|
Castra Of Drumul Carului
The castra of Drumul Carului was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia near Moieciu, Romania. It was part of the Roman frontier system of the Limes Transalutanus and was in a strategic position south of the Bran Pass. The small fort (''castellum''), approx. 40×40 m, was defended by earth works with two ditches.Limes: Roman frontier of Dacia Inferior. A review and an update. MNR. 11 / 2022 https://limesromania.ro/en/articole/covers/ It might have been erected following the First Dacian War before the official integration of Dacia to the Roman Empire. Destroyed by fire, the fort was abandoned around 250. See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra refl ... Notes External linksRoman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman auxiliary forts in Romania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia
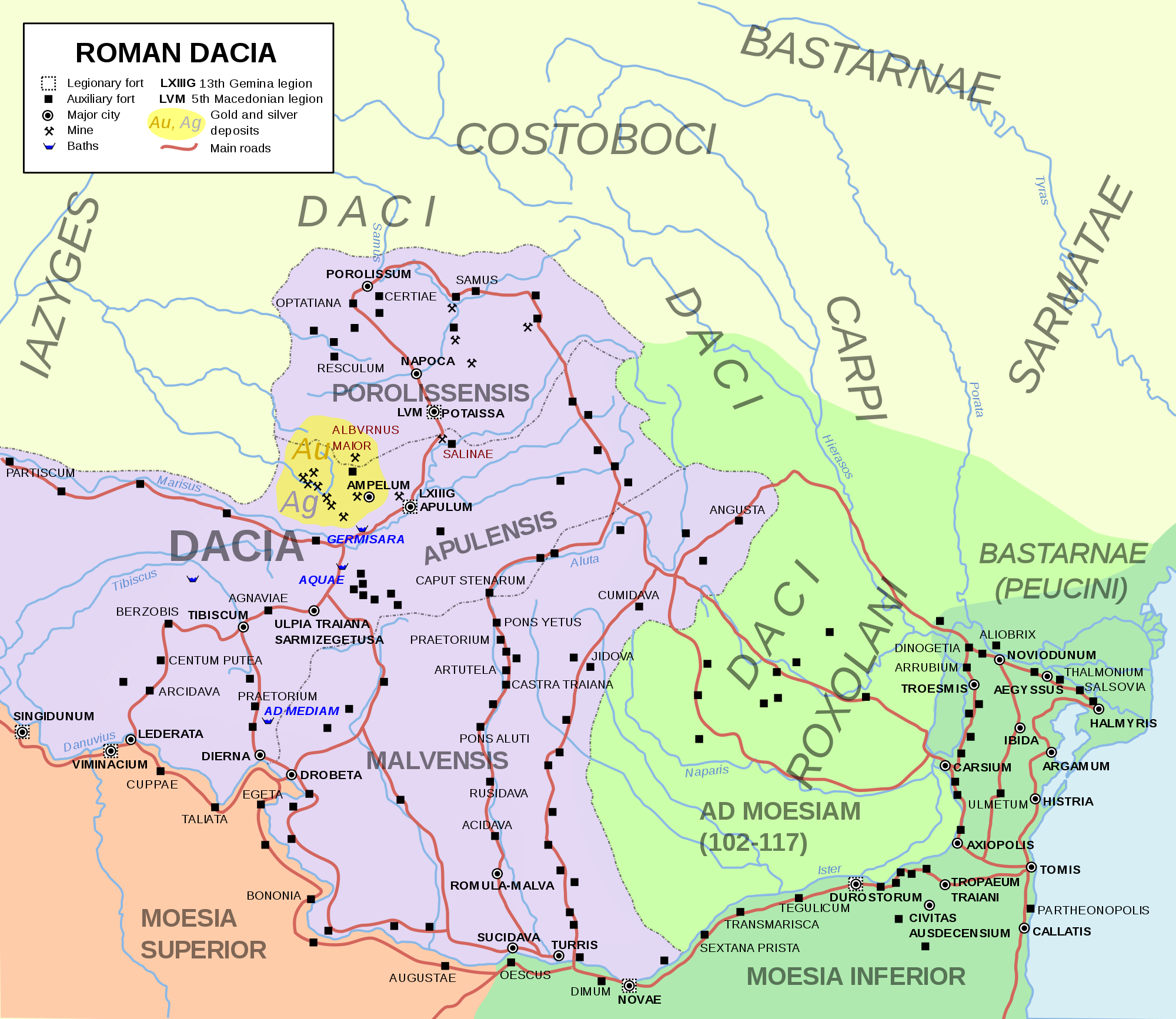
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to present-day Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, Czech Republic, Poland and Ukraine. A Dacian kingdom that united the Dacians and the Getae was formed under the rule of Burebista in 82 BC and lasted until the Roman conquest in AD 106. As a result of the Trajan's Dacian Wars, wars with the Roman Empire, after the conquest of Dacia, the population was dispersed, and the capital city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans. However, the Romans built a settlement bearing the same name, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetuza, 40 km away, to serve as the capital of the newly established Roman Dacia, Roman province of Dacia. A group of "Free Dacians" may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to the east, and the Black Sea to the southeast. It has a mainly continental climate, and an area of with a population of 19 million people. Romania is the List of European countries by area, twelfth-largest country in Europe and the List of European Union member states by population, sixth-most populous member state of the European Union. Europe's second-longest river, the Danube, empties into the Danube Delta in the southeast of the country. The Carpathian Mountains cross Romania from the north to the southwest and include Moldoveanu Peak, at an altitude of . Bucharest is the country's Bucharest metropolitan area, largest urban area and Economy of Romania, financial centre. Other major urban centers, urban areas include Cluj-Napoca, Timiș ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient History Of Transylvania
In ancient times, Romans exploited the gold mines in what is now Transylvania extensively, building access roads and forts to protect them, like Abrud. The region developed a strong infrastructure and economy, based on agriculture, cattle farming and mining. Colonists from Thracia, Moesia, Macedonia, Gaul, Syria, and other Roman provinces were brought in to settle the land, developing cities like Apulum (now Alba Iulia) and Napoca (now Cluj Napoca) into municipiums and colonias. The Dacians rebelled frequently, the biggest rebellion occurring after the death of emperor Trajan. Sarmatians and Burs were allowed to settle inside Dacia Trajana after repeated clashes with the Roman administration. During the 3rd century increasing pressure from the free Dacians ( Carpians) and Visigoths forced the Romans to abandon exposed Dacia Trajana. In 271, the Roman emperor Aurelian abandoned Dacia Trajana and reorganised a new Dacia Aureliana inside former Moesia Superior. The abandon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Auxiliary Forts In Romania
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of Roman civilization *Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter written by Paul, found in the New Testament of the Christian Bible * Ar-Rum (), the 30th sura of the Quran. Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People * Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters * Roman (surnam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Castra
Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra reflects the most important zones of the empire from a military point of view. Many castra were disposed along frontiers particularly in Northern and Central Europe. Another focal point was the Eastern border, where the Roman Empire confronted one of its long-term enemies, the Persian Empire. Other castra were located in strategically important zones, as in Egypt, from which most of the wealth of the empire came. Finally, other castra were located in zones in which the Romans experienced local unrest, such as Northern Spain and Judea. Provinces where the Roman power was unchallenged, such as Italy, Gaul, Africa and Greece, were provided with few or no castra. In the long history of the Roman Empire, the character of the military policy of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Dacian War
Trajan's First Dacian War took place from 101 to 102. The Kingdom of Dacia, under King Decebalus, had become a threat to the Roman Empire, and defeated several of Rome's armies during Domitian's reign (81–96). Despite the peace treaty established after Domitian's Dacian War, Trajan was set on ridding their new threat to Rome's power and in 101 set out determined to defeat Dacia. After a year of heavy fighting, King Decebalus came to terms and accepted peace. Preparation Trajan spent the winter of 98 and the following year with the army in Moesia where he worked out careful plans. Some actions may have been: * a fortified pontoon bridge at the old fording-point at Drobeta-Turnu Severin- Kostol * preparation of the military river fleet * reorganisation of military forts on the northern bank of the Danube * major building for accommodation for the forces * improvement and reconstruction of the towpath and military road along the narrow Iron Gates gorge * canals to enable n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limes Transalutanus
Limes Transalutanus is the modern name given to a fortified frontier system of the Roman Empire, built on the western edge of Teleorman County, Teleorman's forests as part of the Dacian Limes in the Roman province of Roman Dacia, Dacia, modern-day Romania. The Limes Transalutanus, of 235 km length, was needed to shorten the line of communication to the strategic fort at Angustia (castra), Angustia by almost 30 per cent compared to the earlier route via the Limes Alutanus. In first half of the 3rd century AD Septimius Severus advanced the province's eastern frontier by some east of the existing Limes Alutanus although the road and many of the forts on the Limes date from the end of Trajan's Dacian Wars (c.106 AD).C. C. Petolescu, Auxilia dacica. Contribuție la istoria militară a Daciei Roma- ne (Bucharest 2002) p55 Between 244–247, after the Carpi (people), Carpian and Getae (or Goths) attacks, Philip the Arab abandoned the limes for some time. The Romans returned to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moieciu
Moieciu (; ) is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is located 29 km south of Brașov, within the Bran Pass. The commune is composed of six villages: Cheia (''Kheja''), Drumul Carului, Măgura (''Magura''), Moieciu de Jos (the commune center), Moieciu de Sus (''Felsőmoécs'') and Peștera (''Pestera''). Măgura and Peștera are on the eastern side of the Piatra Craiului Mountains The Piatra Craiului Mountains (, ) are a mountain range in the Southern Carpathians in Romania. Its name is translated as ''Kings' Rock'' or ''The Rock of the Prince''. The mountain range is located in Brașov County, Brașov and Argeș Coun .... Image:01 Magura, Romania - Piatra Craiului mountains.jpg, Măgura village Image:MoieciuDeSus1.jpg, Moieciu de Sus scenery Image:MoieciuDeSus5.jpg, Moieciu de Sus scenery Image:MoieciuDeSus6.jpg, Moieciu de Sus scenery References External links Official siteMoeciu - Romania- Information about Moeciu resort {{Authority con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia Superior
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Superi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as ; or Dacia Felix, ) was a province of the Roman Empire from 106 to 271–275 AD. Its territory consisted of what are now the regions of Oltenia, Transylvania and Banat (today all in Romania, except the last region which is split among Romania, Hungary, and Serbia). During Roman rule, it was organized as an imperial province on the borders of the empire. It is estimated that the population of Roman Dacia ranged from 650,000 to 1,200,000. It was conquered by Trajan (98–117) after two campaigns that devastated the Dacian Kingdom of Decebalus. However, the Romans did not occupy its entirety; Crișana, Maramureș, and most of Moldavia remained under the Free Dacians. After its integration into the empire, Roman Dacia saw constant administrative division. In 119 under Hadrian, it was divided into two departments: Dacia Superior ("Upper Dacia") and Dacia Inferior ("Lower Dacia"; later named Dacia Malvensis). Between 124 and around 158, Dacia Sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |