|
Cellulosic Ethanol
Cellulosic ethanol is ethanol (ethyl alcohol) produced from cellulose (the stringy fiber of a plant) rather than from the plant's seeds or fruit. It can be produced from grasses, wood, algae, or other plants. It is generally discussed for use as a biofuel. The carbon dioxide that plants Photosynthesis, absorb as they grow offsets some of the carbon dioxide emitted when ethanol made from them is Combustion, burned, so cellulosic ethanol fuel has the potential to have a lower carbon footprint than fossil fuels. Interest in cellulosic ethanol is driven by its potential to replace Corn ethanol, ethanol made from corn or sugarcane. Since these plants are also used for food products, diverting them for ethanol production can cause food prices to rise; cellulose-based sources, on the other hand, generally do not compete with food, since the fibrous parts of plants are mostly inedible to humans. Another potential advantage is the high diversity and abundance of cellulose sources; grasses, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl group, ethyl. Ethanol is a Volatility (chemistry), volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the Chemical synthesis, synthesis of orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Experiment
A pilot experiment, pilot study, pilot test or pilot project is a small-scale preliminary study conducted to evaluate feasibility, duration, cost, adverse events, and improve upon the study design prior to performance of a full-scale research project. Implementation Pilot experiments are frequently carried out before large-scale quantitative research, in an attempt to avoid time and money being used on an inadequately designed project. A pilot study is usually carried out on members of the relevant population. A pilot study is used to formulate the design of the full-scale experiment which then can be adjusted. The pilot study is potentially a critical insight to clinical trial design, recruitment and sample size of participants, treatment testing, and statistical analysis to improve the power of testing the hypothesis of the study. Analysis from the pilot experiment can be added to the full-scale (and more expensive) experiment to improve the chances of a clear outcome. Appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington University
The George Washington University (GW or GWU) is a Private university, private University charter#Federal, federally-chartered research university in Washington, D.C., United States. Originally named Columbian College, it was chartered in 1821 by the United States Congress and is the first university founded under Washington, D.C.'s jurisdiction. It is one of the nation's six University charter#Federal, federally chartered universities. GW is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among List of research universities in the United States#Universities classified as "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity", "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very High Research Activity." It is a member of the Association of American Universities. The university offers degree programs in seventy-one disciplines, enrolling around 11,500 Undergraduate education, undergraduate and 15,000 Graduate school, graduate students. The school's athletic teams, the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Court Of Appeals For The District Of Columbia
The United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit (in case citations, D.C. Cir.) is one of the thirteen United States Courts of Appeals. It has the smallest geographical jurisdiction of any of the U.S. courts of appeals, and it covers only the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia. It meets at the E. Barrett Prettyman United States Courthouse in Washington, DC. The D.C. Circuit is often considered to be second only to the U.S. Supreme Court in status and prestige, and it is sometimes unofficially termed "the second highest court in the land". Because its jurisdiction covers the District of Columbia, it tends to be the main federal appellate court for issues of U.S. administrative law and constitutional law. Four of the nine current Supreme Court justices were previously judges on the D.C. Circuit: Chief Justice John Roberts and associate justices Clarence Thomas, Brett Kavanaugh, and Ketanji Brown Jackson. Past justices Ruth Bader Ginsburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field in the United States. Member of the National Academy of Sciences, Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve ''pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Congress legislated and President Abraham Lincoln signed an Act of Congress (1863) establishing the National Academy of Sciences as an independent, trusted nongovernmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium. Methane is a colorless and odorless gas, and, after carbon dioxide, is the second-greatest greenhouse gas that contributes to global climate change. Because natural gas is odorless, a commercial odorizer, such as Methanethiol (mercaptan brand), that smells of hydrogen sulfide (rotten eggs) is added to the gas for the ready detection of gas leaks. Natural gas is a fossil fuel that is formed when layers of organic matter (primarily marine microorganisms) are thermally decomposed under oxygen-free conditions, subjected to intense heat and pressure underground over millions of years. The energy that the decayed organisms originally obtained from the sun via photosynthesis is stored as chemical energy within the molecules of methane and other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
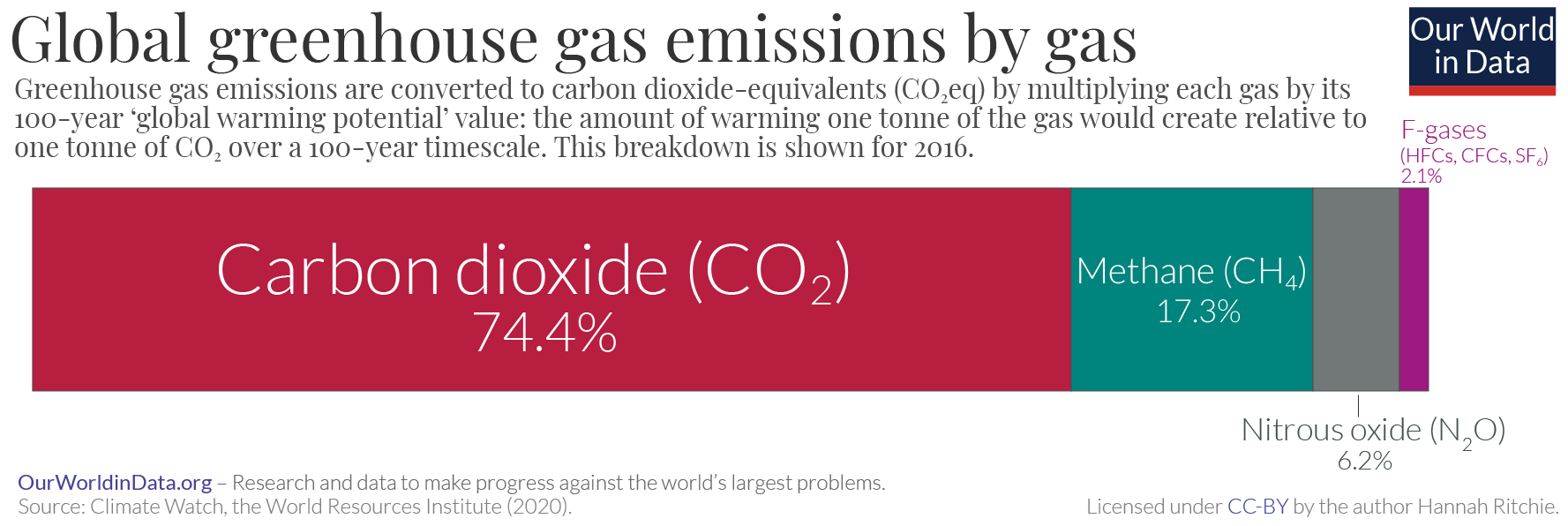
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The top contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has List of countries by greenhouse gas emissions per capita, higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are Big Oil, large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased Carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (177 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miscanthus
''Miscanthus'', or silvergrass'','' is a genus of African, Eurasian, and Pacific Island plants in the grass family, Poaceae. The name is derived from the Greek words "''miskos"'', meaning "stem", and "''anthos"'', meaning "flower", in reference to the stalked spikelets on plants of this genus. Several species are known for their height and biomass production, and may be used as ornamental grasses. Species 14 species are accepted. * '' Miscanthus depauperatus'' Merr. – the Philippines * '' Miscanthus ecklonii'' (Nees) Mabb. – southern Africa * '' Miscanthus floridulus'' – China, Japan, Southeast Asia, Pacific Islands * '' Miscanthus fuscus'' (Roxb.) Benth. – Indian Subcontinent, Indochina, Pen Malaysia * '' Miscanthus × longiberbis'' – northeastern China, Korea, and Japan * '' Miscanthus lutarioriparius'' L.Liu ex S.L.Chen & Renvoize – Hubei, Hunan * '' Miscanthus nepalensis'' (Trin.) Hack. – Indian Subcontinent, Tibet, Yunnan, Myanmar, Vietnam, Peninsular Malays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panicum Virgatum
''Panicum virgatum'', commonly known as switchgrass, is a perennial warm season bunchgrass native to North America, where it occurs naturally from 55th parallel north, 55°N latitude in Canada southwards into the United States and Mexico. Switchgrass is one of the dominant species of the central North American tallgrass prairie and can be found in remnant prairies, in native grass pastures, and naturalized along roadsides. It is used primarily for soil conservation, forage production, game cover, as an ornamental grass, in phytoremediation projects, fiber, electricity, heat production, for biosequestration of atmospheric carbon dioxide, and more recently as a biomass crop for the production of ethanol and butanol. Other common names for switchgrass include tall panic grass, Wobsqua grass, blackbent, tall prairiegrass, wild Agrostis, redtop, thatchgrass, and Virginia switchgrass. Description Switchgrass is a hardy, deep-rooted, Perennial plant, perennial rhizome, rhizomatous gras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood Pulp
Pulp is a fibrous Lignocellulosic biomass, lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulose fiber, cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, Paper recycling, waste paper, or cotton paper, rags. Mixed with water and other chemicals or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other Pulp and paper industry, paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around AD 105, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of Bark (botany), bark or Bast fibre, bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corn Stover
Corn stover consists of the leaves, stalks, and cobs of corn (maize) (''Zea mays'' ssp. ''mays'' L.) plants left in a field after harvest. Such stover makes up about half of the yield of a corn crop and is similar to straw from other cereal grasses; in Britain it is sometimes called corn straw. Corn stover is a very common agricultural product in areas of large amounts of corn production. As well as the non-grain part of harvested corn, the stover can also contain other weeds and grasses. Field corn and sweet corn, two different types of maize, have relatively similar corn stover. Uses Fodder (ensilaged or nonensilaged) Corn stover (like various other kinds of stover) can be used as feed, whether grazed as forage, chopped as silage to be used later for fodder, or collected for direct (nonensilaged) fodder use. Maize forage is usually ensiled in cooler regions, but it can be harvested year-round in the tropics and fed as green forage to the animals. In the silage use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity and do not rot easily. Chemically, lignins are polymers made by cross-linking phenolic precursors. History Lignin was first mentioned in 1813 by the Swiss botanist A. P. de Candolle, who described it as a fibrous, tasteless material, insoluble in water and alcohol but soluble in weak alkaline solutions, and which can be precipitated from solution using acid. He named the substance "lignine", which is derived from the Latin word '' lignum'', meaning wood. It is one of the most abundant organic polymers on Earth, exceeded only by cellulose and chitin. Lignin constitutes 30% of terrestrial non-fossil organic carbon on Earth, and 20 to 35% of the dry mass of wood. Lignin is present in red algae, which suggest that the common ancestor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |