|
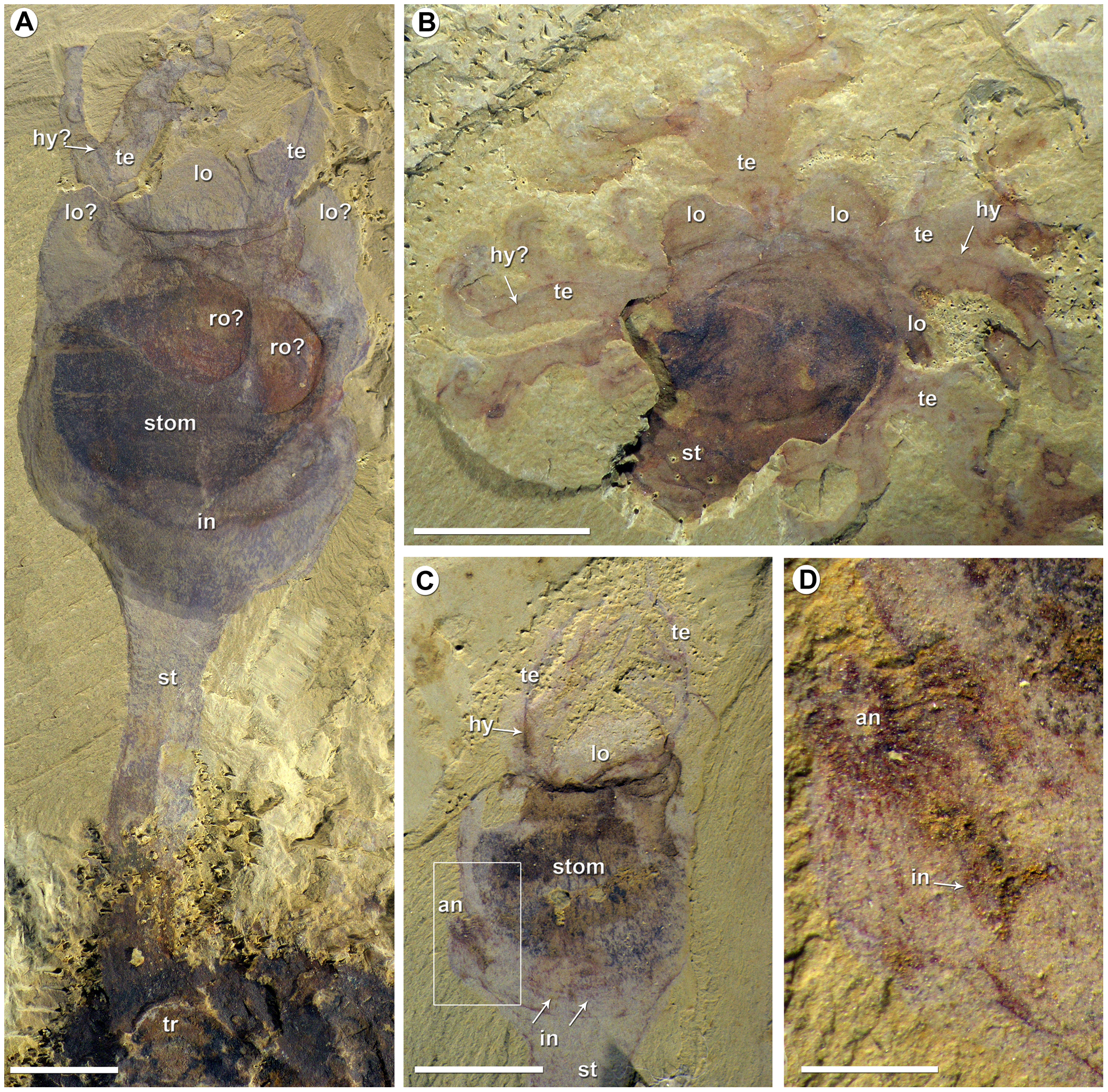
Cheungkongella Ancestralis
''Cheungkongella'' is a fossil organism from the lower Cambrian Chengjiang lagerstatte, the affinity of which has been the subject of debate. It was announced as a "probable" tunicate while noting the lack of definitive Cambrian fossils from that group. However, this affinity was later disputed in a paper announcing the discovery of ''Shankouclava'', also from Chengjiang, as the oldest known tunicate. ''Cheungkongella'' has been accepted as a distinct taxon and possible tunicate by multiple workers not involved in its discovery, but the dispute remains unresolved. Etymology "Cheungkong" is "a metaphor of China" and honors the Cheungkong Scholars Programme's support for the work leading to the fossil's discovery. "Ancestralis" refers to the fossil's possible primitive taxonomic position. Description ''Cheungkongella'' has a club-shaped body similar to the extant ascidian '' Styela'', with a bucket-shaped main body with thick, tapering stem beneath it. A large oral siphon wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Stage 3
Cambrian Stage 3 is the still unnamed third stage of the Cambrian. It succeeds Cambrian Stage 2 and precedes Cambrian Stage 4, although neither its base nor top have been formally defined. The plan is for its lower boundary to correspond approximately to the first appearance of trilobites, about million years ago, though the globally asynchronous appearance of trilobites warrants the use of a separate, globally synchronous marker to define the base. The upper boundary and beginning of Cambrian Stage 4 is informally defined as the first appearance of the trilobite genera ''Olenellus'' or ''Redlichia'' around million years ago. Naming The International Commission on Stratigraphy has not officially named the 3rd stage of the Cambrian. The stage approximately corresponds to the "Atdabanian", which is used by geologists working in Siberia. Biostratigraphy The oldest trilobite known is ''Lemdadella'' which appears at the beginning of the ''Fallotaspis'' zone. The Cambrian radiation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheungkongella And Phlogites
''Cheungkongella'' is a fossil organism from the lower Cambrian Chengjiang lagerstatte, the affinity of which has been the subject of debate. It was announced as a "probable" tunicate while noting the lack of definitive Cambrian fossils from that group. However, this affinity was later disputed in a paper announcing the discovery of ''Shankouclava'', also from Chengjiang, as the oldest known tunicate. ''Cheungkongella'' has been accepted as a distinct taxon and possible tunicate by multiple workers not involved in its discovery, but the dispute remains unresolved. Etymology "Cheungkong" is "a metaphor of China" and honors the Cheungkong Scholars Programme's support for the work leading to the fossil's discovery. "Ancestralis" refers to the fossil's possible primitive taxonomic position. Description ''Cheungkongella'' has a club-shaped body similar to the extant ascidian '' Styela'', with a bucket-shaped main body with thick, tapering stem beneath it. A large oral siphon wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2001
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Though the fossil record is incomplete, numerous studies have demonstrated that there is enough information available to give a good understanding of the pattern of diversification of life on Earth. In addition, the record can predict and fill gaps such as the discovery of '' Tiktaalik'' in the arctic of Canada. Paleontology includes the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are sometimes considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Chordate Genera
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing having spread to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. It is based on an old conception of history that without written records there could be no history. The most common conception today is that history is based on evidence, however the concept of prehistory hasn't been completely discarded. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunicate Genera
Tunicates are marine invertebrates belonging to the subphylum Tunicata ( ). This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. Despite their simple appearance and very different adult form, their close relationship to the vertebrates is certain. Both groups are chordates, as evidenced by the fact that during their mobile larval stage, tunicates possess a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail, and an endostyle. They resemble a tadpole. Tunicates are the only chordates that have lost their myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the seriation of the gill slits. However, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals, but others replicate by budding and become colonies, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambroernid
The Cambroernida are a clade of Paleozoic animals with coiled bodies and filamentous tentacles. They include a number of early to middle Paleozoic (Cambrian to Devonian) genera noted as "bizarre" or "orphan" taxa, meaning that their affinities with other animals, living or extinct, have long been uncertain. While initially defined as an "informal stem group," later work with better-preserved fossils has strengthened the argument for Cambroernida as a monophyletic clade. Description Cambroernids encompass three particular types of enigmatic animals first appearing in the Cambrian: ''Herpetogaster'' (the type genus), ''Phlogites'', and the Eldonioidea. They are united by a set of common features including at least one pair of bifurcated or divided oral tentacles, and a large stomach and narrower intestine enclosed together in a clockwise-coiled sac. Taxonomy and evolution Body coiling increased throughout this group's evolution. ''Herpetogaster'' has a segmented and clockwise-cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophophorate
The Lophophorata (also called Tentaculata; not to be confused with Tentaculata Eschscholtz 1825, a class within the Ctenophora) are a Lophotrochozoan clade consisting of the Brachiozoa and the Bryozoa. They have a lophophore. Molecular phylogenetic analyses suggest that lophophorates are protostomes, but on morphological grounds they have been assessed as deuterostomes. Fossil finds of the "tommotiid" ''Wufengella'' suggest that they evolved from worm-like animals that resembled annelids The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario .... References {{Protostome-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlogites
''Phlogites'' is a member of the extinct ambulacrarian stem group Cambroernida, occupying an intermediate position between the basal ''Herpetogaster'' and the more derived Eldonioidea. It is known from the Cambrian, Lower Cambrian Haikou Chengjiang County, Chengjiang deposits of China. Description Phlogites was a cup-shaped animal with a branching tentacular feeding system leading to a dextrally coiled gut with a lateral anus. Sources differ as to the number of tentacles, with two, three, three or five, or four or five tentacles said to be on the anterior part of the calyx (anatomy), calyx. Smooth semi-circular lobes are present between the tentacles. Compared to the earlier-diverging cambroernid ''Herpetogaster'', ''Phlogites'' lacked segmentation and had a more massive stolon that is contiguous with the body. The coiling present in the external form of ''Herpetogaster'' became internal, except for a small lobate extension with the anus opening laterally. The tentacles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascidiacea
Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians or sea squirts, is a paraphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer test or "tunic" made of the polysaccharide cellulose. Ascidians are found all over the world, usually in shallow water with salinities over 2.5%. While members of the Thaliacea (salps, doliolids and pyrosomes) and Appendicularia (larvaceans) swim freely like plankton, sea squirts are sessile animals after their larval phase: they then remain firmly attached to their substratum, such as rocks and shells. There are 2,300 species of ascidians and three main types: solitary ascidians, social ascidians that form clumped communities by attaching at their bases, and compound ascidians that consist of many small individuals (each individual is called a zooid) forming large colonies. Sea squirts feed by taking in water through a tube, the oral siphon. The water enters the mouth and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovician Period 486.85 Ma. Most of the continents lay in the southern hemisphere surrounded by the vast Panthalassa Ocean. The assembly of Gondwana during the Ediacaran and early Cambrian led to the development of new convergent plate boundaries and continental-margin arc magmatism along its margins that helped drive up global temperatures. Laurentia lay across the equator, separated from Gondwana by the opening Iapetus Ocean. The Cambrian marked a profound change in life on Earth; prior to the Period, the majority of living organisms were small, unicellular and poorly preserved. Complex, multicellular organisms gradually became more common during the Ediacaran, but it was not until the Cambrian that fossil diversity seems to rapidly incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alimentary Canal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore ( osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the human mouth, mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its structure varies across species. The pharynx carries food to the esophagus and air to the larynx. The flap of cartilage called the epiglottis stops food from entering the larynx. In humans, the pharynx is part of the Digestion, digestive system and the conducting zone of the respiratory system. (The conducting zone—which also includes the nostrils of the Human nose, nose, the larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchi, and bronchioles—filters, warms, and moistens air and conducts it into the lungs). The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx (hypopharynx). In humans, two sets of pharyngeal muscles form the pharynx and determine the shape of its lumen (anatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |