|
Carolines Tropical Moist Forests
The Carolines tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It includes the central and eastern Caroline Islands in the Federated States of Micronesia. Geography The ecoregion spans the central and eastern Caroline Islands, and include most of the Federated States of Micronesia it includes the states of Chuuk, Pohnpei, and Kosrae and the eastern islands of Yap State, known as the Remetau. The ecoregion includes both high volcanic islands and low atolls, islands of coralline sand ringing a central lagoon. The Chuuk islands are surrounded by almost circular barrier reef more than 60 km across at its widest point, which encloses a lagoon and 69 low islets composed of coral sand. Within the lagoon are 10 principal and many smaller volcanic islands in two clusters, the Faichuk group to the west and the Nomoneas group to the east. The largest island, Tol, reaches 443 meters elevation. Pohnpei is an extinct volcano 650 km east o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
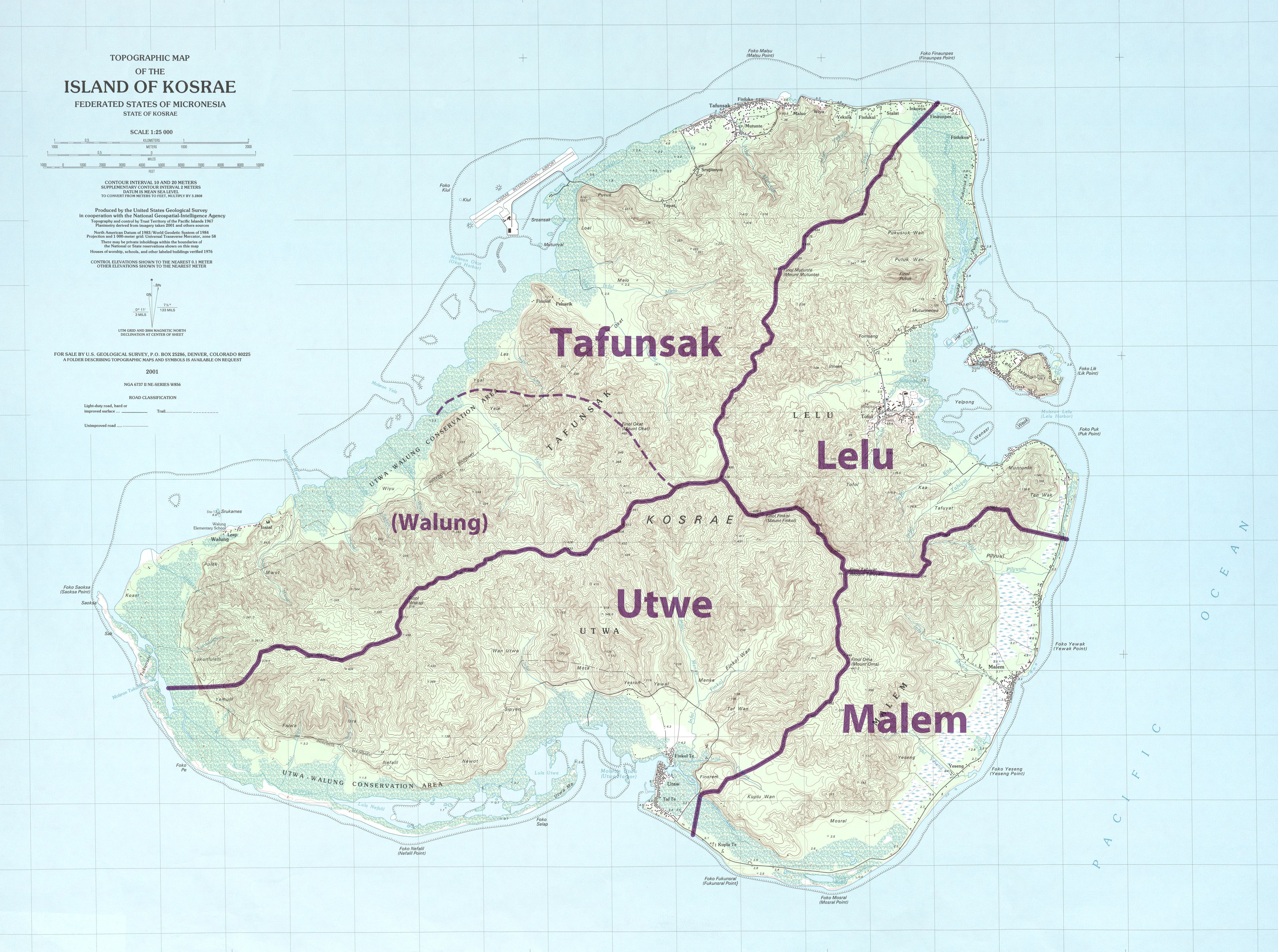
Kosrae
Kosrae ( ), formerly known as Kusaie or Strong's Island, is an island in the Federated States of Micronesia. The State of Kosrae is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia, and includes the main island of Kosrae and a few nearby islands and islets, the most significant of which (Lelu Island) is inhabited by 1,500 people. Kosrae's land area is , sustaining 6,600 people. Tofol is the state capital, and Mt. Finkol is the highest point at . History Archaeological evidence shows that the island was settled at least by the early years of the first millennium AD. This includes the city of Leluh archaeological site, Leluh that existed from about 1250 to 1850 AD, and in its heyday had a population of about 1,500 and covered some 27 hectares. It featured burial pyramids for the nobility. French Visitors The French corvette S. M. ''La Coquille'', arrived at Okat Harbor on 3 June 1824 and visited until 15 June 1824. Commanded by Louis-Isidore Duperrey, ''La Coquil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weno
Weno, formerly Moen, is an island municipality of Chuuk State of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). It is the largest town in the FSM. It has an estimated area of 20 square kilometers. Population The population was 13,856 at the census taken in 2010. Geography It is located in the Chuuk Lagoon. Its villages are in the northwest (Sapuk, Penia, Peniesene, Tunnuk, Mechitiw, Iras, Nepukos, Mwan, Neiwe, and Wichap, Epinup) and serve as the main center of commerce. Weno is the state capital and the second-most populous island of the FSM, with a population of 13,856 at the 2010 census. The highest point is Mount Teroken, elevation 364 m (1,214 ft). Transportation Weno has the only airport An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surfa ... in the state, Chuuk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elaeocarpus
''Elaeocarpus'' is a genus of nearly five hundred species of flowering plants in the family Elaeocarpaceae native to the Western Indian Ocean, Tropical and Subtropical Asia, and the Pacific. Plants in the genus ''Elaeocarpus'' are trees or shrubs with simple leaves, flowers with four or five petals usually, and usually blue fruit. Description Plants in the genus ''Elaeocarpus'' are mostly evergreen trees or shrubs, a few are epiphytes or lianes, and some are briefly deciduous. The leaves are arranged alternately, simple (strictly compound with only one leaflet) with a swelling where the petiole meets the lamina, often have toothed edges, usually have prominent veins and often turn red before falling. The flowers are usually arranged in a raceme, usually bisexual, have four or five sepals and petals and many stamens. The petals usually have finely-divided, linear lobes. The fruit is a oval to spherical drupe that is usually blue, sometimes black, with a sculptured endocarp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrsine
''Myrsine'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Primulaceae. It was formerly placed in the family Myrsinaceae before this was merged into the Primulaceae. It is found nearly worldwide, primarily in tropical and subtropical areas. It contains about 200 species, including several notable radiations, such as the matipo of New Zealand and the kōlea of Hawaii (the New Zealand "black matipo", '' Pittosporum tenuifolium'', is not related to ''Myrsine''). In the United States, members of this genus are known as colicwood. Some species, especially '' M. africana'', are grown as ornamental shrubs. The leathery, evergreen leaves are simple and alternate, with smooth or toothed margins and without stipules. The one-seeded, indehiscent fruit is a thin-fleshed globose drupe. The flowers and fruits often do not develop until after leaf fall and thus appear naked on the branches. The fruits often do not mature until the year after flowering. The calyx is persistent. The Pacifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glochidion
''Glochidion'' is a genus of flowering plants, of the family Phyllanthaceae, known as cheese trees or buttonwood in Australia, and leafflower trees in the scientific literature. It comprises about 300 species, distributed from Madagascar to the Pacific Islands. ''Glochidion'' species are used as food plants by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including ''Aenetus eximia'' and ''Endoclita damor''. The Nicobarese people have attested to the medicinal properties found in ''G. calocarpum'', saying that its bark and seed are most effective in curing abdominal disorders associated with amoebiasis. ''Glochidion'' are of note in the fields of pollination biology and coevolution because they have a specialized mutualism with moths in the genus ''Epicephala'' (leafflower moths), in which the moths actively pollinate the flowers—thereby ensuring that the tree may produce viable seeds—but also lay eggs in the flowers' ovaries, where their larvae consume a subset of the developi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathea Nigricans
''Cyathea'' is a genus of tree ferns, the type genus of the fern order Cyatheales. The genus name ''Cyathea'' is derived from the Greek ''kyatheion'', meaning "little cup", and refers to the cup-shaped sori on the underside of the fronds. Description The species of ''Cyathea'' are mostly terrestrial ferns, usually with a single tall stem. Rarely, the trunk may be branched or creeping. Many species also develop a fibrous mass of roots at the base of the trunk. The genus has a pantropical distribution, with over 470 species. They grow in habitats ranging from tropical rain forests to temperate woodlands. Classification Conant ''et al.'' in 1996, concluded on molecular cpDNA and morphological evidence that a system of three clades – ''Alsophila'', ''Cyathea'' and ''Sphaeropteris'' was the most accurate reflection of evolutionary lineages within the Cyatheaceae, ''Alsophila'' being the most basal and ''Cyathea'' and ''Sphaeropteris'' derived sister groups. In the Pteridophyte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinostigma Ponapensis
''Clinostigma'' is a genus of flowering plant in the Arecaceae (palm) family, native to various islands in the western Pacific. It contains the following species:Govaerts, R. & Dransfield, J. (2005). World Checklist of Palms: 1-223. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. * '' Clinostigma carolinense'' (Becc.) H.E.Moore & Fosberg - Chuuk ( Truk) in Micronesia * '' Clinostigma collegarum'' J.Dransf. - Bismarck Archipelago * '' Clinostigma gronophyllum'' H.E.Moore - Solomon Islands * '' Clinostigma exorrhizum'' (H.Wendl.) Becc. - Fiji * ''Clinostigma haerestigma'' H.E.Moore - Solomon Islands * '' Clinostigma harlandii'' Becc. - Vanuatu * '' Clinostigma onchorhynchum'' Becc. - Samoa * '' Clinostigma ponapense'' (Becc.) H.E.Moore & Fosberg - Pohnpei in Micronesia * '' Clinostigma samoense'' H.Wendl. - Samoa * '' Clinostigma savoryanum'' (Rehder & E.H.Wilson) H.E.Moore & Fosberg - Arrack Tree - Ogasawara-shoto (Bonin Islands) * '' Clinostigma warburgii'' Becc. - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandanus Patina
''Pandanus'' is a genus of monocots with some 750 accepted species. They are palm-like, dioecious trees and shrubs native to the Old World tropics and subtropics. The greatest number of species are found in Madagascar and Malaysia. Common names include pandan, screw palm, and screw pine. They are classified in the order Pandanales, family Pandanaceae. Description Often called pandanus palms, these plants are not closely related to palm trees. The species vary in size from small shrubs less than tall, to medium-sized trees tall, typically with a broad canopy, heavy fruit, and moderate growth rate. The trunk is stout, wide-branching, and ringed with many leaf scars. Mature plants can have branches. Depending on the species, the trunk can be smooth, rough, or warty. The roots form a pyramidal tract to hold the trunk. They commonly have many thick stilt roots near the base, which provide support as the tree grows top-heavy with leaves, fruit, and branches. These roots are advent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyathea Ponapeana
''Cyathea'' is a genus of tree ferns, the type genus of the fern order Cyatheales. The genus name ''Cyathea'' is derived from the Greek ''kyatheion'', meaning "little cup", and refers to the cup-shaped sori on the underside of the fronds. Description The species of ''Cyathea'' are mostly terrestrial ferns, usually with a single tall stem. Rarely, the trunk may be branched or creeping. Many species also develop a fibrous mass of roots at the base of the trunk. The genus has a pantropical distribution, with over 470 species. They grow in habitats ranging from tropical rain forests to temperate woodlands. Classification Conant ''et al.'' in 1996, concluded on molecular cpDNA and morphological evidence that a system of three clades – ''Alsophila'', ''Cyathea'' and ''Sphaeropteris'' was the most accurate reflection of evolutionary lineages within the Cyatheaceae, ''Alsophila'' being the most basal and ''Cyathea'' and ''Sphaeropteris'' derived sister groups. In the Pteridophyte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maesa Carolinensis
''Maesa'' is a genus of flowering plants. It is placed in the family Primulaceae, subfamily Maesoideae, for which it is the sole genus (monotypic).''Maesa''. The Plant List. Previously it was placed in , or in a family of its own, Maesaceae.Kallersjo, M., Bergqvist, G., & Anderberg, A. A. (2000) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, and quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production. The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and woods is termed '' silvology''. Silviculture also focuses on making sure that the treatment(s) of forest stands are used to conserve and improve their productivity. Generally, silviculture is the science and art of growing and cultivating forest crops, based on a knowledge of silvics (the study of the life-history and general characteristics of forest trees and stands, with particular reference to local/regional factors). The focus of silviculture is the control, establishment and management of forest stands. The distinction between forestry and silviculture is that silviculture is applied at the stand-level, while forestry is a broader concept. Adaptive management is common in silviculture, while forestry can include natural/conserved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hibiscus Tiliaceus
''Hibiscus tiliaceus'', commonly known as the sea hibiscus or coast cottonwood, is a species of flowering tree in the mallow family, Malvaceae, with a pantropical distribution along coastlines. It has also been introduced to Florida and New Zealand. It has been debated whether this species is native or introduced to Hawaii. Names Common names include sea hibiscus, beach hibiscus, coastal (or coast) hibiscus, coastal (or coast) cottonwood, green cottonwood, native hibiscus, native rosella, cottonwood hibiscus, kurrajong, sea rosemallow and dhigga ( Maldivian). The plant was introduced by Austronesian peoples that voyaged across Southeast Asia and Oceania as a source of wood and fibre. This is reflected in the names of the plant as spoken in many related languages spoken in those regions including ''balibago'' (Tagalog), ''malobago'' ( Bikol), ''malabago'' or ''malbago'' ( Cebuano – Southern), ''maribago'' ( Cebuano – Northern), ''lambago'' (Cebuano - Cagayan de Oro), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |