|
Charles Read (naval Officer)
Charles William Read (May 12, 1840 – January 25, 1890), known commonly as "Savez", was an officer in the antebellum United States Navy and then in the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War. He was nicknamed the "Seawolf of the Confederacy" for his exploits and daring. Early life and career Charles William Read was born in Satartia, Mississippi in 1840. He was appointed to the United States Naval Academy in 1856 and graduated in 1860. He served briefly aboard USS ''Powhatan'' after graduation. American Civil War At the outbreak of the American Civil War Read resigned his commission with the United States Navy and accepted a position with the Confederate States Navy. Read was initially assigned to the at New Orleans, Louisiana as a midshipman and participated in the battle between batteries on Ship Island and the on July 9, 1861. On October 12, 1861, he participated in the attack on the Union blockading squadron at Head of the Passes on the Mississippi River. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Read (other)
Charles Read may refer to: * Charles Read (Australian politician) (1814–1910), politician in Geelong, Victoria, Australia * Charles A. Read (1837–1865), American Civil War sailor and Medal of Honor recipient * Charles Read (Medal of Honor) (1840–?), American Civil War sailor and Medal of Honor recipient * Charles Read (naval officer) (1840–1890), United States Navy and Confederate States Navy officer * Charles Anderson Read (1841–1878), Irish writer * Charles Hercules Read (1857–1929), British archaeologist and curator * Charles C. Reid (1868–1922), Arkansas lawyer and politician * Charles Read (squash player) (1889–?), British professional squash player * Charles Read (RAAF officer) (1918–2014), commander in the Royal Australian Air Force * Charles Read (mathematician) (1958–2015), British mathematician * Sir Charles D. Read (1902–1957), New Zealand surgeon * Charles Read (Philadelphia) (died 1736), merchant and mayor of Philadelphia * Charles Read (historian), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Clarence
CSS ''Clarence'', also known as ''Coquette'', was originally a brig from Baltimore captured by the Confederate cruiser CSS ''Florida'' during the American Civil War and converted into a Confederate cruiser for commerce raiding. Built in 1857 for Baltimore, Maryland fruit dealer J. Crosby, it was transporting a cargo of coffee from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, to Baltimore when the CSS ''Florida'' captured the ''Clarence'' off the coast of Brazil. Lt. Charles W. Read was appointed commander and a sufficient number of the ''Florida'''s crew were transferred to the new cruiser to man the ship. Lieutenant Read had requested that, rather than burn ''Clarence'', he might try, with the ship's papers, to sail into Hampton Roads, Virginia, and if possible destroy or capture a Union gunboat and burn Union merchant vessels congregated at Fortress Monroe. ''Florida'''s Commander John Newland Maffitt armed ''Clarence'' with one gun so that Read might capture prizes on his way to Hampton Roads. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Naval Academy
The United States Naval Academy (USNA, Navy, or Annapolis) is a United States Service academies, federal service academy in Annapolis, Maryland. It was established on 10 October 1845 during the tenure of George Bancroft as United States Secretary of the Navy, Secretary of the Navy. The Naval Academy is the second oldest of the five United States service academies, U.S. service academies and it educates midshipmen for service in the officer corps of the United States Navy and United States Marine Corps. It is part of the Naval University System. The campus is located on the former grounds of Fort Severn at the confluence of the Severn River (Maryland), Severn River and Chesapeake Bay in Anne Arundel County, Maryland, Anne Arundel County, east of Washington, D.C., and southeast of Baltimore. The entire campus, known colloquially as the Yard, is a National Historic Landmark and home to many historic sites, buildings, and monuments. It replaced Philadelphia Naval Asylum in Phila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate Navy
The Confederate States Navy (CSN) was the Navy, naval branch of the Confederate States Armed Forces, established by an act of the Confederate States Congress on February 21, 1861. It was responsible for Confederate naval operations during the American Civil War against the United States's Union Navy. The three major tasks of the Confederate States Navy during its existence were the protection of Confederate harbors and coastlines from outside invasion, making the war costly for the United States by attacking its merchant ships worldwide, and Blockade runners of the American Civil War, running the Union blockade, U.S. blockade by drawing off Union ships in pursuit of Confederate commerce raiders and warships. It was ineffective in these tasks, as the coastal blockade by the United States Navy reduced trade by the South to 5 percent of its pre-war levels. Additionally, the control of inland rivers and coastal navigation by the US Navy forced the south to overload its limited railroa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antebellum Era
The ''Antebellum'' South era (from ) was a period in the history of the Southern United States that extended from the conclusion of the War of 1812 to the start of the American Civil War in 1861. This era was marked by the prevalent practice of slavery and the associated societal norms it cultivated. Over the course of this period, Southern leaders underwent a transformation in their perspective on slavery. Initially regarded as an awkward and temporary institution, it gradually evolved into a defended concept, with proponents arguing for its positive merits, while simultaneously vehemently opposing the burgeoning abolitionist movement. Society was stratified, inegalitarian, and perceived by immigrants as lacking in opportunities. Consequently, the manufacturing base lagged behind that of the non-slave states. Wealth inequality grew as the larger landholders took the greater share of the profits generated by enslaved persons, which also helped to entrench their power as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
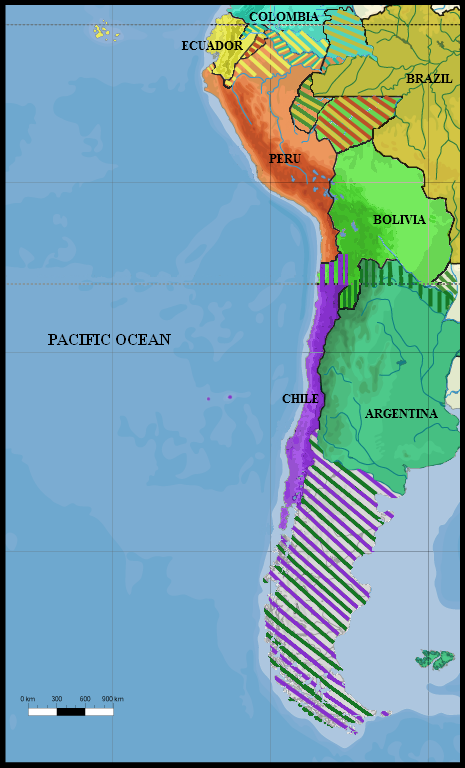
War Of The Pacific
The War of the Pacific (), also known by War of the Pacific#Etymology, multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Treaty of Defensive Alliance (Bolivia–Peru), Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought over Atacama Desert border dispute, Chilean claims on Litoral Department, coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert, the war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. The direct cause of the war was a nitrate taxation dispute between Bolivia and Chile, with Peru being drawn in due to its secret alliance with Bolivia. Some historians have pointed to deeper origins of the war, such as the interest of Chile and Peru in the nitrate business, a long-standing rivalry between Chile and Peru for regional hegemony, as well as the political and economical disparities between the stability of Chile and the volatility of Peru and Bolivia. In February 1878, Bolivia increased taxes on the Chile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Trent's Reach
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and the Battle of France, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas batt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Portland Harbor
The Battle of Portland Harbor was an incident during the American Civil War, in June 1863, in the waters off Portland, Maine. Two civilian ships engaged two vessels under Confederate States Navy employment. Background Around June 24, a Confederate raider named the ''Tacony'', commanded by Lieutenant Charles Read, CSN, was being pursued by the Union Navy. To thwart their pursuers, at about 2 AM on June 25, the Confederates captured the ''Archer'', a Maine fishing schooner out of Southport. After transferring their supplies and cargo onto ''Archer'', the Confederates set fire to ''Tacony'', hoping the Union Navy would believe the ship was destroyed. On June 26, a Confederate raiding party entered the harbor at Portland late in the evening, sailing past Portland Head Light. The rebels disguised themselves as fishermen; they planned to try to destroy the area's commercial shipping capability, and then to escape out of the harbor. Battle When the raiders left the port area on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Baton Rouge (1862)
The Battle of Baton Rouge was a ground and naval battle in the American Civil War fought in East Baton Rouge Parish, Louisiana, on August 5, 1862. The Union victory halted Confederate attempts to recapture the capital city of Louisiana. Background On April 25, 1862, the day before New Orleans fell to the US Navy fleet under Admiral David Farragut, the Confederate state government decided to abandon Baton Rouge, moving first to Opelousas, and then to Shreveport. All cotton in the area was set afire to prevent it falling into Union hands. On May 9, Navy Commander James S. Palmer of the federal gunboat landed at the town wharf and took possession, without resistance, of the Pentagon Barracks and the arsenal. Two weeks later, a party of guerrillas attacked a rowboat carrying a naval officer. In retaliation, Farragut's flagship, the , bombarded the town, causing civilian casualties and damaging St. Joseph's Church and other buildings. On May 29, US Brigadier General Thomas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Head Of Passes
The Battle of the Head of Passes was a bloodless naval battle of the American Civil War. It was a naval raid made by the Confederate river defense fleet, also known as the “mosquito fleet” in the local media, on ships of the Union blockade squadron anchored at the Head of Passes. The ''mosquito fleet'' deployed three fire rafts, which were ignited and followed the ironclad ram into the action. The attack occurred after moonset in the early hours of October 12, 1861, and routed the Union fleet, which fled in disorder down the Southwest pass of the delta. After sunrise Commodore George N. Hollins, running low on ammunition and fuel, ordered the ''mosquito fleet'' to withdraw upriver. Background Louisiana seceded from the Union on January 26, 1861. A navy department was established by the newly created Confederate government by February 21, 1861. Commodore Lawrence Rousseau was sent by Confederate Naval Secretary Stephen Mallory to manage the naval defense of New Orleans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CSS Webb
CSS ''Webb'', a 655-ton side-wheel Naval ram#Steam rams, steam ram, was originally built in New York City in 1856 as the civilian steamship ''William H. Webb''. She received a Confederate privateer's commission at New Orleans in May 1861, but was instead employed as a transport until January 1862. Converted to a "Cottonclad warship, cotton clad" ram by the Confederate Army, thereafter served on the Mississippi River, Mississippi and Red River of the South, Red Rivers. On February 24, 1863, under the command of Captain Charles Pierce, she participated in the sinking of the Federal ironclad . ''Webb'' was transferred to the Confederate Navy in early 1865. On April 23–24, 1865, under the command of Charles S. Read, ''Webb'' broke through the Federal blockade at the mouth of the Red River, Louisiana, and made a dramatic run down the Mississippi toward the Gulf of Mexico. After eluding several United States Navy vessels and passing New Orleans, Louisiana, New Orleans, she was confront ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |