|
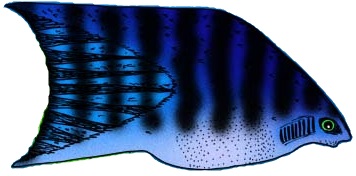
Caucasian Dwarf Goby
''Knipowitschia caucasica'', the Caucasian dwarf goby, is a species of goby native to marine, fresh and brackish waters along the coasts of the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov, the Caspian Sea and the Aegean Sea and to the Haliacmon drainage of Greece. It inhabits shallow waters () with plentiful weed growth where it can find its prey consisting of small crustaceans, the larvae of chironomids and the larvae of the mussel ''Dreissena polymorpha The zebra mussel (''Dreissena polymorpha'') is a small freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Dreissenidae. The species originates from the lakes of southern Russia and Ukraine, but has been accidentally introduced to nume ...''. Spawning takes place after their first winter with the eggs being deposited onto the roof of a cavity formed by rocks, shells or plant materials. The male will remain to defend the eggs. This species can reach a length of TL References Caucasian dwarf goby Fish of the Mediterranea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Berg
Lev Semyonovich Berg, also known as Leo S. Berg (; 14 March 1876 – 24 December 1950) was a leading Russian geographer, biologist and ichthyologist who served as President of the Soviet Geographical Society between 1940 and 1950. He is known for his own evolutionary theory, nomogenesis (a form of orthogenesis incorporating mutationism) as opposed to the theories of Darwin and Lamarck. Life Lev Berg was born in Bessarabia in a Jewish family, the son of Simon Gregoryevich Berg, a notary, and Klara Lvovna Bernstein-Kogan. He graduated from the Second Kishinev Gymnasium in 1894. Like some of his relatives, Berg converted to Christianity in order to pursue his studies at Moscow State University. At Moscow University, Berg studied hydrobiology and geography. He later studied ichthyology and in 1928 was awarded he was also a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Lev Berg graduated from the Moscow State University in 1898. Between 1903 and 1914, he worked in the Museum of Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which are often more or less rounded or oval. The word "mussel" is frequently used to mean the bivalves of the marine family Mytilidae, most of which live on exposed shores in the intertidal zone, attached by means of their strong Byssus, byssal threads ("beard") to a firm substrate. A few species (in the genus ''Bathymodiolus'') have colonised hydrothermal vents associated with deep ocean ridges. In most marine mussels the shell is longer than it is wide, being wedge-shaped or asymmetrical. The external colour of the shell is often dark blue, blackish, or brown, while the interior is silvery and somewhat nacreous. The common name "mussel" is also used for many freshwater bivalves, including the freshwater pearl mussels. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Caspian Sea
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of Asia
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Black Sea
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Mediterranean Sea
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knipowitschia
''Knipowitschia'' is a genus of marine, fresh and brackish water gobies native to Eurasia. The genus name almost certainly honours Nikolai Mikhailovich Knipovich (1862-1938), a biologist who led a number of expeditions to the Caspian Sea. Species There are currently 17 recognized species in this genus: * '' Knipowitschia byblisia'' Ahnelt, 2011 (Byblis goby) * '' Knipowitschia cameliae'' Nalbant Nalbant is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Nalbant, Nicolae Bălcescu (since 1948; until 1923 ''Bașchioi''; '' Principele Mihai'' from 1923 to 1948) and Trestenic. The commune's name comes ... & Oţel, 1995 (Danube delta dwarf goby) * '' Knipowitschia caucasica'' ( L. S. Berg, 1916) (Caucasian dwarf goby) * '' Knipowitschia caunosi'' Ahnelt, 2011 (Caunos goby) * '' Knipowitschia croatica'' Mrakovčić, Kerovec, Mišetić & D. Schneider, 1996 (Neretva dwarf goby) * '' Knipowitschia ephesi'' Ahnelt, 1995 * '' Knipowitschia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
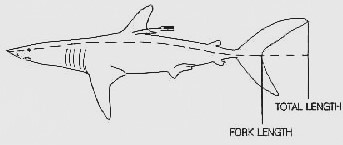
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dreissena Polymorpha
The zebra mussel (''Dreissena polymorpha'') is a small freshwater mussel, an aquatic bivalve mollusk in the family Dreissenidae. The species originates from the lakes of southern Russia and Ukraine, but has been accidentally introduced to numerous other areas and has become an invasive species in many countries worldwide. Since the 1980s, the species has invaded the Great Lakes, Hudson River, Lake Travis, Finger Lakes, Lake Bonaparte, and Lake Simcoe. The adverse effects of dreissenid mussels on freshwater systems have led to their ranking as one of the world's most invasive aquatic species. The species was first described in 1769 by German zoologist Peter Simon Pallas in the Ural, Volga, and Dnieper Rivers. Zebra mussels get their name from a striped pattern commonly seen on their shells, though it is not universally present. They are usually about the size of a fingernail, but can grow to a maximum length around . Their shells are D-shaped, and attached to the substrate wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chironomid
Chironomidae , commonly known as non-biting midges or chironomids , are a family of Nematoceran flies with a global distribution. They are closely related to the families Ceratopogonidae, Simuliidae, and Thaumaleidae. Although many chironomid species superficially resemble mosquitoes, they can be distinguished by the absence of wing scales and elongated mouthparts characteristic of the Culicidae (true mosquitoes). The name Chironomidae stems from the Ancient Greek word ''kheironómos'', "a pantomimist". Common names and biodiversity This is a large taxon of insects. Some estimates of the species numbers suggest well over 10,000 world-wide. Males are easily recognized by their plumose antennae. Adults are known by a variety of vague and inconsistent common names, largely by confusion with other insects. For example, chironomids are known as "lake flies" in parts of Canada and Lake Winnebago, Wisconsin, but "bay flies" in the areas near the bay of Green Bay, Wisconsin. They ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Kessler
Karl Fedorovich Kessler (; – ) was a Baltic German zoologist who worked as a professor of biology at Saint Petersburg Imperial University. Among his contributions was the idea that evolution at an infraspecific level involved mutual aid and that Charles Darwin had placed too much emphasis on competition which he accepted as occurring at the interspecies level. Life and work Kessler was born in Damrau, Konigsberg, where his father was a royal forester (''oberforestmeister''). His father moved to Novgorod Governorate, where Kessler grew up. In 1828, he joined the with a scholarship and went to Saint Petersburg Imperial University in 1834. He attended the zoology lectures of Stepan Kutorga. After graduation he worked as a school mathematics teacher. In 1837, Kessler and his botanist friend from student days, went on an expedition to Finland. In 1840, he defended a master's dissertation on the legs of birds in relation to systematics. In 1842, his doctoral dissertation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |