|
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure used to reduce the risk of stroke from carotid artery stenosis (narrowing the internal carotid artery). In an endarterectomy, the surgeon opens the artery and removes the plaque. The plaque forms and thickens the inner layer of the artery, or ''intima'', hence the name of the procedure which simply means removal of part of the internal layers of the artery. An alternative procedure is carotid stenting, which can also reduce the risk of stroke for some patients. Medical uses Carotid endarterectomy is used to reduce the risk of strokes caused by carotid artery stenosis over time. Carotid stenosis can either have symptoms (i.e., be symptomatic), or be found by a doctor in the absence of symptoms (asymptomatic) - and the risk-reduction from endarterectomy is greater for symptomatic than asymptomatic patients. Carotid endarterectomy itself can cause strokes, so to be of benefit in preventing strokes over time, the risks for combined ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
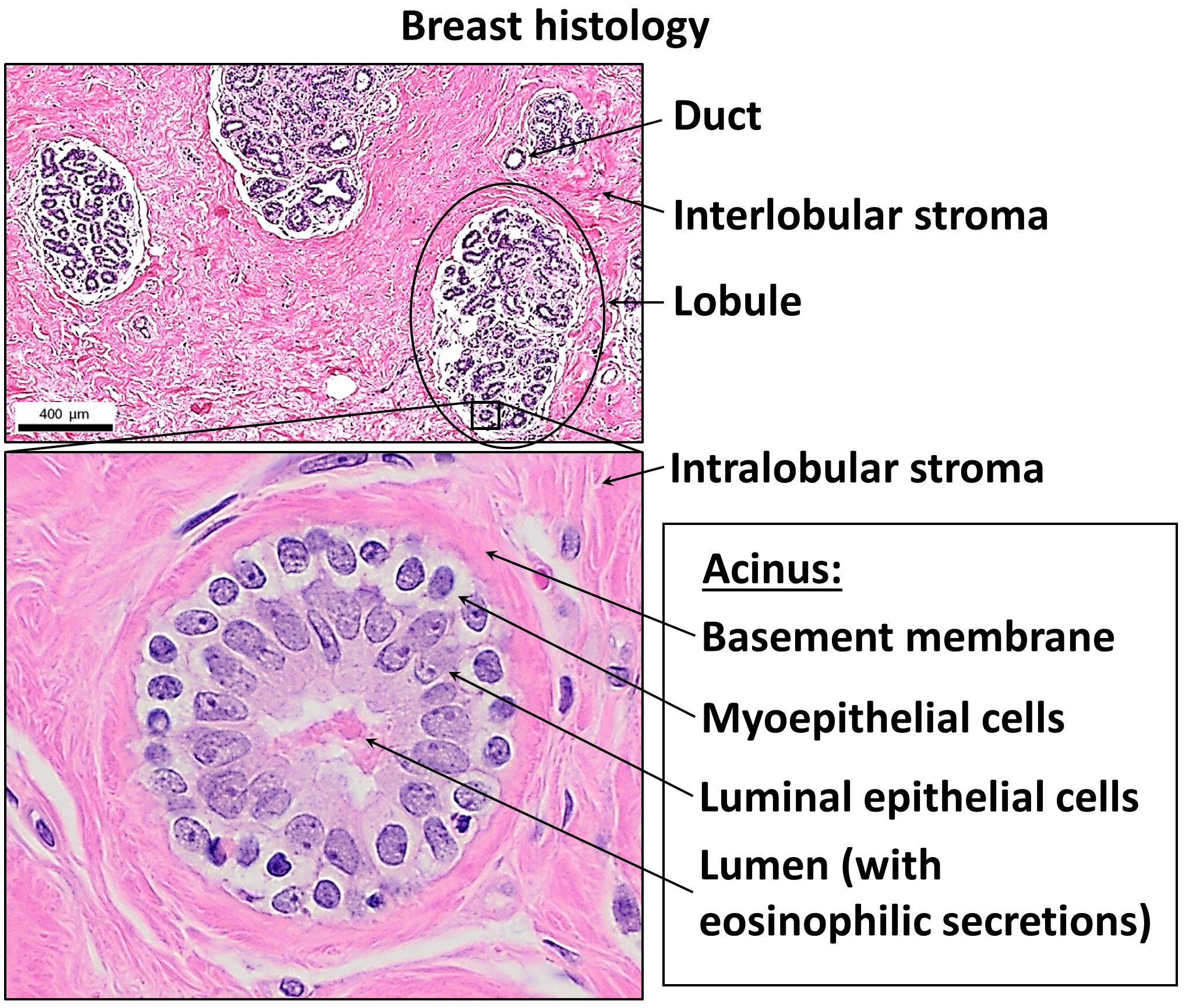
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (: lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *the interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows *the interior of the gastrointestinal tract *the pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *the interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *the pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the fallopian tubes *the fluid-filled cavity forming in the blastocyst during pre-implantation development called the blastocoel In cell biology, lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures, including thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, and microtubule. Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity refers to the simultaneous presence of two or more medical conditions in a patient; often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary condition. It originates from the Latin term (meaning "sickness") prefixed with ("together") and suffixed with ''-ity'' (to indicate a state or condition). Comorbidity includes all additional ailments a patient may experience alongside their primary diagnosis, which can be either physiological or psychological in nature. In the context of mental health, comorbidity frequently refers to the concurrent existence of mental disorders, for example, the co-occurrence of depressive and anxiety disorders. The concept of multimorbidity is related to comorbidity but is different in its definition and approach, focusing on the presence of multiple diseases or conditions in a patient without the need to specify one as primary. Definition The term "comorbid" has three definitions: # to indicate a medical con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Mary's Hospital, London
St Mary's Hospital is a teaching hospital in Paddington, in the City of Westminster, London, founded in 1845. Since the UK's first academic health science centre was created in 2008, it has been operated by Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, which also operates Charing Cross Hospital, Hammersmith Hospital, Queen Charlotte's and Chelsea Hospital and the Western Eye Hospital. Until 1988 the hospital ran St Mary's Hospital Medical School, part of the federal University of London. In 1988 it merged with Imperial College London, and then with Charing Cross and Westminster Medical School in 1997 to form Imperial College School of Medicine. In 2007 Imperial College became an independent institution when it withdrew from the University of London. History Development of the hospital The original block of St Mary's Hospital in Norfolk Place was designed by Thomas Hopper (architect), Thomas Hopper in the Classical architecture, classical style. It first opened its doors to patients i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Methodist Hospital
Houston Methodist Hospital is the flagship quaternary care hospital of Houston Methodist academic medical center. Located in the Texas Medical Center in Houston, Texas, Houston Methodist Hospital was established in 1919 during the height of the Spanish influenza epidemic as an outreach ministry of Methodist Episcopal Church. Houston Methodist comprises eight hospitals, an academic institute, a primary care group, and more than 300 locations throughout greater Houston. The hospital has consistently ranked as "One of America's Best Hospitals" according to '' U.S. News & World Report''. The hospital has earned worldwide recognition in multiple specialties including cardiovascular surgery, cancer, epilepsy treatment and organ transplantation. Houston Methodist System changed its official name to Houston Methodist in 2013, to distinguish themselves from the 80+ Methodist Hospitals in the U.S. and to reflect their Houston roots. History Originally located near downtown Houston, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael E
SS ''Michael E'' was a cargo ship that was built in 1941. She was the first British catapult aircraft merchant ship (CAM ship): a merchant ship fitted with a rocket catapult to launch a single Hawker Hurricane fighter aircraft to defend a convoy against long-range German bombers. She was sunk on her maiden voyage by a German submarine. Description ''Michael E'' was built by William Hamilton & Co Ltd, Port Glasgow. Launched in 1941, she was completed in May of that year. She was the United Kingdom's first CAM ship, armed with an aircraft catapult on her bow to launch a Hawker Sea Hurricane. The ship was long between perpendiculars ( overall), with a beam of . She had a depth of and a draught of . She was measured at and . She had six corrugated furnaces feeding two single-ended boilers with a combined heating surface of . The boilers fed a 443 nominal horsepower triple-expansion steam engine that had cylinders of , and diameter by stroke. The engine was buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Lisbon
The University of Lisbon (ULisboa; ) is a public university, public research university in Lisbon, and Portugal's largest university. It was founded in 1911, but the university's present structure dates to the 2013 merger of the former University of Lisbon (1911–2013) and the Technical University of Lisbon, Technical University of Lisbon (1930–2013). History University of Coimbra, the first Portuguese university, was established in Lisbon between 1288 and 1290, when Denis of Portugal, Dinis I promulgated the letter ''Scientiae thesaurus mirabili'', granting several privileges to the students of the ''studium generale'' in Lisbon, proving that it was already founded on that date. There was an active participation in this educational activity by the Portuguese Crown and its king, through its commitment of part of the subsidy of the same, as by the fixed incomes of the Church. This institution moved several times between Lisbon and Coimbra, where it settled permanently in 1537. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignal, bio signals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex and allocortex. It is typically non-invasive, with the EEG electrodes placed along the scalp (commonly called "scalp EEG") using the 10–20 system (EEG), International 10–20 system, or variations of it. Electrocorticography, involving surgical placement of electrodes, is sometimes called Electrocorticography, "intracranial EEG". Clinical interpretation of EEG recordings is most often performed by visual inspection of the tracing or quantitative EEG, quantitative EEG analysis. Voltage fluctuations measured by the EEG bioamplifier, bio amplifier and electrodes allow the evaluation of normal Brain activity and meditation, brain activity. As the electrical activity monitored by EEG originates in neurons in the underlying Huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaesthesia
Anesthesia (American English) or anaesthesia (British English) is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise require physical restraint in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * ''General anesthesia'' suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of Sensation (psychology), sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * ''Sedation'' suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiolysis, anxiety and creation of long-term memory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shunt (medical)
In medicine, a shunt is a hole or a small passage that moves, or allows movement of, fluid from one part of the body to another. The term may describe either congenital or acquired shunts; acquired shunts (sometimes referred to as iatrogenic shunts) may be either biological or mechanical. __TOC__ Types * Cardiac shunts may be described as right-to-left, left-to-right or bidirectional, or as systemic-to-pulmonary or pulmonary-to-systemic. * Cerebral shunt: In cases of hydrocephalus and other conditions that cause chronic increased intracranial pressure, a one-way valve is used to drain excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain and carry it to other parts of the body. This valve usually sits outside the skull but beneath the skin, somewhere behind the ear. Cerebral shunts that drain fluid to the peritoneal cavity (located in the upper abdomen) are called ''ventriculoperitoneal'' (''VP'') shunts. * Lumbar-peritoneal shunt (a.k.a. ''lumboperitoneal'', ''LP''): In cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemostasis
In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). It is the first stage of wound healing. Hemostasis involves three major steps: * vasoconstriction * temporary blockage of a hole in a damaged blood vessel by a platelet plug * blood coagulation (formation of fibrin clots) Coagulation, the changing of blood from a liquid to a gel which forms the fibrin clots, is essential to hemostasis. Intact blood vessels moderate blood's tendency to form clots. The endothelial cells of intact vessels prevent blood clotting with a heparin-like molecule and thrombomodulin, and prevent platelet aggregation with nitric oxide and prostacyclin. When endothelium of a blood vessel is damaged, the endothelial cells stop secretion of coagulation and aggregation inhibitors and instead secrete von Willebrand factor, which initiates the maintenance of hemostasis after in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (: lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *the interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows *the interior of the gastrointestinal tract *the pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *the interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *the pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the fallopian tubes *the fluid-filled cavity forming in the blastocyst during pre-implantation development called the blastocoel In cell biology, lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures, including thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, and microtubule. Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
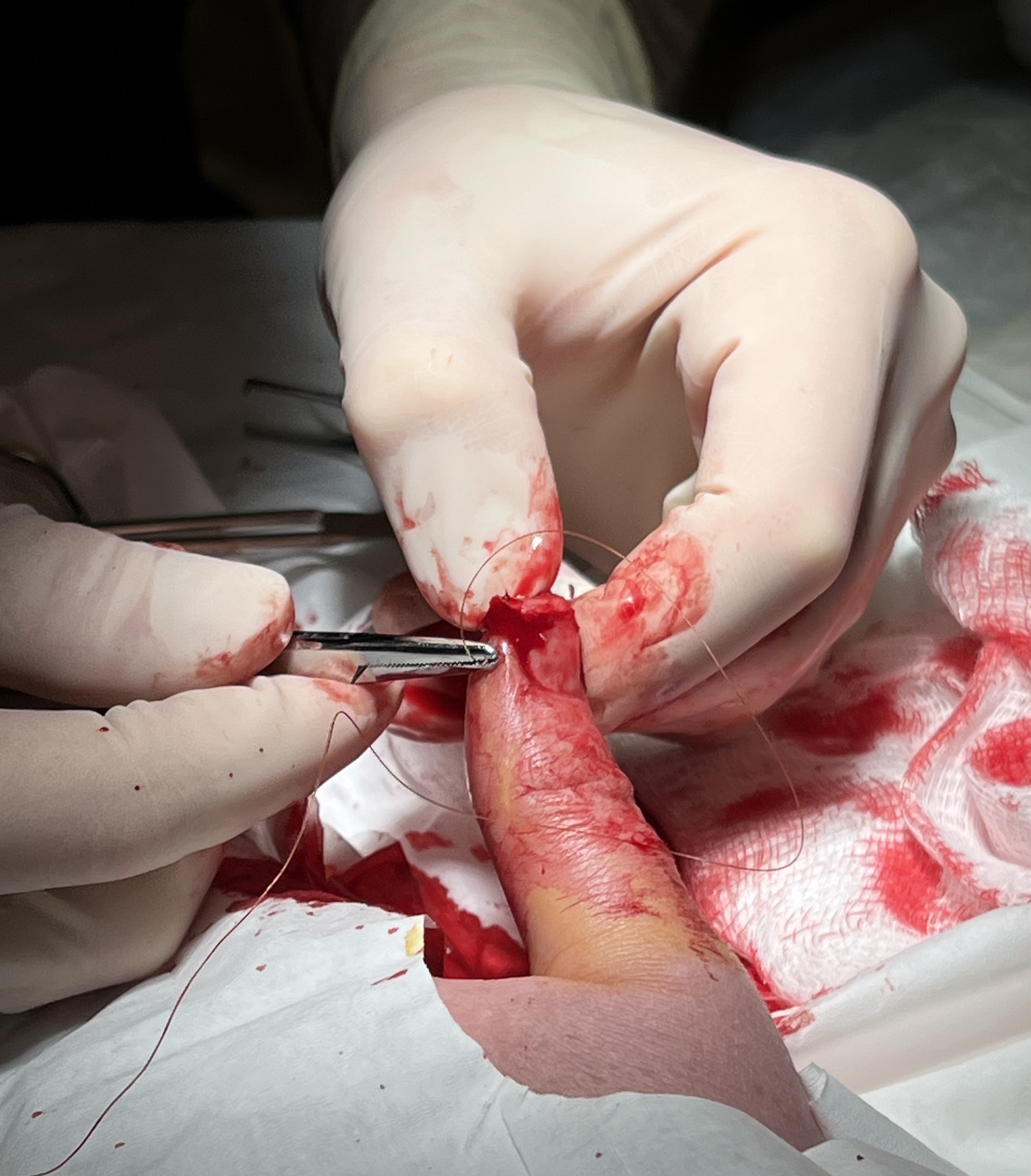
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold Tissue (biology), body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a Sewing needle, needle with an attached length of thread (yarn), thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |