|
Cave Of The Minor Sanhedrin
The Cave of the Minor Sanhedrin is a burial cave located next to the Tomb of Simeon the Just in the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood of Jerusalem. It contains 26 burial niches, in which the 26{{citation needed, date=October 2016 members of the Minor Sanhedrin are said to be buried. There are also other burial caves in the complex. The cave was plundered in the 19th century by Louis Félicien de Saulcy and another French archaeologist. They plundered the contents of the caves, scattering the bones of the buried people around the cave, before fleeing to the Jaffa port. This infuriated the local Jewish community, who turned to public figures like Moses Montefiore who acted to get the Turkish government to cancel their license to excavate. The bones were collected by local Jews, and buried in a grave next to the nearby Tomb of Simeon the Just. Artifacts from within the cave, including burial vaults and stones with Hebrew writing on them, are now displayed in the Louvre museum. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Simeon The Just
The Tomb of Simeon the Just or Simeon the Righteous ( he, קבר שמעון הצדיק; translit. ''Kever Shimon haTzadik'') is an ancient tomb in Jerusalem. According to scholarly consensus, based on an ''in situ'' inscription, it is the 2nd-century CE burial site of a Roman matron named Julia Sabina. However, according to a medieval Jewish tradition, is believed to be the burial place of Simeon the Just and his students. It is located adjacent to the Cave of the Minor Sanhedrin in the Shimon HaTzadik settlement within the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood. Identification Galilee location In the 12th century, Benjamin of Tudela wrote that the tomb of Simeon was at "Tymin or Timnathah", between Tiberias and Meiron. Jerusalem location Rabbi Jacob, the messenger of Jehiel of Paris, wrote in 1238–1244 that "the cave of Simeon the Just and his disciples is near Jerusalem". Obadiah da Bertinoro wrote around 1490 that "The sepulchre of the seventy Elders, which lies about 2,000 cubits fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheikh Jarrah
Sheikh Jarrah ( ar, الشيخ جراح, he, שייח' ג'ראח) is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, north of the Old City, on the road to Mount Scopus. It received its name from the 13th-century tomb of Sheikh Jarrah, a physician of Saladin, located within its vicinity. The modern neighborhood was founded in 1865 and gradually became a residential center of Jerusalem's Muslim elite, particularly the al-Husayni family. After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, it bordered the no-man's land area between Jordanian-held East Jerusalem and Israeli-held West Jerusalem until the neighborhood was occupied by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. Most of its present Palestinian population is said to come from refugees expelled from Jerusalem's Talbiya neighbourhood in 1948. Certain properties are subject of legal proceedings based on the application of two Israeli laws, the Absentee Property Law and the Legal and Administrative Matters Law of 1970. Israeli natio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. is a city in Western Asia. Situated on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea, it is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world and is considered to be a holy city for the three major Abrahamic religions: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their Capital city, capital, as Israel maintains its primary governmental institutions there and the State of Palestine ultimately foresees it as its seat of power. Because of this dispute, Status of Jerusalem, neither claim is widely recognized internationally. Throughout History of Jerusalem, its long history, Jerusalem has been destroyed at least twice, Sie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
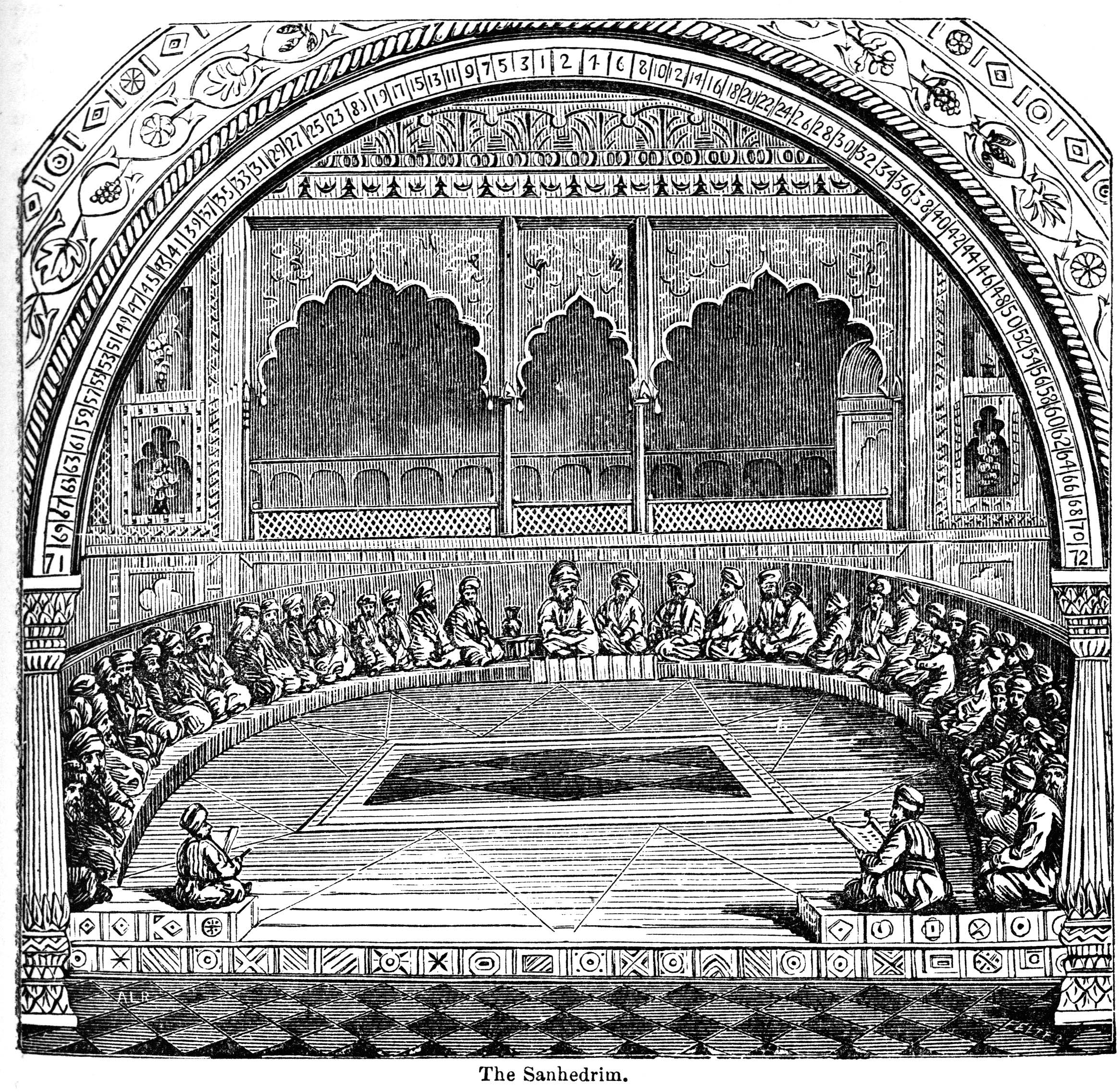
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the '' Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the '' Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Félicien De Saulcy
Louis Félicien Joseph Caignart de Saulcy (19 March 1807 – 4 November 1880), better known as simply Félicien or Félix de Saulcy, was a French numismatist, Orientalist, and archaeologist. Early life Louis Felicien de Saulcy was born in Lille, France, the scion of a noble family. Career In 1843, De Saulcy deciphered the Libyco-Berber script almost fully, thanks to the Punic-Libyan Inscription. He travelled though Syria and Palestine in 1850–51, 1863, and 1869. On his first trip to Palestine in 1850, searching for something of interest "in a place fraught with danger", he toured the Dead Sea area, misidentified Sodom and Gomorrah, and sketched the first map of Masada.A royal return '''' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaffa
Jaffa, in Hebrew Yafo ( he, יָפוֹ, ) and in Arabic Yafa ( ar, يَافَا) and also called Japho or Joppa, the southern and oldest part of Tel Aviv-Yafo, is an ancient port city in Israel. Jaffa is known for its association with the biblical stories of Jonah, Solomon and Saint Peter as well as the mythological story of Andromeda and Perseus, and later for its oranges. Today, Jaffa is one of Israel's mixed cities, with approximately 37% of the city being Arab. Etymology The town was mentioned in Egyptian sources and the Amarna letters as ''Yapu''. Mythology says that it is named for Yafet (Japheth), one of the sons of Noah, the one who built it after the Flood. The Hellenist tradition links the name to ''Iopeia'', or Cassiopeia, mother of Andromeda. An outcropping of rocks near the harbor is reputed to have been the place where Andromeda was rescued by Perseus. Pliny the Elder associated the name with Iopa, daughter of Aeolus, god of the wind. The medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moses Montefiore
Sir Moses Haim Montefiore, 1st Baronet, (24 October 1784 – 28 July 1885) was a British financier and banker, activist, philanthropist and Sheriff of London. Born to an Italian Sephardic Jewish family based in London, after he achieved success, he donated large sums of money to promote industry, business, economic development, education and health among the Jewish community in the Levant. He founded Mishkenot Sha'ananim in 1860, the first settlement outside the Old City of Jerusalem. As President of the Board of Deputies of British Jews, he corresponded with Charles Henry Churchill, the British consul in Damascus, in 1841–42; his contributions are seen as pivotal to the development of Proto-Zionism. Early life Moses Montefiore was born in Leghorn (Livorno in Italian), Tuscany, in 1784, to a Sephardic Jewish family based in Great Britain. His grandfather, Moses Vital (Haim) Montefiore, had emigrated from Livorno to London in the 1740s, but retained close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louvre Museum
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central landmark of the city, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement (district or ward). At any given point in time, approximately 38,000 objects from prehistory to the 21st century are being exhibited over an area of 72,735 square meters (782,910 square feet). Attendance in 2021 was 2.8 million due to the COVID-19 pandemic, up five percent from 2020, but far below pre-COVID attendance. Nonetheless, the Louvre still topped the list of most-visited art museums in the world in 2021."The Art Newspaper", 30 March 2021. The museum is housed in the Louvre Palace, originally built in the late 12th to 13th century under Philip II. Remnants of the Medieval Louvre fortress are visible in the basemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalistic
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The definition of Kabbalah varies according to the tradition and aims of those following it, from its origin in medieval Judaism to its later adaptations in Western esotericism (Christian Kabbalah and Hermetic Qabalah). Jewish Kabbalah is a set of esoteric teachings meant to explain the relationship between the unchanging, eternal God—the mysterious ''Ein Sof'' (, ''"The Infinite"'')—and the mortal, finite universe (God's creation). It forms the foundation of mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. Jewish Kabbalists originally developed their own transmission of sacred texts within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. These teachings are held by Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock-cut Tombs In Israel
Rock-cut tombs were a form of burial and interment chamber used in ancient Israel. Cut into the landscapes surrounding ancient Judean cities, their design ranges from single chambered, with simple square or rectangular layouts, to multi-chambered with more complex designs. Almost all burial chambers contain a platform for primary burial and an ossuary or other receptacle for secondary burial. There is debate on if these tombs were originally intended for secondary burials, or if that practice arose later. The use of rock-cut cave tombs in the region began in the early Canaanite period, from 3100–2900 BCE. The custom lapsed a millennium, however, before re-emerging in the earliest Israelite tombs, dating to the 9th century BCE in Jerusalem. The use of rock-cut tombs reached its peak in the 7th and 8th centuries BCE, before rapidly declining and eventually falling out of use in the 6th century BCE in some regions. Use of the tombs has been recorded as recently as the late Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tombs Of The Sanhedrin
Tombs of the Sanhedrin ( he, קברי הסנהדרין, ''Kivrei HaSanhedrin''), also Tombs of the Judges, is an underground complex of 63 rock-cut tombs located in a public park in the northern Jerusalem neighborhood of Sanhedria. Built in the 1st century CE, the tombs are noted for their elaborate design and symmetry. They have been a site for Jewish pilgrimage since the medieval period. The popular name of the complex, which has the most magnificently carved pediment of ancient Jerusalem, is due to the fact that the number of burial niches it contains is somewhat close to that of the members of the ancient Jewish supreme court, the Great Sanhedrin, namely 71. Name In 1235 Rabbi Jacob the Emissary called them the "Tombs of the Righteous", writing that the tombs housed the remains of "many wise men". They were first called the Tombs of the Sanhedrin by Rabbi Joseph Halevi in 1450, and have been known by that name among Jews ever since. In Christian literature, Joannes Cotovic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |