|
Chan–Lam Coupling
The Chan–Lam coupling reaction, also known as the Chan–Evans–Lam coupling, is a cross-coupling reaction between an aryl boronic acid and an alcohol (chemistry), alcohol or an amine to form the corresponding secondary aryl amines or aryl ethers, respectively. The Chan–Lam coupling is catalyzed by copper complexes. It can be conducted open to air at room temperature. The more popular Buchwald–Hartwig coupling relies on the use of palladium. History Dominic Chan, David A. Evans, David Evans, and Patrick Lam published their work nearly simultaneously. The mechanism however remained uncertain for many years. Later developments by others extended the scope to include using carboxylic acids, giving aryl-ester products. Mechanism Analysis of the mechanism is complicated by the lability of copper reagents and the multicomponent nature of the reaction. The reaction proceeds via the formation of copper-aryl complexes. A copper(III)-aryl-alkoxide or copper(III)-aryl-amide intermedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-coupling Reaction
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this: : (R, R' = organic fragments, usually aryl; M = main group center such as Li or MgX; X = halide) These reactions are used to form carbon–carbon bonds but also carbon-heteroatom bonds. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism Many mechanisms exist reflecting the myriad types of cross-couplings, including those that do not require metal catalysts. Often, however, cross-coupling refers to a metal-catalyzed reaction of a nucleophilic partner with an electrophilic partner. In such cases, the mechanism generally involves reduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boronic Acid
A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid () in which one of the three hydroxyl groups () is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group (represented by R in the general formula ). As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, members of this class thus belong to the larger class of organoboranes. Boronic acids act as Lewis acids. Their unique feature is that they are capable of forming reversible covalent complexes with sugars, amino acids, hydroxamic acids, etc. (molecules with vicinal, (1,2) or occasionally (1,3) substituted Lewis base donors (alcohol, amine, carboxylate)). The p''K''a of a boronic acid is ~9, but they can form tetrahedral boronate complexes with p''K''a ~7. They are occasionally used in the area of molecular recognition to bind to saccharides for fluorescent detection or selective transport of saccharides across membranes. Boronic acids are used extensively in organic chemistry as chemical building blocks and intermediates predominantly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of electrons. Amines can also exist as hetero cyclic compounds. Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine, consisting of a benzene ring bonded to an amino group. Amines are classified into three types: primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) amines. Primary amines (1°) contain one alkyl or aryl substituent and have the general formula RNH2. Secondary amines (2°) have two alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, with the general formula R2NH. Tertiary amines (3°) contain three substituent groups bonded to the nitrogen atom, and are represented by the formula R3N. The functional group present in primary amines is called the amino group. Classification of amines Amines can be classified according to the nature and number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aryl Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the organyl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the organyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
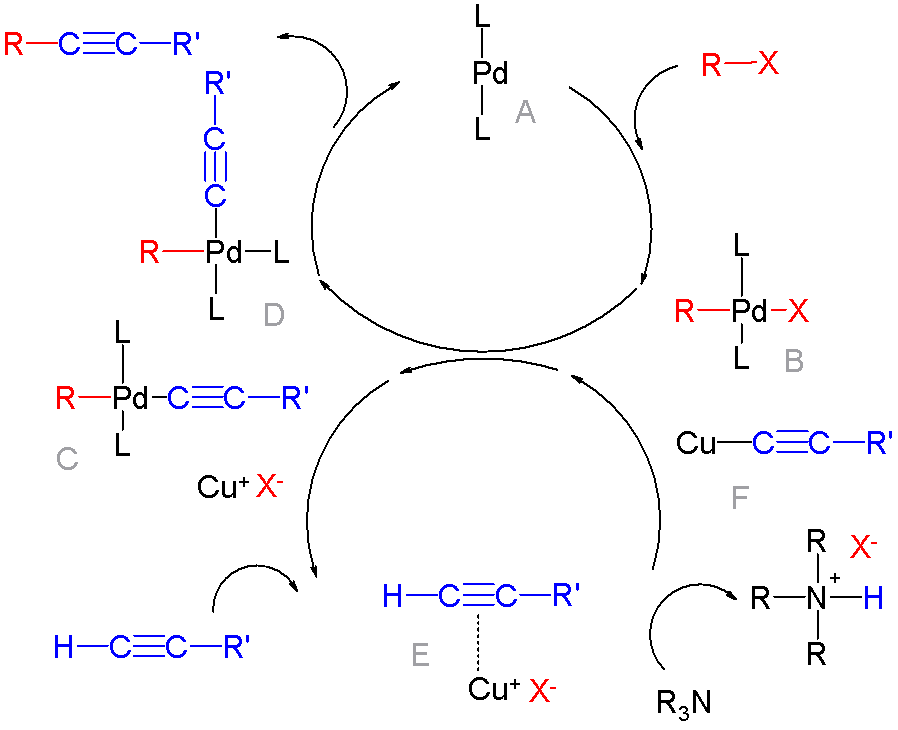
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired by her when she slew Pallas. Palladium, platinum, rhodium, ruthenium, iridium and osmium form together a group of elements referred to as the platinum group metals (PGMs). They have similar chemical properties, but palladium has the lowest melting point and is the least dense of them. More than half the supply of palladium and its congener platinum is used in catalytic converters, which convert as much as 90% of the harmful gases in automobile exhaust (hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide) into nontoxic substances (nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapor). Palladium is also used in electronics, dentistry, medicine, hydrogen purification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David A
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboxylic Acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl group (e.g., alkyl, alkenyl, aryl), or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion. Examples and nomenclature Carboxylic acids are commonly identified by their trivial names. They often have the suffix ''-ic acid''. IUPAC-recommended names also exist; in this system, carboxylic acids have an ''-oic acid'' suffix. For example, butyric acid () is butanoic acid by IUPAC guidelines. For nomenclature of complex molecules containing a carboxylic acid, the carboxyl can be considered position one of the parent chain even if there are other substituents, such as 3-chloropropanoic acid. Alternately, it can be named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Elimination
Reductive elimination is an elementary step in organometallic chemistry in which the oxidation state of the metal center decreases while forming a new covalent bond between two ligands. It is the microscopic reverse of oxidative addition, and is often the product-forming step in many catalytic processes. Since oxidative addition and reductive elimination are reverse reactions, the same mechanisms apply for both processes, and the product equilibrium depends on the thermodynamics of both directions. General information Reductive elimination is often seen in higher oxidation states, and can involve a two-electron change at a single metal center (mononuclear) or a one-electron change at each of two metal centers (binuclear, dinuclear, or bimetallic). For mononuclear reductive elimination, the oxidation state of the metal decreases by two, while the d-electron count of the metal increases by two. This pathway is common for d8 metals Ni(II), Pd(II), and Au(III) and d6 metals Pt(I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |