|
Charles Ross (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice Admiral Charles Bayne Hodgson Ross (July 1776 – 2 March 1849) was a Royal Navy officer who served during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, who later commanded the ship that took Napoleon Bonaparte into his finale exile on St Helena, and who went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Pacific Station. Biography Background and early career Charles Ross was the son of Lieutenant Robert Hunter Ross, RN, and a great-great grandson of William Ross, 12th Lord Ross. He entered the navy on 1 March 1788 as a captain's servant aboard the sloop , commanded by Captain Robert Carthew Reynolds. He remained in her, stationed at Newfoundland, until December. From February to April 1790 he served aboard the 74-gun , the guard ship at Portsmouth, under Captain Anthony James Pye Molloy, then moved into the (50), flagship of Vice-Admiral Mark Milbanke, Commodore-Governor at Newfoundland, before returning to the ''Edgar'', under Captain Albemarle Bertie. French Revolutionary Wars B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth
Portsmouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary authority in Hampshire, England. Most of Portsmouth is located on Portsea Island, off the south coast of England in the Solent, making Portsmouth the only city in England not located primarily on the Great Britain, mainland. The city is located south-east of Southampton, west of Brighton and Hove and south-west of London. With a population last recorded at 208,100, it is the most densely populated city in the United Kingdom. Portsmouth forms part of the South Hampshire urban area with Gosport, Borough of Fareham, Fareham, Borough of Havant, Havant, Borough of Eastleigh, Eastleigh and Southampton. Portsmouth's history can be traced to Roman Britain, Roman times and has been a significant Royal Navy dockyard and base for centuries. Portsmouth was founded by Anglo-Norman merchant Jean de Gisors in the south-west area of Portsea Island, a location now known as Old Portsmouth. Around this time, de Gis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ross, 12th Lord Ross
William Ross, 12th Lord Ross (c.1656 – 15 March 1738), was a Scottish nobleman, soldier and politician. Origins Ross was born in about 1656. He was the son and heir of George Ross, 11th Lord Ross, who died in 1682, by Grizel, daughter of William Cochrane, 1st Earl of Dundonald. The Rosses of Halkhead, or Hawkhead, in Renfrewshire, were a Lowland family, not apparently related to the Earls of Ross or the Highland family of Ross of Balnagown.Sir James Balfour Paul, '' The Scots Peerage'', Volume VII Military career Lord Ross began his military career with commissions as lieutenant (27 September 1678) and captain (4 September 1680) in Lord Home's troop of horse. Subsequently, he held commissions as captain (26 December 1682) and major (4 August 1686) in Claverhouse's regiment of horse, although he resigned the latter position shortly afterward. In 1685, he sustained injuries during an action while pursuing the Earl of Argyll. Lord Ross maintained a close relationship w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyde Parker (admiral)
Admiral Sir Hyde Parker (1739 – 16 March 1807) was a Royal Navy officer who served in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Biography He was born in Devonshire, England, the second son of Admiral Sir Hyde Parker, 5th Baronet (1714–1782). He entered the Royal Navy at an early age, and became lieutenant on 25 January 1758, having passed most of his early service in his father's ships. On 16 December 1762 was promoted to command ''Manila'', from which, on 18 July 1763, he was posted to .DNB From 1766 onwards for many years he served in the West Indies and in North American waters, particularly distinguishing himself in breaking the defences of the North River at New York in 1776 as captain of . His services on this occasion earned him a knighthood in 1779. In 1778 he was engaged in the Savannah expedition, and in the following year his ship was wrecked on the hostile Cuban coast. His men, however, entrenched themselves, and were in the end brought off safely. He be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Fremantle (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral Sir Thomas Francis Fremantle, Baron Fremantle, (20 November 1765 – 19 December 1819) was a Royal Navy officer whose accolades include three separate fleet actions, a close friendship with Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson and being granted an Austrian barony. He was the father of Admiral Sir Charles Fremantle, after whom the city Fremantle in Western Australia is named. Early career Fremantle was born in 1765, son of John Fremantle, of Aston Abbotts, Buckinghamshire, and Frances, daughter of John Edwards, of Bristol. His younger brother was the politician Sir William Fremantle. He joined the navy in 1777 aged eleven, aboard the frigate HMS ''Hussar''. Profiting from family influence, active commissions in the American War of Independence and a keen sense of seamanship and aggressive tactical awareness, promotion came easily. He was made a lieutenant on 13 March 1782 while on duty in Jamaica and promoted to commander on 13 November 1790, in command of the sloo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
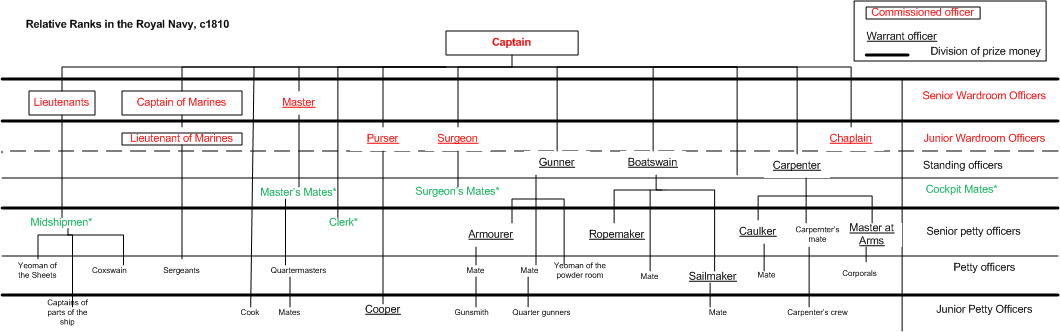
Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest Military rank#Subordinate/student officer, rank in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Royal Canadian Navy, Canada (Naval Cadet), Royal Australian Navy, Australia, Bangladesh Navy, Bangladesh, Namibian Navy, Namibia, Royal New Zealand Navy, New Zealand, South African Navy, South Africa, Indian Navy, India, Pakistan Navy, Pakistan, Republic of Singapore Navy, Singapore, Sri Lanka Navy, Sri Lanka, and Kenya Navy, Kenya. In the 17th century, a midshipman was a Naval rating, rating for an experienced seaman, and the word derives from the area aboard a ship, amidships, either where he worked on the ship, or where he was Berth (sleeping), berthed. Beginning in the 18th century, a commissioned officer candidate was rated as a midshipman, and the seaman rating began to slowly die out. By the Napoleonic era (1793–1815), a midshipman was an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master's Mate
Master's mate is an obsolete rating which was used by the British Royal Navy, Royal Navy, United States Navy and merchant services in both countries for a senior petty officer who assisted the sailing master, master. Master's mates evolved into the modern rank of sub-lieutenant in the Royal Navy, while in the merchant service they evolved into the numbered mates or officers. Royal Navy Originally, a master's mate was an experienced petty officer who assisted the sailing master, master but was not in line for promotion to lieutenant. By the mid-eighteenth century, he was far more likely to be a senior midshipman, still waiting to pass his examination for lieutenant or to receive his Commissioned officer#Commissioned officers, commission, but taking rather more responsibility aboard ship. Six master's mates were allowed on a First-rate, first rate, three on a Third-rate, third rate, and two on most frigates. Duties Master's mates were experienced seamen, and were usually selected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Albemarle Bertie, 1st Baronet
Admiral Sir Albemarle Bertie, 1st Baronet, (20 January 1755 – 24 February 1824) was a long-serving and at the time controversial officer of the Royal Navy who saw extensive service in his career, but also courted controversy with several of his actions. Bertie won recognition for unsuccessfully defending his ship against superior odds in the American Revolutionary War. He was later criticised however for failing to close with the enemy at the Glorious First of June and later superseding a subordinate officer just days before the Invasion of Isle de France, capture of the French island of Mauritius and taking credit for the victory. Despite these controversies, Bertie was rewarded for his service with a baronetcy and the Order of the Bath, retiring in 1813 to his country estate at Donnington, Berkshire. Childhood Albemarle Bertie was born at Swinstead in Lincolnshire in 1755, the natural son of Lord Albemarle Bertie, the brother of Peregrine Bertie, 3rd Duke of Ancaster and Ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Milbanke
Admiral Mark Milbanke (12 April 1724 – 9 June 1805) was a British naval officer and colonial governor. Military career Milbanke was born into an aristocratic Yorkshire family with naval connections, his father was Sir Ralph Milbanke, 4th Baronet. Mark Milbanke graduated from the Royal Naval Academy, Portsmouth in 1740. He was made Lieutenant in 1744 and in 1746 was given command of HMS ''Serpent''. He became Port Admiral at Plymouth in 1783. In 1789, Milbanke was appointed governor of Newfoundland. In the years when settlement was prohibited on the Island of Newfoundland, Milbanke did his best to enforce this prohibition. He did so by demolishing buildings, and by limiting the number of Irish people immigrating to Newfoundland. He also refused to allow the building of a Roman Catholic chapel at Ferryland. He was appointed Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth in 1799. Milbanke was promoted to admiral of the white in 1795. In 1805 he fell over the banisters at his home and die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of navy, naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest quality, best known, or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony James Pye Molloy
Anthony James Pye Molloy ( – 25 July 1814) was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served during the American War of Independence and the French Revolutionary Wars. Molloy rose through the ranks to command a number of ships during the war with America, and saw action in most of the naval engagements of the conflict, both off the North American coast and in the Caribbean. He commanded several ships during the peace that followed, and after the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars, he served with the fleet in the Atlantic. He was part of Lord Howe's fleet at the Glorious First of June, but was sharply criticised by Howe in the aftermath. Molloy was then tried by court martial for failing to obey orders, or to do his utmost to engage the enemy. The charges were subsequently proved and Molloy was dismissed from his ship. Molloy's personal life was later the subject of some speculation, with rumours that he had acted dishonourably to a woman, who had then cursed him, resulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guard Ship
A guard ship is a warship assigned as a stationary guard in a port or harbour, as opposed to a coastal patrol boat, which serves its protective role at sea. Royal Navy In the Royal Navy of the eighteenth century, peacetime guard ships were usually third-rate or fourth-rate ships of the line. The larger ships in the fleet would be laid up " in ordinary" with skeleton crews, the spars, sails and rigging removed and the decks covered by canvas – the historic equivalent of a reserve fleet. By contrast the guard ships would carry sails and rigging aboard, be cleaned below the waterline to increase their speed under sail, and be manned by at least one quarter of their normal crew. A port or major waterway may be assigned a single guardship which would also serve as the naval headquarters for the area. Multiple guardships were required at larger ports and Royal Dockyards, with the largest single vessel routinely serving as the Port Admiral's flagship. If war was declared, or an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |