|
Cepola Macrophthalma
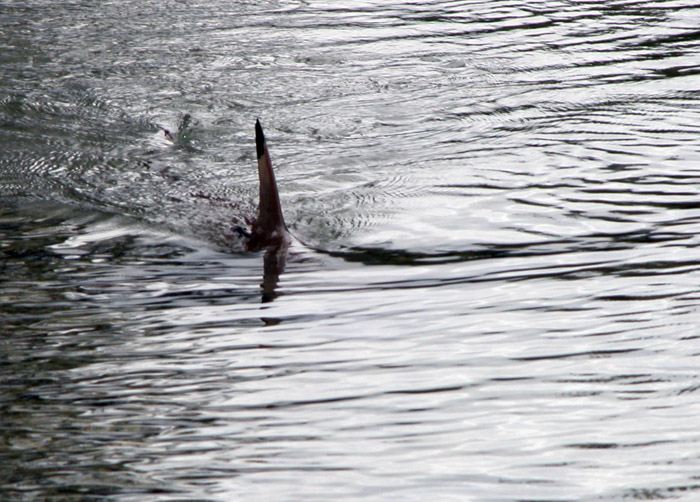
''Cepola macrophthalma'' is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Cepolidae, the bandfishes. It is found in the eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean from Senegal north to the British Isles. This species is known as the red bandfish, though this name is also given to other members of the genus '' Cepola''. Taxonomy ''Cepola macrophthalma'' was first formally described as ''Ophidion macrophthalmum'' in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus with the type locality given as Algiers. In 1764 Linnaeus described the genus '' Cepola'' with ''O. macrophthalmum'' as its type species by monotypy. The specific name, ''macrophthalma'' is a compound of ''macro'' meaning "large" and ''ophthalmus'' which means "eyed", a reference to the large eyes which are larger than a third of the length of the head. Distribution It is found on the coast and inner continental shelf of the eastern Atlantic between northern Senegal and Scotland and the Mediterranean west of the Aegean Sea and the Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet, species epithet, or epitheton) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Etymology Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden Eel
The garden eels are the subfamily Heterocongrinae in the conger eel family Congridae. The majority of the 36 known species of garden eels live in the Indo-Pacific, but can be found in warm ocean water worldwide. These small eels Eels are ray-finned fish belonging to the order (biology), order Anguilliformes (), which consists of eight suborders, 20 Family (biology), families, 164 genus, genera, and about 1000 species. Eels undergo considerable development from the earl ... live in burrows on the sea floor and get their name from the behavior of poking their heads from their burrows to feed on plankton while most of their bodies remain hidden. Since they tend to live in groups, the many eel heads "growing" from the sea floor resemble the plants in a garden. They vary in color and size depending on the species. The largest species reaches about in length, but most species do not surpass . Garden eel colonies can grow as large as one acre in surface area and number up to severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Times
''The Times'' is a British Newspaper#Daily, daily Newspaper#National, national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its modern name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (founded in 1821), are published by Times Media, since 1981 a subsidiary of News UK, in turn wholly owned by News Corp. ''The Times'' and ''The Sunday Times'' were founded independently and have had common ownership only since 1966. It is considered a newspaper of record in the UK. ''The Times'' was the first newspaper to bear that name, inspiring numerous other papers around the world. In countries where these other titles are popular, the newspaper is often referred to as or , although the newspaper is of national scope and distribution. ''The Times'' had an average daily circulation of 365,880 in March 2020; in the same period, ''The Sunday Times'' had an average weekly circulation of 647,622. The two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west. The city of Plymouth is the largest settlement, and the city of Exeter is the county town. The county has an area of and a population of 1,194,166. The largest settlements after Plymouth (264,695) are the city of Exeter (130,709) and the Seaside resort, seaside resorts of Torquay and Paignton, which have a combined population of 115,410. They all are located along the south coast, which is the most populous part of the county; Barnstaple (31,275) and Tiverton, Devon, Tiverton (22,291) are the largest towns in the north and centre respectively. For local government purposes Devon comprises a non-metropolitan county, with eight districts, and the Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority areas of Plymouth City Council, Plymouth an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
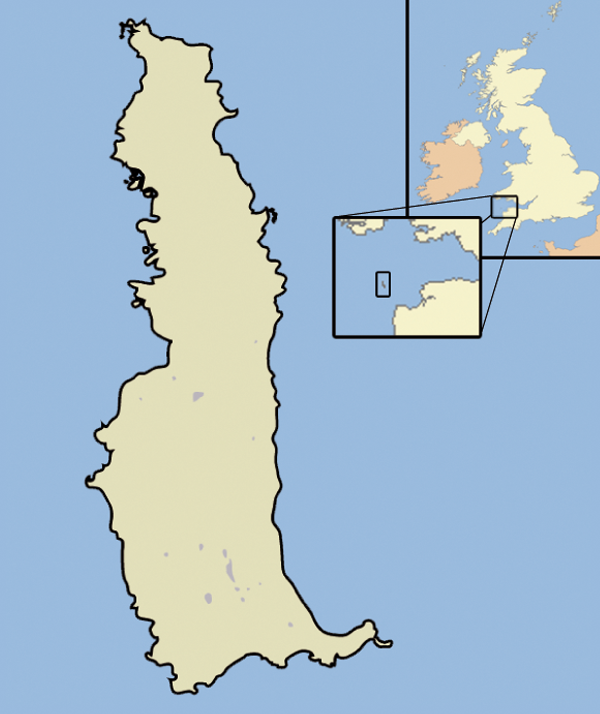
Lundy
Lundy is an English island in the Bristol Channel. It forms part of the district of Torridge in the county of Devon. About long and wide, Lundy has had a long and turbulent history, frequently changing hands between the British crown and various usurpers. In the 1920s, the island's owner, Martin Harman, tried to issue his own coinage and was fined. In 1941, two German Heinkel He 111 bombers crash landed on the island, and their crews were captured. In 1969, Lundy was purchased by British millionaire Jack Hayward, who donated it to the National Trust. It is now managed by the Landmark Trust, a conservation charity that derives its income from day trips and holiday lettings, most visitors arriving by boat from Bideford or Ilfracombe. A local tourist curiosity is the special "Puffin" postage stamp, a category known by philatelists as "local carriage labels", a collectors' item. As a steep, rocky island, often shrouded by fog, Lundy has been the scene of many shipwrec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Anatomy
Fish anatomy is the study of the form or Morphology (biology), morphology of fish. It can be contrasted with fish physiology, which is the study of how the component parts of fish function together in the living fish. In practice, fish anatomy and fish physiology complement each other, the former dealing with the structure of a fish, its organs or component parts and how they are put together, such as might be observed on the dissecting table or under the microscope, and the latter dealing with how those components function together in living fish. The anatomy of fish is often shaped by the physical characteristics of water, the medium in which fish live. Water is much density, denser than air, holds a relatively small amount of dissolved oxygen, and absorbs more light than air does. The body of a fish is divided into a head, trunk and tail, although the divisions between the three are not always externally visible. The skeleton, which forms the support structure inside the fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
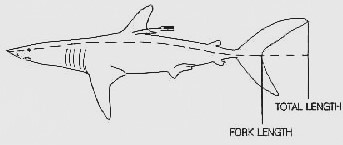
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal Fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only by muscles. Fish fins are distinctive anatomical features with varying structures among different clades: in ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii), fins are mainly composed of bony spines or rays covered by a thin stretch of scaleless skin; in lobe-finned fish ( Sarcopterygii) such as coelacanths and lungfish, fins are short rays based around a muscular central bud supported by jointed bones; in cartilaginous fish ( Chondrichthyes) and jawless fish ( Agnatha), fins are fleshy " flippers" supported by a cartilaginous skeleton. Fins at different locations of the fish body serve different purposes, and are divided into two groups: the midsagittal ''unpaired fins'' and the more laterally located ''paired fins''. Unpaired fins are pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found in most fish, in mammals such as whales, and in extinct ancient marine reptiles such as ichthyosaurs. Most have only one dorsal fin, but some have two or three. Wildlife biologists often use the distinctive nicks and wear patterns which develop on the dorsal fins of whales to identify individuals in the field. The bones or cartilages that support the dorsal fin in fish are called pterygiophores. Functions The main purpose of the dorsal fin is usually to stabilize the animal against rolling and to assist in sudden turns. Some species have further adapted their dorsal fins to other uses. The sunfish uses the dorsal fin (and the anal fin Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Ecology (journal)
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms that inhabit the sea. Given that in biology many scientific classification, phyla, family (biology), families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment (biophysical), environment rather than on taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. A large proportion of all life, life on Earth lives in the ocean. The exact size of this "large proportion" is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world, covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
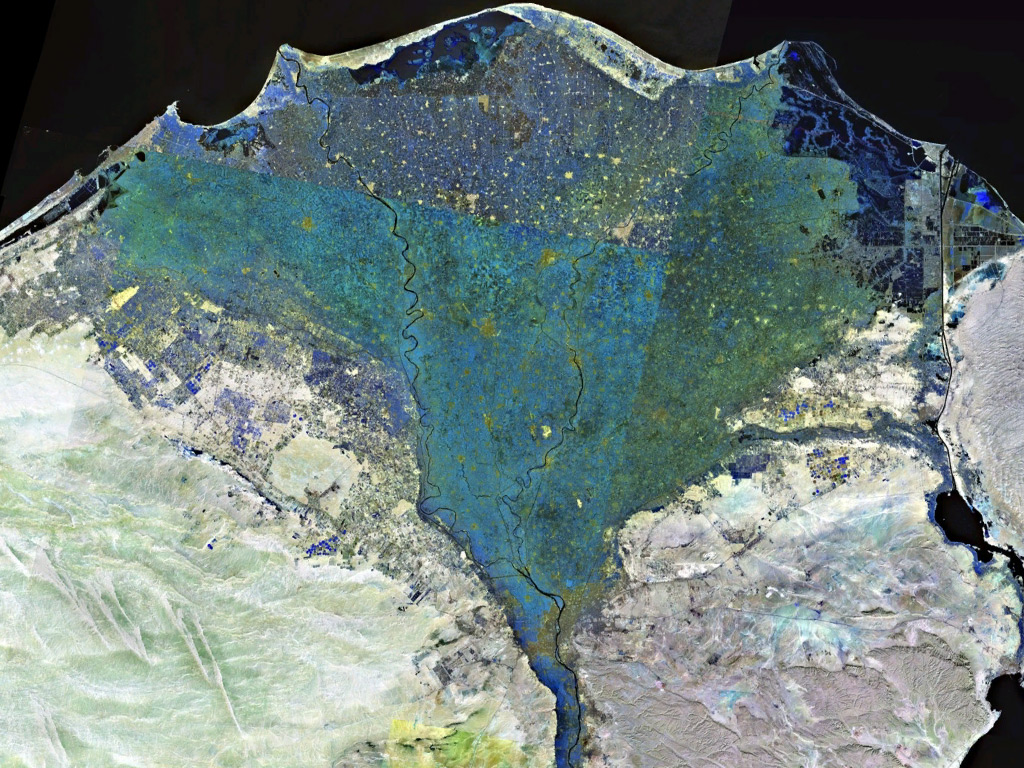
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta (, or simply , ) is the River delta, delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's larger deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east; it covers of the Mediterranean coastline and is a rich agricultural region. From north to south the delta is approximately in length. The Delta begins slightly down-river from Cairo. Geography From north to south, the delta is approximately in length. From west to east, it covers some of coastline. The delta is sometimes divided into sections, with the Nile dividing into two main distributary, distributaries, the Damietta and the Rosetta, flowing into the Mediterranean at port cities with the same names. In the past, the delta had several distributaries, but these have been lost due to flood management, flood control, silting and changing relief. One such defunct distributary is Wadi Tumilat. The Suez Canal is east of the delta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |