|
Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) is an antimicrobial peptide encoded in the human by the ''CAMP'' gene. The active form is LL-37. In humans, ''CAMP'' encodes the peptide precursor CAP-18 (18 kDa), which is processed by proteinase 3-mediated extracellular cleavage into the active form LL-37. The cathelicidin family includes 30 types of which LL-37 is the only cathelicidin in the human. Cathelicidins are stored in the secretory granules of neutrophils and macrophages and can be released following activation by leukocytes. Cathelicidin peptides are dual-natured molecules called amphiphiles: one end of the molecule is attracted to water and repelled by fats and proteins, and the other end is attracted to fat and proteins and repelled by water. Members of this family react to pathogens by disintegrating, damaging, or puncturing cell membranes. Cathelicidins thus serve a critical role in mammalian innate immune defense against invasive bacterial infection. The cathelicidin f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
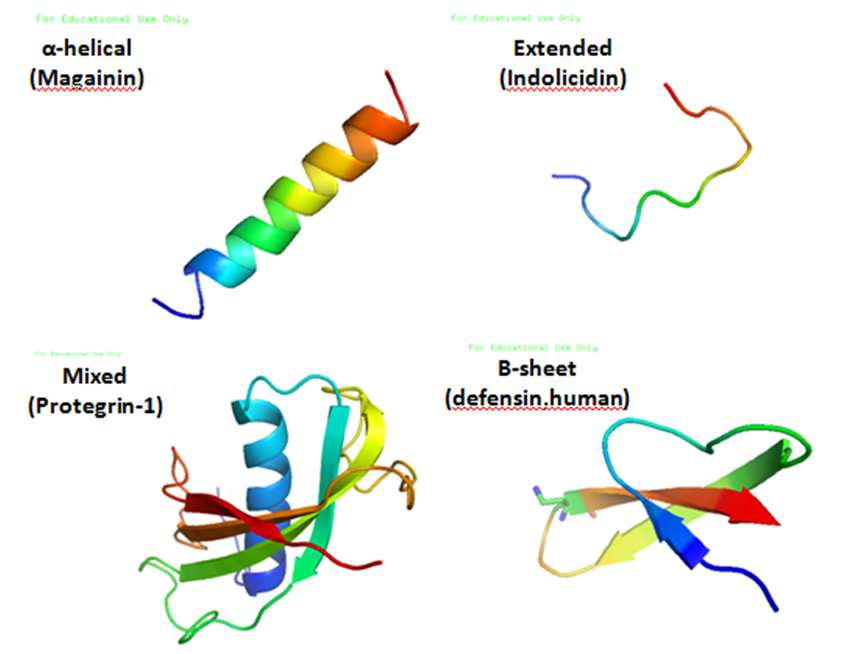
Antimicrobial Peptide
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells that may represent targets for antimicrobial peptides. These peptides are potent, broad spectrum antimicrobials which demonstrate potential as novel therapeutic agents. Antimicrobial peptides have been demonstrated to kill Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi and even transformed or cancerous cells. Unlike the majority of conventional antibiotics it appears that antimicrobial peptides frequently destabilize biological membranes, can form transmembrane channels, and may also have the ability to enhance immunity by functioning as immunomodulators. Structure Antimicrobial peptides are a unique and diverse group of molecules, which are divided into subgroups on the basis of their amino acid composition and structure. Antimicrobial peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle that is found in all mammalian cells, with the exception of red blood cells (erythrocytes). There are normally hundreds of lysosomes in the cytosol, where they function as the cell’s degradation center. Their primary responsibility is catabolic degradation of proteins, polysaccharides and lipids into their respective building-block molecules: amino acids, monosaccharides, and free fatty acids. The breakdown is done by various enzymes, for example proteases, glycosidases and lipases. With an acidic lumen limited by a single-bilayer lipid membrane, the lysosome holds an environment isolated from the rest of the cell. The lower pH creates optimal conditions for the over 60 different Hydrolase, hydrolases inside. Lysosomes receive extracellular particles through endocytosis, and intracellular components through autophagy. They can also fuse with the plasma membrane and secrete their contents, a process called lysosomal exocytosis. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratum Corneum Tryptic Enzyme
Kallikrein-5, formerly known as stratum corneum tryptic enzyme (SCTE), is a serine protease expressed in the epidermis. In humans it is encoded by the ''KLK5'' gene. This gene is one of the fifteen kallikrein subfamily members located in a cluster on chromosome 19. Its expression is up-regulated by estrogens and progestins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding the same protein. KLK5 has been suggested to regulate cell shedding (desquamation) in conjunction with KLK7 and KLK14, given its ability to degrade proteins which form the extracellular component of cell junctions in the stratum corneum. It is proposed that KLK5 regulates this process since it is able to self-activate in addition to activating KLK7 and KLK14. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * The MEROPS MEROPS is an online database for peptidases (also known as proteases, proteinases and proteolytic enzymes) and their inhibitors. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarged nose may occur in severe disease, a condition known as rhinophyma. The cause of rosacea is unknown. Risk factors are believed to include a family history of the condition. Factors that may potentially worsen the condition include heat, exercise, sunlight, cold, spicy food, alcohol, menopause, psychological stress, or steroid cream on the face. Diagnosis is based on symptoms. While not curable, treatment usually improves symptoms. Treatment is typically with metronidazole, doxycycline, minocycline, or tetracycline. When the eyes are affected, azithromycin eye drops may help. Other treatments with tentative benefit include brimonidine cream, ivermectin cream, and isotretinoin. Dermabrasion or laser surgery may also be used. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amolops Loloensis
''Amolops loloensis'' is a species of frog in the family Ranidae that is found in southern and western Sichuan and one locality in north-central Yunnan, China. Its natural habitats are small mountain streams in forests and grasslands. It is threatened by infrastructure development for human settlement, potentially also by water pollution from the mining industry. T Male ''Amolops loloensis'' grow to a snout–vent length of and females to . Tadpole A tadpole or polliwog (also spelled pollywog) is the Larva, larval stage in the biological life cycle of an amphibian. Most tadpoles are fully Aquatic animal, aquatic, though some species of amphibians have tadpoles that are terrestrial animal, ...s are up to in length. References loloensis Amphibians described in 1950 Amphibians of China Endemic fauna of China Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Ranidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystatin
The cystatins are a family of cysteine protease inhibitors which share a sequence homology and a common tertiary structure of an alpha helix lying on top of an anti-parallel beta sheet. The family is subdivided as described below. Cystatins show similarity to fetuins, kininogens, histidine-rich glycoproteins and cystatin-related proteins. Cystatins mainly inhibit peptidase enzymes (another term for ''proteases'') belonging to peptidase families C1 (papain family) and C13 ( legumain family). They are known to mis-fold to form amyloid deposits and are implicated in several diseases. Types The cystatin family includes: * The Type 1 cystatins, which are intracellular and are present in the cytosol of many cell types, but can also appear in body fluids at significant concentrations. They are single-chain polypeptides of about 100 residues, which have neither disulfide bonds nor carbohydrate side-chains. Type 1 cystatins are also known as Stefins (after the Stefan Institute where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyproline Helix
A polyproline helix is a type of protein secondary structure which occurs in proteins comprising repeating proline residues. A left-handed polyproline II helix (PPII, poly-Pro II, κ-helix) is formed when sequential residues all adopt (φ,ψ) backbone dihedral angles of roughly (-75°, 150°) and have ''Cis–trans isomerism, trans'' isomers of their peptide bonds. This PPII conformation is also common in proteins and polypeptides with other amino acids apart from proline. Similarly, a more compact right-handed polyproline I helix (PPI, poly-Pro I) is formed when sequential residues all adopt (φ,ψ) backbone dihedral angles of roughly (-75°, 160°) and have ''Cis–trans isomerism, cis'' isomers of their peptide bonds. Of the twenty common naturally occurring amino acids, only proline is likely to adopt the ''cis'' isomer of the peptide bond, specifically the X-Pro peptide bond; steric and electronic factors heavily favor the ''trans'' isomer in most other peptide bonds. However, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the protonated form (NH2+) under biological conditions, while the carboxyl group is in the deprotonated −COO− form. The "side chain" from the α carbon connects to the nitrogen forming a pyrrolidine loop, classifying it as a aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate. It is encoded by all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG). Proline is the only proteinogenic amino acid which is a secondary amine, as the nitrogen atom is attached both to the α-carbon and to a chain of three carbons that together form a five-membered ring. History and etymology Proline was first isolated in 1900 by Richard Willstätter who obtained the amino a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
α-helices
An alpha helix (or α-helix) is a sequence of amino acids in a protein that are twisted into a coil (a helix). The alpha helix is the most common structural arrangement in the secondary structure of proteins. It is also the most extreme type of local structure, and it is the local structure that is most easily predicted from a sequence of amino acids. The alpha helix has a right-handed helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid that is four residues earlier in the protein sequence. Other names The alpha helix is also commonly called a: * Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix (from the names of three scientists who described its structure) * 3.613-helix because there are 3.6 amino acids in one ring, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond (starting with amidic hydrogen and ending with carbonyl oxygen) Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were dras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR; ErbB-1; HER1 in humans) is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor (biochemistry), receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family (EGF family) of extracellular protein ligand (biochemistry), ligands. The epidermal growth factor receptor is a member of the ErbB, ErbB family of receptors, a subfamily of four closely related receptor tyrosine kinases: EGFR (ErbB-1), HER2/neu (ErbB-2), ERBB3, Her 3 (ErbB-3) and Her 4 (ErbB-4). In many cancer types, mutations affecting EGFR expression or activity could result in cancer. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor was discovered by Stanley Cohen (biochemist), Stanley Cohen of Vanderbilt University. Cohen shared the 1986 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Rita Levi-Montalcini for their discovery of growth factors. Deficient signaling of the EGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases in humans is associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's, while over-expression is associated with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purinergic Receptor P2X
P2X purinoceptor 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''P2RX7'' gene. The product of this gene belongs to the family of purinoceptors for ATP. Multiple alternatively spliced variants which would encode different isoforms have been identified although some fit nonsense-mediated decay criteria. The receptor is found in the central and peripheral nervous systems, in microglia, in macrophages, in uterine endometrium, and in the retina. The P2X7 receptor also serves as a pattern recognition receptor for extracellular ATP-mediated apoptotic cell death, regulation of receptor trafficking, mast cell degranulation, and inflammation. Regarding inflammation, P2X7 receptor induces the NLRP3 inflammasome in myeloid cells and leads to interleukin-1beta release. Structure and kinetics The P2X7 subunits can form homomeric receptors only with a typical P2X receptor structure. The P2X7 receptor is a ligand-gated cation channel that opens in response to ATP binding and leads to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |