|
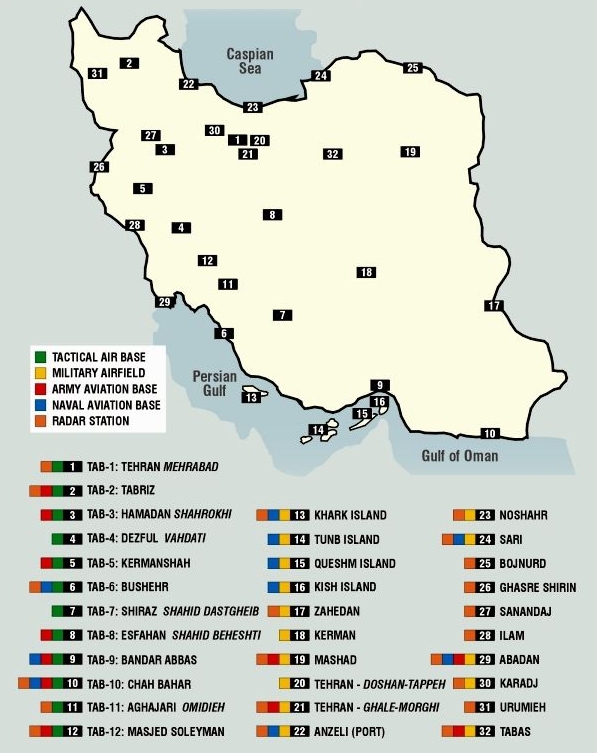
Censorship Of Maps
Cartographic censorship is the deliberate modification of publicly available maps in order to disguise, remove, or obfuscate potentially strategic locations or buildings, such as military bases, power plants or transmitters. Sensitive objects and places have been removed from maps since historic times, sometimes as a disinformation tactic in times of war, and also to serve competitive political and economic interests, such as during the Age of Discovery when strategic geographic information was highly sought after. In modern times requests for censorship are sent to Google Earth for certain sites that are deemed to pose security risks for national governments. History The renowned map historian, J.B. Harley, wrote in 1989: Throughout the history of modern cartography in the West ... there have been numerous instances of where maps have been falsified, of where they have been censored or kept secret, or of where they have surreptitiously contradicted the rules of their proclaimed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Base
A military base is a facility directly owned and operated by or for the military or one of its branches that shelters military equipment and personnel, and facilitates training and operations. A military base always provides accommodations for one or more units, but it may also be used as a command center, training ground or proving ground. In most cases, military bases rely on outside help to operate. However, certain complex bases are able to endure on their own for long periods because they are able to provide food, drinking water, and other necessities for their inhabitants while under siege. Bases for military aviation are called air bases. Bases for military ships are called naval bases. Jurisdictional definition Military bases within the United States are considered federal property and are subject to federal law. Civilians (such as family members of military officers) living on military bases are generally subject to the civil and criminal laws of the stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
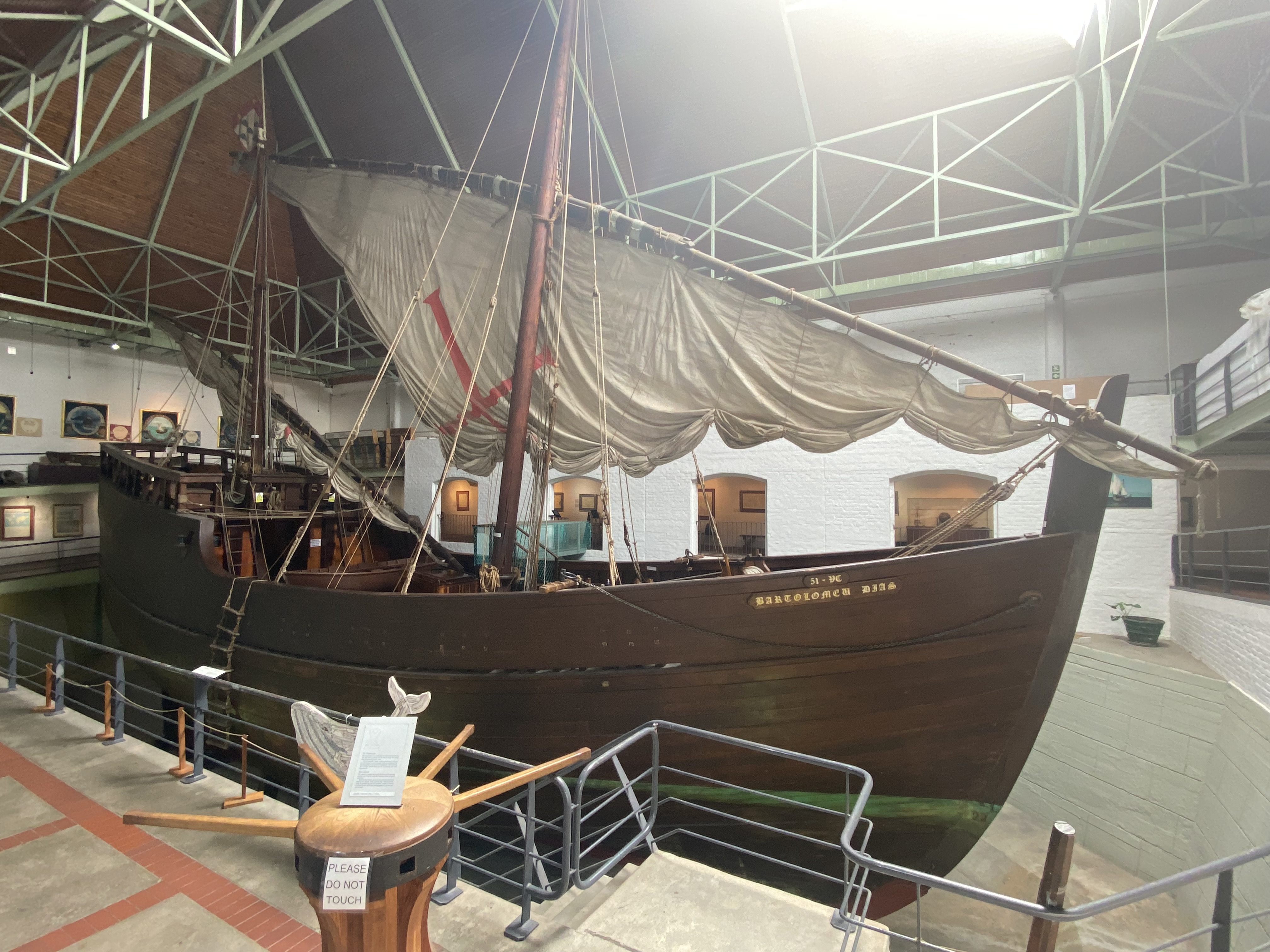
Bartolomeu Dias
Bartolomeu Dias ( – 29 May 1500) was a Portuguese mariner and explorer. In 1488, he became the first European navigator to round the Cape Agulhas, southern tip of Africa and to demonstrate that the most effective southward route for ships lies in the open ocean, well to the west of the African coast. His discoveries were later used by Vasco da Gama to establish a sea route between Europe and Asia. Early life Bartolomeu Dias was born around 1450 in the Faro District of Portugal. His family had a maritime background, and one of his ancestors, Dinis Dias, explored the African coast in the 1440s and discovered the Cap-Vert peninsula in today's Senegal in 1445. Tracing his biography is complicated by the existence of several contemporary Portuguese seafarers with the same name. In 1481, Dias accompanied an expedition, led by Diogo de Azambuja, to construct a fortress and trading post called São Jorge da Mina in the Gulf of Guinea. Indirect evidence also points to his possible pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bass Strait
Bass Strait () is a strait separating the island state of Tasmania from the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland (more specifically the coast of Victoria (Australia), Victoria, with the exception of the land border across Boundary Islet). The strait provides the most direct waterway between the Great Australian Bight and the Tasman Sea, and is also the only maritime route into the economically prominent Port Phillip Bay. Formed 8,000 years ago by rising sea levels at the end of the last glacial period, the strait was named after English explorer and physician George Bass (1771–1803) by History of Australia (1788–1850), European colonists. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of Bass Strait as follows: :''On the west.'' The eastern limit of the Great Australian Bight [being a line from Cape Otway, Australia, to King Island (Tasmania), King Island and thence to Cape Grim, the northwest extreme of Tasmania]. :''On the east.'' The western li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany Bay
Botany Bay (Dharawal language, Dharawal: ''Kamay'') is an open oceanic embayment, located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia, south of the Sydney central business district. Its source is the confluence of the Georges River at Taren Point and Sans Souci, New South Wales, Sans Souci as well as the Cooks River at Kyeemagh, which flows to the east before meeting its river mouth, mouth at the Tasman Sea, midpoint between the suburbs of La Perouse, New South Wales, La Perouse and Kurnell. The northern headland of the entrance to the bay from the Tasman Sea is Cape Banks, and, on the southern side, the outer headland is Cape Solander, and the inner headland is Sutherland Point. The total catchment area of the bay is approximately . Despite its relative shallowness, the bay now serves as greater metropolitan Sydney's main cargo port, seaport, located at Port Botany (seaport), Port Botany, with Port operator, facilities managed by Port Authority of New South Wales, Sydney Ports Cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Jackson
Port Jackson, commonly known as Sydney Harbour, is a natural harbour on the east coast of Australia, around which Sydney was built. It consists of the waters of Sydney Harbour, Middle Harbour, North Harbour and the Lane Cove and Parramatta Rivers. The harbour is an inlet of the Tasman Sea (part of the South Pacific Ocean). It is the location of significant landmarks such as the Sydney Opera House and Sydney Harbour Bridge. The location of the first European settlement and colony on the Australian mainland, Port Jackson has continued to play a key role in the history and development of Sydney. Port Jackson, in the early days of the colony, was also used as a shorthand for Sydney and its environs. Thus, many botanists, see, e.g., Robert Brown's '' Prodromus Florae Novae Hollandiae et Insulae Van Diemen'', described their specimens as having been collected at Port Jackson. Many recreational events are based on or around the harbour itself, particularly Sydney New Year's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Hundred Years War
The Second Hundred Years' War is a periodization or historical era term used by some historians to describe the series of military conflicts around the globe between Great Britain and France that occurred from about 1689 (or some say 1714) to 1815, including several separate wars such as the Nine Years' War, the War of the Spanish Succession, the War of the Austrian Succession, the Seven Years' War, the American Revolutionary War and the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. The Second Hundred Years' War is named after the Hundred Years' War, which occurred in the 14th and 15th centuries. The term appears to have been coined by J. R. Seeley in his influential work '' The Expansion of England'' (1883). Background Like the Hundred Years' War, this term does not describe a single military event but a persistent general state of war between the two primary belligerents. The use of the phrase as an overarching category indicates the interrelation of all the wars as components of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 1768 and 1779. He completed the first recorded circumnavigation of the main islands of New Zealand and was the first known European to visit the eastern coastline of Australia and the Hawaiian Islands. Cook joined the British merchant navy as a teenager before enlisting in the Royal Navy in 1755. He served during the Seven Years' War, and subsequently surveyed and mapped much of the entrance to the St. Lawrence River during the Battle of the Plains of Abraham, siege of Quebec. In the 1760s, he mapped the coastline of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland and made important astronomical observations which brought him to the attention of the Admiralty (United Kingdom), Admiralty and the Royal Society. This acclaim came at a crucial moment in Brit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy. Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the United Kingdom, Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early Admiralty in the 18th century, 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board (United Kingdom), Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), Navy Department (later Navy Command (Ministry of Defence), Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( 1540 – 28 January 1596) was an English Exploration, explorer and privateer best known for making the Francis Drake's circumnavigation, second circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition between 1577 and 1580 (being the first English expedition to accomplish this). He is also known for participating in the early English slaving voyages of his cousin, John_Hawkins_(naval_commander), John Hawkins, and John_Lovell_(slave_trader), John Lovell. Having started as a simple seaman, in 1588 he was part of the fight against the Spanish Armada as a vice admiral. At an early age, Drake was placed into the household of a relative, William Hawkins (died c. 1554), William Hawkins, a prominent sea captain in Plymouth. In 1572, he set sail on his Francis Drake's expedition of 1572–1573, first independent mission, privateering along the Spanish Main. Drake's circumnavigation began on 15 December 1577. He crossed the Pacific Ocean, until then an area of exclusive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Passage
The Northeast Passage (abbreviated as NEP; , ) is the Arctic shipping routes, shipping route between the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific Oceans, along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Russia. The western route through the islands of Canada is accordingly called the Northwest Passage (NWP). The NEP traverses (from west to east) the Barents Sea, Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, East Siberian Sea, and Chukchi Sea, and it includes the Northern Sea Route (NSR). The Northern Sea Route is a portion of the NEP. It is defined in Russian law and does not include the Barents Sea and therefore does not reach the Atlantic Ocean. However, since the NSR has a significant overlap over the majority of the NEP, the NSR term is often used to refer to the entirety of the Northeast Passage. This practice injects confusion in understanding the specifics of both navigational procedures and jurisdiction. The Northeast Passage is one of several Arctic maritime routes, the others being the Northwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk, and Omsk are the largest cities in the area. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, with the Ural River usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Engel
Samuel Engel (2 December 1702 – 26 March 1784) was a Swiss librarian, civil servant, economist and agronomist working in Bern who introduced innovations in several fields. The son of a Vogt (Switzerland), Landvogt, he studied at the University of Bern before starting a career in administration. In 1736, he became head librarian of the city library of Bern. He assembled a large collection of rare books that was intended for the library, but had to sell them at a loss. In 1745, he became a member of the Grand Council of Bern; from 1748, he was a Landvogt himself. He introduced several innovations in forestry and agriculture such as promoting potato farming in Vaud. A keen amateur geographer, Engel was convinced of the existence of a Northeast Passage and published several influential books about the Arctic. His theories about an Open Polar Sea, ice-free polar sea influenced the British Admiralty's decision in favour of the 1773 Phipps expedition towards the North Pole. Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |