|
Cerebral Achromatopsia
Cerebral achromatopsia is a type of color blindness caused by damage to the cerebral cortex of the brain, rather than abnormalities in the cells of the eye's retina. It is often confused with congenital achromatopsia but the underlying physiological deficits of the disorders are completely distinct. A similar, but distinct, deficit called color agnosia exists in which a person has intact color perception (as measured by a matching task) but has deficits in color recognition, such as knowing which color they are looking at. Signs and symptoms Patients with cerebral achromatopsia deny having any experience of color when asked and fail standard clinical assessments like the Farnsworth-Munsell 100-hue test (a test of color ordering with no naming requirements). Patients may often not notice their loss of color vision and merely describe the world they see as being "drab". Most describe seeing the world in "shades of gray". This observation notes a key difference between cerebral and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Blindness
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a Sex linkage, sex-linked Heredity, inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
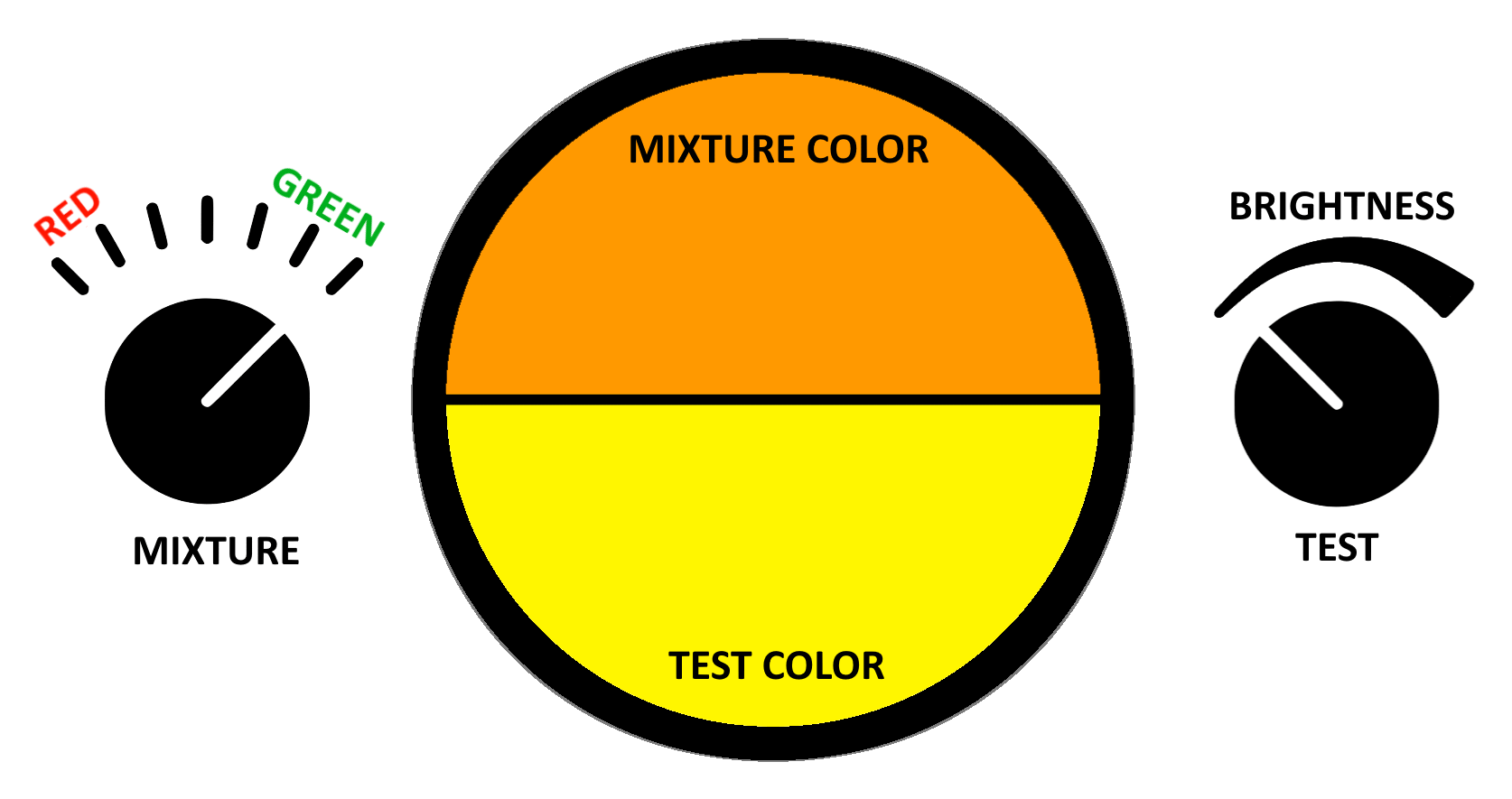
Color Vision Tests
A color vision test is used for measuring color vision against a standard. These tests are most often used to diagnose color vision deficiencies ("CVD"; color blindness''), though several of the standards are designed to categorize normal color vision into sub-levels. With the large prevalence of color vision deficiencies (8% of males) and the wide range of professions that restrict hiring the colorblind for safety or aesthetic reasons, clinical color vision standards must be designed to be fast and simple to implement. Color vision standards for academic use trade speed and simplicity for accuracy and precision. Applications Color vision standards are used to evaluate the color vision of a subject. They are most commonly applied to job applicants during pre-job screening. The evaluation may be to select against the color vision deficient for roles where basic color vision is required, or to select for individuals with superior color vision for roles where recognition of subtle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishihara Color Test
The Ishihara test is a color vision test for detection of red–green color deficiencies. It was named after its designer, Shinobu Ishihara, a professor at the University of Tokyo, who first published his tests in 1917.S. Ishihara, Tests for color-blindness (Handaya, Tokyo, Hongo Harukicho, 1917). The test consists of a number of Ishihara plates, which are a type of pseudoisochromatic plate. Each plate depicts a solid circle of colored dots appearing randomized in color and size. Within the pattern are dots which form a number or shape clearly visible to those with normal color vision, and invisible, or difficult to see, to those with a red–green color vision deficiency. Other plates are intentionally designed to reveal numbers only to those with a red–green color vision deficiency, and be invisible to those with normal red–green color vision. The full test consists of 38 plates, but the existence of a severe deficiency is usually apparent after only a few plates. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Blindness
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a Sex linkage, sex-linked Heredity, inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortical Blindness
Cortical blindness is the total or partial loss of vision in a normal-appearing eye caused by damage to the brain's occipital cortex. Cortical blindness can be acquired or congenital, and may also be transient in certain instances. Acquired cortical blindness is most often caused by loss of blood flow to the occipital cortex from either unilateral or bilateral posterior cerebral artery blockage (ischemic stroke) and by cardiac surgery. In most cases, the complete loss of vision is not permanent and the patient may recover some of their vision (cortical visual impairment). Congenital cortical blindness is most often caused by perinatal ischemic stroke, encephalitis, and meningitis. Rarely, a patient with acquired cortical blindness may have little or no insight that they have lost vision, a phenomenon known as Anton–Babinski syndrome. Cortical blindness and cortical visual impairment (CVI), which refers to the partial loss of vision caused by cortical damage, are both classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achromatopsia
Achromatopsia, also known as rod monochromacy, is a medical syndrome that exhibits symptoms relating to five conditions, most notably monochromacy. Historically, the name referred to monochromacy in general, but now typically refers only to an autosomal recessive congenital color vision condition. The term is also used to describe cerebral achromatopsia, though monochromacy is usually the only common symptom. The conditions include: monochromatic color blindness, poor visual acuity, and day-blindness. The syndrome is also present in an ''incomplete'' form that exhibits milder symptoms, including residual color vision. Achromatopsia is estimated to affect 1 in 30,000 live births worldwide. Signs and symptoms The five symptoms associated with achromatopsia are: # Color blindness – usually monochromacy # Reduced visual acuity – uncorrectable with lenses # Hemeralopia – with the subject exhibiting photophobia # Nystagmus # Iris operating abnormalities The syndrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Sacks
Oliver Wolf Sacks (9 July 1933 – 30 August 2015) was a British neurology, neurologist, Natural history, naturalist, historian of science, and writer. Born in London, Sacks received his medical degree in 1958 from The Queen's College, Oxford, before moving to the United States, where he spent most of his career. He interned at UCSF Medical Center, Mount Zion Hospital in San Francisco and completed his residency in neurology and neuropathology at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). Later, he served as neurologist at Beth Abraham Hospital's chronic-care facility in the Bronx, where he worked with a group of survivors of the 1920s sleeping sickness encephalitis lethargica epidemic, who had been unable to move on their own for decades. His treatment of those patients became the basis of his 1973 book ''Awakenings (book), Awakenings'', which was adapted into an Academy Award-nominated Awakenings, feature film, in 1990, starring Robin Williams and Robert De Niro. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishihara Plate
The Ishihara test is a color vision test for detection of red–green color deficiencies. It was named after its designer, Shinobu Ishihara, a professor at the University of Tokyo, who first published his tests in 1917.S. Ishihara, Tests for color-blindness (Handaya, Tokyo, Hongo Harukicho, 1917). The test consists of a number of Ishihara plates, which are a type of pseudoisochromatic plate. Each plate depicts a solid circle of colored dots appearing randomized in color and size. Within the pattern are dots which form a number or shape clearly visible to those with normal color vision, and invisible, or difficult to see, to those with a red–green color vision deficiency. Other plates are intentionally designed to reveal numbers only to those with a red–green color vision deficiency, and be invisible to those with normal red–green color vision. The full test consists of 38 plates, but the existence of a severe deficiency is usually apparent after only a few plates. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prosopagnosia
Prosopagnosia, also known as face blindness, (" illChoisser had even begun tpopularizea name for the condition: face blindness.") is a cognitive disorder of face perception in which the ability to recognize familiar faces, including one's own face (self-recognition), is impaired, while other aspects of visual processing (e.g., object discrimination) and intellectual functioning (e.g., decision-making) remain intact. The term originally referred to a condition following acute brain damage (acquired prosopagnosia), but a congenital or developmental form of the disorder also exists, with a prevalence of 2.5%. Etymology ''Prosopagnosia'' is a medical Latin term adopted in 1948 into English from the German . It is derived from the Greek , , and , . The latter is formed from , , and , . Physiology The brain area usually associated with prosopagnosia is the fusiform gyrus, which activates specifically in response to faces. The functionality of the fusiform gyrus allows most people to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of Neuron, neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The six-layered neocortex makes up approximately 90% of the Cortex (anatomy), cortex, with the allocortex making up the remainder. The cortex is divided into left and right parts by the longitudinal fissure, which separates the two cerebral hemispheres that are joined beneath the cortex by the corpus callosum and other commissural fibers. In most mammals, apart from small mammals that have small brains, the cerebral cortex is folded, providing a greater surface area in the confined volume of the neurocranium, cranium. Apart from minimising brain and cranial volume, gyrification, cortical folding is crucial for the Neural circuit, brain circuitry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infarction
Infarction is tissue death (necrosis) due to Ischemia, inadequate blood supply to the affected area. It may be caused by Thrombosis, artery blockages, rupture, mechanical compression, or vasoconstriction. The resulting lesion is referred to as an infarct (from the Latin ''infarctus'', "stuffed into"). Causes Infarction occurs as a result of prolonged ischemia, which is the insufficient supply of oxygen and nutrition to an area of tissue due to a disruption in blood supply. The blood vessel supplying the affected area of tissue may be blocked due to an obstruction in the vessel (e.g., an arterial embolus, thrombus, or atherosclerotic plaque), compressed by something outside of the vessel causing it to narrow (e.g., tumor, volvulus, or hernia), ruptured by trauma causing a loss of blood pressure downstream of the rupture, or vasoconstricted, which is the narrowing of the blood vessel by contraction of the muscle wall rather than an external force (e.g., cocaine vaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue, i.e., hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction (such as vasoconstriction, thrombosis, or embolism). Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial (poor perfusion) or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |