609), after his third birthday, and is buried in Jannat al-Mu'alla cemetery, Mecca. Sunan ibn Majah, Ibn Majah mentioned that he died before completing his milk age.''Ibn Majah''; Chapter:Funerals, 1512. Siblings *Abd Allah ibn Muhammad *Ibrahim ibn Muhammad *Zainab bint Muhammad *Ruqayya bint Muhammad *Umm Kulthum bint Muhammad *Fatima, Fatima al-Zahra References Bibliography * External links The Tribe of Quraish Children of Muhammad 598 births 601 deaths Arab Muslims 6th-century Arab people People from Mecca Burials at Jannat al-Mu'alla Child deaths from disease {{Islam-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God in Abrahamic religions, God of Abraham (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the last Islamic prophet. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Tawrat (Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Injeel (Gospel). These earlier revelations are associated with Judaism and Christianity, which are regarded by Muslims as earlier versions of Islam. The majority of Muslims also follow the teachings and practices attributed to Muhammad (''sunnah'') as recorded in traditional accounts (hadith). With an estimated population of almost 2 billion followers, Muslims comprise around 26% of the world's total population. In descending order, the percentage of people who identify as Muslims on each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ( companions in Sunni Islam, Ahl al-Bayt in Shiite Islam). Each hadith is associated with a chain of narrators ()—a lineage of people who reportedly heard and repeated the hadith from which the source of the hadith can be traced. The authentication of hadith became a significant discipline, focusing on the ''isnad'' (chain of narrators) and '' matn'' (main text of the report). This process aimed to address contradictions and questionable statements within certain narrations. Beginning one or two centuries after Muhammad's death, Islamic scholars, known as muhaddiths, compiled hadith into distinct collections that survive in the historical works of writers from the second and third centuries of the Muslim era ( 700−1000 CE). For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the original Anno Domini (AD) and Before Christ (BC) notations used for the same calendar era. The two notation systems are numerically equivalent: " CE" and "AD " each describe the current year; "400 BCE" and "400 BC" are the same year. The expression can be traced back to 1615, when it first appears in a book by Johannes Kepler as the (), and to 1635 in English as " Vulgar Era". The term "Common Era" can be found in English as early as 1708, and became more widely used in the mid-19th century by Jewish religious scholars. Since the late 20th century, BCE and CE have become popular in academic and scientific publications on the grounds that BCE and CE are religiously neutral terms. They have been promoted as more sensitive to non-Christia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umamah Bint Abi Al-As
Umāma bint Abī al-ʿĀṣ ibn al-Rabīʿ (), was a granddaughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Khadija, via their daughter Zaynab, and is thus also known as ''Umāma bint Zaynab'' (). Muhammad was her maternal grandfather, and thus she is a member of his Ahl al-Bayt. She is also numbered among the Companions of the Prophet. Biography She was the daughter of Abu al-As ibn al-Rabi', who married Muhammad's eldest daughter Zaynab. She had one sibling, Ali. Her maternal aunts were Muhammad's daughters Ruqayya, Umm Kulthum and Fatima. When Umama was a small child, Muhammad used to carry her on his shoulder while he prayed. He used to put her down to prostrate and then pick her up again as he rose. Muhammad once promised to give an onyx necklace to "her whom I love best." His wives expected him to give it to Aisha, but he presented it to Umama. On a different occasion, he gave her a gold ring that had arrived from the Emperor of Abyssinia. Her aunt Fatima requested her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Ibn Abi Al-As
ʿAlī ibn Abī al-ʿĀṣ or ʿAlī ibn Zaynab bint Muḥammad was a companion and a grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ... through his eldest daughter. Ali was born to Abu al-As ibn al-Rabi' and Zaynab bint Muhammad, and his sister was Umamah bint Zaynab. Ali ibn Zaynab is reported to have died in infancy in 630 CE (9 AH). Family tree * * indicates that the marriage order is disputed * Note that direct lineage is marked in bold. External links Holy prophet's life Companions of the Prophet 630s deaths Family of Muhammad Year of birth unknown Burials at Jannat al-Baqī {{Islam-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abd Allah Ibn Uthman
Abd Allah ibn Uthman (; ), was the son of the third caliph Uthman () and Ruqayya bint Muhammad. Born in Abyssinia, Abd Allah is believed by Sunni Muslims to be the first grandson of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Biography By 615 Ruqayya was married to a prominent Muslim, Uthman ibn Affan. She accompanied him on the first Migration to Abyssinia,Ibn Saad/Bewley p. 25.Tabari/Landau-Tasseron p. 162. where she suffered a miscarriage. They returned to Abyssinia in 616, and there Ruqayya gave birth to a son, Abdallah in 619. His parents, Uthman and Ruqayya were among those who returned to Mecca in 619. Uthman emigrated to Medina Medina, officially al-Madinah al-Munawwarah (, ), also known as Taybah () and known in pre-Islamic times as Yathrib (), is the capital of Medina Province (Saudi Arabia), Medina Province in the Hejaz region of western Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, ... in 622, and Ruqayya followed him later. Muhammad asked Usama, "Have you ever seen a more handsome coupl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Companions Of The Prophet
The Companions of the Prophet () were the Muslim disciples and followers of the Islamic prophet Muhammad who saw or met him during his lifetime. The companions played a major role in Muslim battles, society, hadith narration, and governance during and after the life of Muhammad. The era of the companions began following the death of Muhammad in 632 CE, and ended in 110 AH (728 CE) when the last companion Abu al-Tufayl died. Later Islamic scholars accepted their testimony of the words and deeds of Muhammad, the occasions on which the Quran was revealed and other important matters in Islamic history and practice. The testimony of the companions, as it was passed down through trusted chains of narrators ('' asānīd''), was the basis of the developing Islamic tradition. From the traditions (''hadith'') of the life of Muhammad and his companions are drawn the Muslim way of life (''sunnah''), the code of conduct (''sharia'') it requires, and Islamic jurisprudence (''fiqh''). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-As Ibn Al-Rabi'
Abū al-ʿĀṣ ibn al-Rabīʿ (, died in February, AD 634), was a son-in-law and Companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. His original name was said to have been Hushaym or Yasser. Family He was the son of Hala bint Khuwaylid.Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir'' vol. 8. Translated by Bewley, A. (1995). ''The Women of Madina'', p. 21. London: Ta-Ha Publishers. His legal father was Al-Rabi ibn Abd al-Uzza of the Abdshams clan of the Quraysh tribe.Ibn Hajar, ''Al-Isaba'' vol. 7 #10176. He became a successful merchant and was considered an important person in Mecca.Muhammad ibn Ishaq. ''Sirat Rasul Allah''. Translated by Guillaume, A. (1955). ''The Life of Muhammad'', p. 313. Oxford: Oxford University Press. His aunt Khadija regarded him as her son, and he frequently visited her home. In due course Khadija asked her husband Muhammad to find him a wife. Muhammad gave Abu al-As their eldest daughter, Zaynab, apparently with some reluctance. Later, however, he sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharif
Sharīf or Sherif (, 'noble', 'highborn'), also spelled shareef, feminine sharīfa (), plural ashrāf (), shurafāʾ (), or (in the Maghreb) shurfāʾ, is a title used to designate a person descended, or claiming to be descended, from the family of the Islamic prophet Muhammad ( ). It may be used in three senses: #In the broadest sense, it refers to any descendant of Muhammad's great-grandfather Hashim (the Banu Hashim or Hashimites, already in Muhammad's day an established clan within the Meccan tribe of the Quraysh), including all descendants of Muhammad's paternal uncles Abu Talib (the Talibids) and al-Abbas (the Abbasids).. #More often, it refers to a descendant of Ali, a son of Abu Talib and a paternal cousin of Muhammad (the Alids), especially but not exclusively through Ali's marriage with Muhammad's daughter Fatima (the Fatimids). In the sense of descendants of Fatima and Ali (the most common one), the term effectively refers to all descendants of Muhammad. # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayyid
''Sayyid'' is an honorific title of Hasanid and Husaynid lineage, recognized as descendants of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his daughter Fatima and Ali's sons Hasan ibn Ali, Hasan and Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn. The title may also refer to the descendants of the family of the Bani Hashim through the Prophet’s great-grandfather Hashim ibn Abd Manaf, Hashim, and others including Hamza ibn Abd al-Muttalib, Hamza, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib, Abbas, Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib, Abu Talib, and Asad ibn Hashim. Etymology A few Arabic, Arabic language experts state that it has its roots in the word ''al-asad'' , meaning "lion", probably because of the qualities of valor and leadership. The word is derived from the verb sāda, meaning to rule. The title seyyid/sayyid existed before Islam, however not in light of a specific descent, but as a meritocratic sign of respect. Hans Wehr's ''Dictionary of Modern Written Arabic'' defines seyyid as a translation for master, chief, sov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
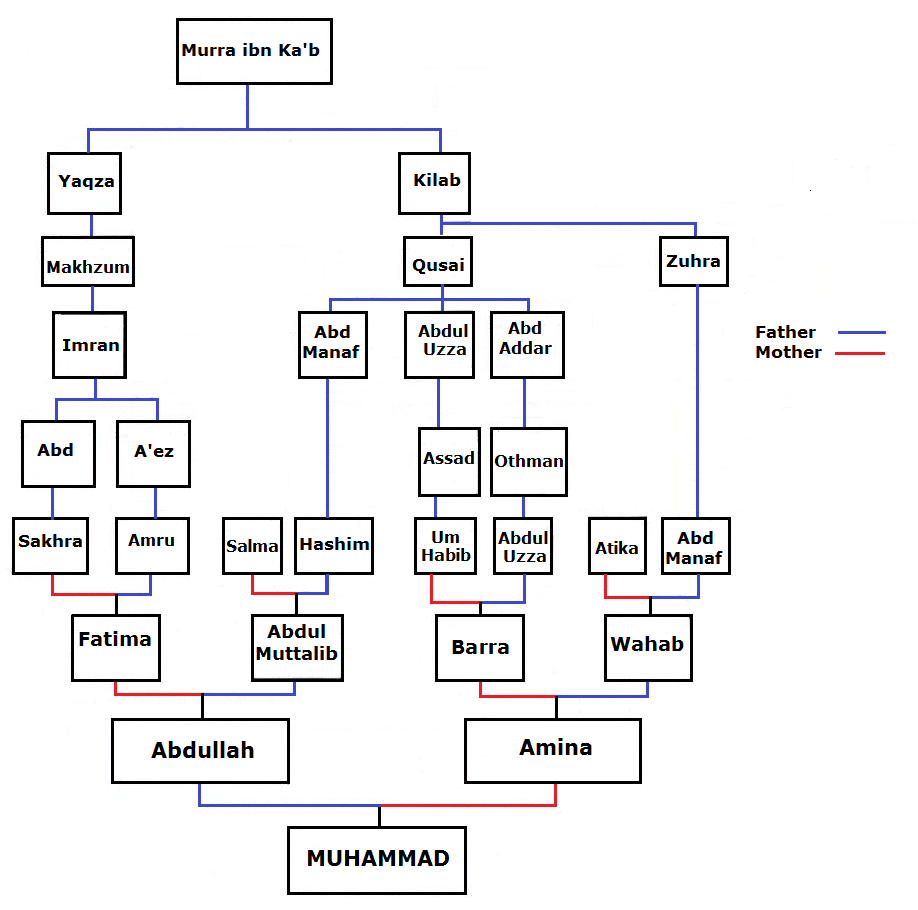
Family Tree Of Muhammad
This family tree is about the relatives of the Islamic prophet Muhammad as a family member of the family of Hashim and the Quraysh tribe which is ‘Adnani. "The ‘arabicised or arabicising Arabs’, on the contrary, are believed to be the descendants of Ishmael through Adnan, but in this case the genealogy does not match the Biblical line exactly. The label ‘arabicised’ is due to the belief that Ishmael spoke Hebrew until he got to Mecca, where he married a Yemeni woman and learnt Arabic. Both genealogical lines go back to Sem, son of Noah, but only Adnanites can claim Abraham as their ascendant, and the lineage of Mohammed, the Seal of Prophets (khatim al-anbiya'), can therefore be traced back to Abraham. Contemporary historiography unveiled the lack of inner coherence of this genealogical system and demonstrated that it finds insufficient matching evidence; the distinction between Qahtanites and Adnanites is even believed to be a product of the Umayyad Age, when the war o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |