|
Cheque Truncation System
Cheque Truncation System (CTS) or Image-based Clearing System (ICS), in India, is a project of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), commenced in 2010, for faster clearing of cheques. CTS is based on a cheque truncation or online image-based cheque clearing system where cheque images and magnetic ink character recognition (MICR) data are captured at the collecting bank branch and transmitted electronically. Cheque truncation means stopping the flow of the physical cheques issued by a drawer to the drawee branch. The physical instrument is truncated at some point in route to the drawee branch and an electronic image of the cheque is sent to the drawee branch along with the relevant information like the MICR fields, date of presentation, presenting banks etc. This would eliminate the need to move the physical instruments across branches, except in exceptional circumstances, resulting in an effective reduction in the time required for payment of cheques, the associated cost of transit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Reserve Bank Of India
Reserve Bank of India, abbreviated as RBI, is the central bank of the Republic of India, and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system and Indian rupee, Indian currency. Owned by the Ministry of Finance (India), Ministry of Finance, Government of India, Government of the Republic of India, it is responsible for the control, issue, and maintenance of the supply of the Indian rupee. It also manages the country's main payment systems and works to promote its economic development. The RBI, along with the Indian Banks' Association, established the National Payments Corporation of India to promote and regulate the payment and settlement systems in India. Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran, Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran (BRBNM) is a specialised division of RBI through which it prints and mints Indian currency notes (INR) in two of its currency printing presses located in Mysore (Karnataka; Southern India) and Salboni (West Bengal; Eastern India). Depos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cheque Truncation
Cheque truncation (check truncation in American English) is a cheque clearance system that involves the digitization of a physical paper cheque into a substitute electronic form for transmission to the paying bank. The process of cheque clearance, involving data matching and verification, is done using digital images instead of paper copies. Cheque truncation reduces or eliminates the physical movement of paper cheques and reduces the time and cost of cheque clearance. Cheque truncation also offers the potential reduction in settlement periods with the electronic processing of the cheque payment system. History For cheque clearance, a cheque has to be presented to the drawee bank for payment. Originally, this was done by taking the cheque to the drawee bank, but as cheque usage increased, this became cumbersome and banks arranged to meet each day at a central location to exchange cheques and receive payment in money. This became known as central clearing. Bank customers who r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition
Magnetic ink character recognition code, known in short as MICR code, is a character recognition technology used mainly by the banking industry to streamline the processing and clearance of cheques and other documents. MICR encoding, called the ''MICR line'', is at the bottom of cheques and other vouchers and typically includes the document-type indicator, bank code, bank account number, cheque number, cheque amount (usually added after a cheque is presented for payment), and a control indicator. The format for the bank code and bank account number is country-specific. The technology allows MICR readers to scan and read the information directly into a data-collection device. Unlike barcode and similar technologies, MICR characters can be read easily by humans. MICR encoded documents can be processed much faster and more accurately than conventional OCR encoded documents. Pre-Unicode standard representation The ISO standard ISO 2033:1983, and the corresponding Japanese In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cheque Truncation
Cheque truncation (check truncation in American English) is a cheque clearance system that involves the digitization of a physical paper cheque into a substitute electronic form for transmission to the paying bank. The process of cheque clearance, involving data matching and verification, is done using digital images instead of paper copies. Cheque truncation reduces or eliminates the physical movement of paper cheques and reduces the time and cost of cheque clearance. Cheque truncation also offers the potential reduction in settlement periods with the electronic processing of the cheque payment system. History For cheque clearance, a cheque has to be presented to the drawee bank for payment. Originally, this was done by taking the cheque to the drawee bank, but as cheque usage increased, this became cumbersome and banks arranged to meet each day at a central location to exchange cheques and receive payment in money. This became known as central clearing. Bank customers who r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
MICR
Magnetic ink character recognition code, known in short as MICR code, is a character recognition technology used mainly by the banking industry to streamline the processing and clearance of cheques and other documents. MICR encoding, called the ''MICR line'', is at the bottom of cheques and other vouchers and typically includes the document-type indicator, bank code, bank account number, cheque number, cheque amount (usually added after a cheque is presented for payment), and a control indicator. The format for the bank code and bank account number is country-specific. The technology allows MICR readers to scan and read the information directly into a data-collection device. Unlike barcode and similar technologies, MICR characters can be read easily by humans. MICR encoded documents can be processed much faster and more accurately than conventional OCR encoded documents. Pre-Unicode standard representation The ISO standard ISO 2033:1983, and the corresponding Japanese In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
National Capital Region (India)
The National Capital Region (NCR; ) is a region centred upon the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi in India. It encompasses Delhi and several districts surrounding it from the states of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan. The NCR and the associated National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB) were created in 1985 to plan the development of the region and to evolve ''harmonized policies for the control of land-uses and development of infrastructure'' in the region. Prominent cities of the NCR include Delhi, Faridabad, Ghaziabad, Gurgaon and Noida. The NCR is a ''rural-urban'' region, with a population of over 46,069,000 and an urbanisation level of 62.6%. As well as cities and towns, the NCR contains ecologically sensitive areas like the Aravalli ridge, forests, wildlife and bird sanctuaries. The Delhi Extended Urban Agglomeration, a part of the NCR, had an estimated GDP of $370 billion (measured in terms of GDP PPP) in 2015–16. Despite being a part of the NCR, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
New Delhi
New Delhi (; ) is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the Government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Parliament House, New Delhi, Sansad Bhavan, and the Supreme Court of India, Supreme Court. New Delhi is a Municipal governance in India, municipality within the NCT, administered by the New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC), which covers mostly Lutyens' Delhi and a few adjacent areas. The municipal area is part of a larger List of districts in India, administrative district, the New Delhi district. Although colloquially ''Delhi'' and ''New Delhi'' are used interchangeably to refer to the National Capital Territory of Delhi, both are distinct entities, with the municipality and the New Delhi district forming a relatively small part within the megacity of Delhi. The National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region is an even larger entity, compris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Chennai
Chennai, also known as Madras (List of renamed places in India#Tamil Nadu, its official name until 1996), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost states and territories of India, state of India. It is located on the Coromandel Coast of the Bay of Bengal. According to the 2011 Census of India, 2011 Indian census, Chennai is the List of most populous cities in India, sixth-most-populous city in India and forms the List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, fourth-most-populous urban agglomeration. Incorporated in 1688, the Greater Chennai Corporation is the oldest municipal corporation in India and the second oldest in the world after City of London Corporation, London. Historically, the region was part of the Chola dynasty, Chola, Pandya dynasty, Pandya, Pallava dynasty, Pallava and Vijayanagara Empire, Vijayanagara kingdoms during various eras. The coastal land which then contained th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
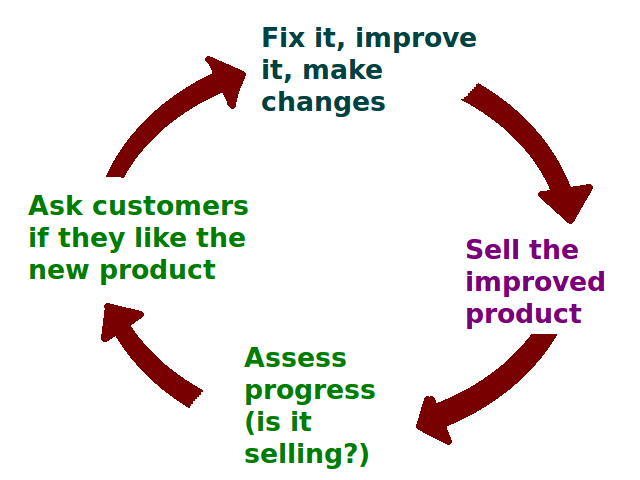 |
Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction is a term frequently used in marketing to evaluate customer experience. It is a measure of how products and services supplied by a company meet or surpass customer expectation. Customer satisfaction is defined as "the number of customers, or percentage of total customers, whose reported experience with a firm, its products, or its services (ratings) exceeds specified Contentment, satisfaction goals".. Enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering customer loyalty are pivotal for businesses, given the significant importance of improving the balance between customer Attitude (psychology), attitudes before and after the consumption process. Expectation confirmation theory, Expectancy disconfirmation theory is the most widely accepted theoretical framework for explaining customer satisfaction. However, other frameworks, such as equity theory, attribution theory, Contrast theory of meaning, contrast theory, assimilation theory, and various others, are also used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cheque Fraud
Cheque fraud or check fraud (American English) refers to a category of criminal acts that involve making the unlawful use of cheques in order to illegally acquire or borrow funds that do not exist within the account balance or account-holder's legal ownership. Most methods involve taking advantage of the '' float'' (the time between the negotiation of the cheque and its clearance at the cheque writer's financial institution) to draw out these funds. Specific kinds of cheque fraud include cheque kiting, where funds are deposited before the end of the float period to cover the fraud, and paper hanging, where the float offers the opportunity to write fraudulent cheques but the account is never replenished. Types of cheque fraud Cheque kiting Cheque kiting full refers to use of the float to take advantage and delay the notice of non-existent funds. Embezzlement While some cheque kiters fully intend to bring their accounts into good standing, others, often known as ''paper hange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Cheques
A cheque (or check in American English) is a document that orders a bank, building society, or credit union, to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The person writing the cheque, known as the ''drawer'', has a transaction banking account (often called a current, cheque, chequing, checking, or share draft account) where the money is held. The drawer writes various details including the monetary amount, date, and a payee on the cheque, and signs it, ordering their bank, known as the ''drawee'', to pay the amount of money stated to the payee. Although forms of cheques have been in use since ancient times and at least since the 9th century, they became a highly popular non-cash method for making payments during the 20th century and usage of cheques peaked. By the second half of the 20th century, as cheque processing became automated, billions of cheques were issued annually; these volumes peaked in or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |