|
Cavity Dumper
In laser science, an output coupler (OC) is the component of an optical resonator that allows the extraction of a portion of the light from the laser's intracavity beam. An output coupler most often consists of a partially reflective mirror, allowing a certain portion of the intracavity beam to transmit through. Other methods include the use of almost-totally reflective mirrors at each end of the cavity, emitting the beam either by focusing it into a small hole drilled in the center of one mirror, or by redirecting through the use of rotating mirrors, prisms, or other optical devices, causing the beam to bypass one of the end mirrors at a given time. Partially reflective mirror In its most common form, an output coupler consists of a partially reflective mirror, sometimes called a beamsplitter. The reflectance and transmittance of the mirror is usually determined by the gain of the laser medium. In some lasers the gain is very low, so the beam must make hundreds of passes thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lasing Threshold
The lasing threshold is the lowest excitation level at which a laser's output is dominated by stimulated emission rather than by spontaneous emission. Below the threshold, the laser's output power rises slowly with increasing excitation. Above threshold, the slope of power vs. excitation is orders of magnitude greater. The linewidth of the laser's emission also becomes orders of magnitude smaller above the threshold than it is below. Above the threshold, the laser is said to be ''lasing''. The term "lasing" is a back formation from "laser," which is an acronym, not an agent noun. Theory The lasing threshold is reached when the optical gain of the laser medium is exactly balanced by the sum of all the losses experienced by light in one round trip of the laser's optical cavity. This can be expressed, assuming steady-state operation, as :R_1 R_2\exp(2g_\text\,l) \exp(-2\alpha l) = 1. Here R_1 and R_2 are the mirror (power) reflectivities, l is the length of the gain medium, \exp( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmittance
Electromagnetic radiation can be affected in several ways by the medium in which it propagates. It can be Scattering, scattered, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorbed, and Fresnel equations, reflected and refracted at discontinuities in the medium. This page is an overview of the last 3. The transmittance of a material and any surfaces is its effectiveness in transmitting radiant energy; the fraction of the initial (incident) radiation which propagates to a location of interest (often an observation location). This may be described by the transmission coefficient. Surface Transmittance Hemispherical transmittance Hemispherical transmittance of a surface, denoted ''T'', is defined as :T = \frac, where *Φet is the radiant flux ''transmitted'' by that surface into the hemisphere on the opposite side from the incident radiation; *Φei is the radiant flux received by that surface. Hemispheric transmittance may be calculated as an integral over the directional trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunable Laser
A tunable laser is a laser whose wavelength of operation can be altered in a controlled manner. While all active laser medium, laser gain media allow small shifts in output wavelength, only a few types of lasers allow continuous tuning over a significant wavelength range. There are many types and categories of tunable lasers. They exist in the gas, liquid, and solid states. Among the types of tunable lasers are excimer lasers, gas lasers (such as CO2 laser, CO2 and helium–neon laser, He-Ne lasers), dye lasers (liquid and solid state), transition-metal solid-state lasers, semiconductor crystal and diode lasers, and free electron laser, free-electron lasers. Tunable lasers find applications in spectroscopy, photochemistry, atomic vapor laser isotope separation, and optical communications. Types of tunability Single line tuning No real laser is truly monochromatic#In physics, monochromatic; all lasers can emit light over some range of frequencies, known as the linewidth of the las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin film, thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, one can design an optical coating with specified reflectivity at different wavelengths of light. Dielectric mirrors are also used to produce ultra-high reflectivity mirrors: values of 99.999% or better over a narrow range of wavelengths can be produced using special techniques. Alternatively, they can be made to reflect a broad spectrum of light, such as the entire visible range or the spectrum of the Ti-sapphire laser. Dielectric mirrors are very common in optics experiments, due to improved techniques that allow inexpensive manufacture of high-quality mirrors. Examples of their applications include laser optical cavity, cavity end mirrors, Hot mirror, hot and cold mirrors, thin-film beam splitter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superradiance
In physics, superradiance, or superradiation, is the radiation enhancement effects in several contexts including quantum mechanics, astrophysics and relativity. Quantum optics In quantum optics, superradiance is a phenomenon that occurs when a group of ''N'' emitters, such as excited atoms, interact with a common light field. If the wavelength of the light is much greater than the separation of the emitters, then the emitters interact with the light in a collective and coherent fashion. This causes the group to emit light as a high-intensity pulse (with rate proportional to ''N''2). This is a surprising result, drastically different from the expected exponential decay (with rate proportional to ''N'') of a group of independent atoms (see spontaneous emission). Superradiance has since been demonstrated in a wide variety of physical and chemical systems, such as quantum dot arrays and J-aggregates. This effect has been used to produce a superradiant laser. Rotational superra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Laser
A nitrogen laser is a gas laser operating in the ultraviolet rangeC. S. Willett, ''Introduction to Gas Lasers: Population Inversion Mechanisms'' (Pergamon, New York,1974). (typically 337.1 nm) using molecular nitrogen as its gain medium, laser pumping, pumped by an electrical discharge. The wall-plug efficiency of the nitrogen laser is low, typically 0.1% or less, though nitrogen lasers with efficiency of up to 3% have been reported in the literature. The wall-plug efficiency is the product of the following three efficiencies: * electrical: TEA laser * gain medium: This is the same for all nitrogen lasers and thus has to be at least 3% ** inversion by electron impact is 10 to 1 due to Franck–Condon principle ** energy lost in the lower laser level: 40% * optical: More stimulated emission than spontaneous emission Gain medium The gain medium is nitrogen molecules in the gas phase. The nitrogen laser is a three-level laser. In contrast to more typical four-level lasers, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium–neon Laser
A helium–neon laser or He–Ne laser is a type of gas laser whose high energetic gain medium consists of a mixture of helium and neon (ratio between 5:1 and 10:1) at a total pressure of approximately 1 Torr (133.322 Pa) inside a small electrical discharge. The best-known and most widely used He-Ne laser operates at a center wavelength of 632.81646 nm (in air), 632.99138 nm (vac), and frequency 473.6122 THz, in the red part of the visible spectrum. Because of the mode structure of the laser cavity, the instantaneous output of a laser can be shifted by up to 500 MHz in either direction from the center. History of He-Ne laser development The first He-Ne lasers emitted infrared at 1150 nm, and were the first gas lasers and the first lasers with continuous wave output. However, a laser that operated at visible wavelengths was much more in demand. A number of other neon transitions were investigated to identify ones in which a population inversion could be achi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
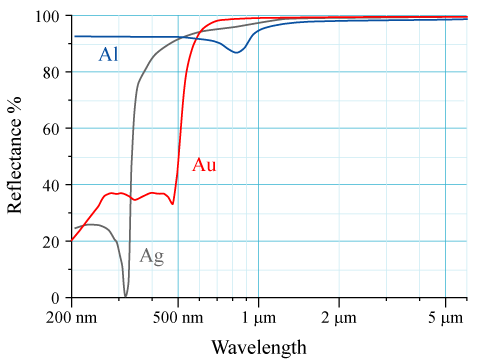
Reflectance
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Flat
An optical flat is an Optics, optical-grade piece of glass lapping, lapped and polishing, polished to be extremely flat on one or both sides, usually within a few tens of nanometres (billionths of a metre). They are used with a monochromatic light to determine the flatness (manufacturing), flatness (surface accuracy) of other surfaces (whether optical, metallic, ceramic, or otherwise), by means of Interference (wave propagation), wave interference. When an optical flat is placed on another surface and illuminated, the light waves reflect off both the bottom surface of the flat and the surface it is resting on. This causes a phenomenon similar to thin-film interference. The reflected waves interfere, creating a pattern of interference fringes visible as light and dark bands. The spacing between the fringes is smaller where the gap is changing more rapidly, indicating a departure from flatness in one of the two surfaces. This is comparable to the contour lines one would find on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy (and its applications to chemistry), quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms. Interferometers are devices that extract information from interference. They are widely used in science and industry for the measurement of microscopic displacements, refractive index changes and surface irregularities. In the case with most interferometers, light from a single source is split into two beams that travel in different optical paths, which are then combined again to produce interference; two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |