|
Carmarthen To Aberystwyth Line
Carmarthen (, ; , 'Merlin's fort' or possibly 'Sea-town fort') is the county town of Carmarthenshire and a community in Wales, lying on the River Towy north of its estuary in Carmarthen Bay. At the 2021 census the community had a population of 14,636, and the built up area had a population of 16,455. It stands on the site of a Roman town, and has a claim to be the oldest town in Wales. In the middle ages it comprised twin settlements: ''Old Carmarthen'' around Carmarthen Priory and ''New Carmarthen'' around Carmarthen Castle. The two were merged into one borough in 1546. It was the most populous borough in Wales in the 16th–18th centuries, described by William Camden as "chief citie of the country". It was overtaken in size by the mid-19th century, following the growth of settlements in the South Wales Coalfield. History Early history When Britannia was a Roman province, Carmarthen was the civitas capital of the Demetae tribe, known as Moridunum ("Sea Fort"). It is po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmarthen East And Dinefwr (National Assembly For Wales Constituency)
Carmarthen East and Dinefwr () is a United Kingdom constituencies, constituency of the Senedd. It elects one Member of the Senedd by the first past the post method of election. It is one of eight constituencies in the Mid and West Wales (Senedd electoral region), Mid and West Wales Senedd constituencies and electoral regions, electoral region, which elects four additional member system, additional members, in addition to eight constituency members, to produce a degree of proportional representation for the region as a whole. It had been held since its formation in 1999 by the Plaid Cymru politician, Rhodri Glyn Thomas until his retirement in 2016. It is now held by Plaid Cymru politician Adam Price, who became leader of the party in 2018. Boundaries 1999 to 2007 The constituency was created for the 1999 National Assembly for Wales election, first election to the Assembly, in 1999, with the name and boundaries of the Carmarthen East and Dinefwr (UK Parliament constituency), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
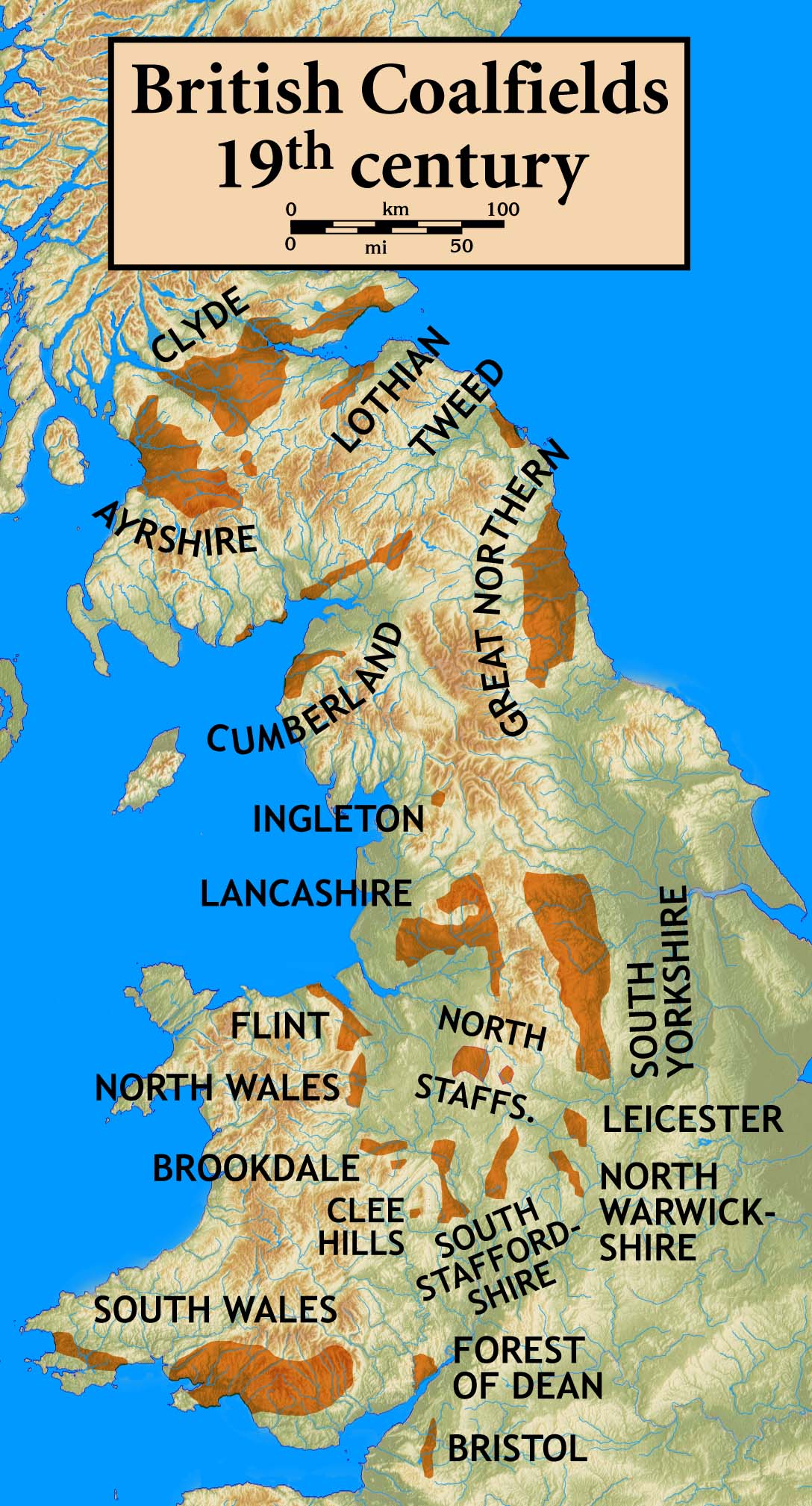
South Wales Coalfield
The South Wales Coalfield () extends across Pembrokeshire, Carmarthenshire, Swansea, Neath Port Talbot, Bridgend, Rhondda Cynon Taf, Merthyr Tydfil, Caerphilly, Blaenau Gwent and Torfaen. It is rich in coal deposits, especially in the South Wales Valleys. Description The area comprises a fully exposed synclinorium which gave rise to dramatic upland areas () rising to 300–600 metres above sea level, and intersected by steep-sided valleys in which most of the area's deep mines were developed. The coal measures (Upper Carboniferous/Pennsylvanian) are thick, workable seams in the lower parts and generally thinner and sparser seams in the upper parts, with a development of sandstones ( Pennant Sandstone) much used in local construction, (including the characteristic terraced houses). The coal generally increases in grade or "rank" from east to west, with bituminous coals in the east, and anthracite in the west, mostly to the north and west of Neath. The Rhondda Valley was par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavea
The ''cavea'' (Latin language, Latin for "enclosure") are the seating sections of Theatre of ancient Greece, Greek and Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatres and Roman amphitheatre, amphitheatres. In Roman theatres, the ''cavea'' is traditionally organised in three horizontal sections, corresponding to the social class of the spectators: * the ''ima cavea'' is the lowest part of the ''cavea'' and the one directly surrounding the arena. It was usually reserved for the upper echelons of society. * the ''media cavea'' directly follows the ''ima cavea'' and was open to the general public, though mostly reserved for men. * the ''summa cavea'' is the highest section and was usually open to women and children. Similarly, the front row was called the ''prima cavea'' and the last row was called the ''cavea ultima''. The ''cavea'' was further divided vertically into ''cunei''. A ''cuneus'' (Latin for "wedge"; plural, ''cunei'') was a wedge-shaped division separated by the ''scalae'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caerleon
Caerleon ( ; ) is a town and Community (Wales), community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman Empire, Roman legionary Castra, fortress, Isca Augusta, and an Iron Age hillfort. Close to the remains of Isca Augusta are the National Roman Legion Museum and the Roman Baths Museum. The town also has strong historical and literary associations: Geoffrey of Monmouth elevated the significance of Caerleon as a major centre of British history in his ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (c. 1136), and Alfred Lord Tennyson wrote ''Idylls of the King'' (1859–1885) while staying in Caerleon. History Pre-Roman history The area around Caerleon is of considerable archaeological interest, with a number of important Neolithic sites. By the British Iron Age, Iron Age, the area was home to the powerful Silures tribe and appears to have been the centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isca Augusta
Isca, variously specified as Isca Augusta or Isca Silurum, was the site of a Roman legionary fortress and settlement or ''vicus'', the remains of which lie beneath parts of the present-day suburban town of Caerleon in the north of the city of Newport in South Wales. The site includes Caerleon Amphitheatre and is protected by Cadw. Headquarters of the Legion " II Augusta", which took part in the invasion under Emperor Claudius in 43, Isca is uniquely important for the study of the conquest, pacification and colonisation of Britannia by the Roman army. It was one of only three permanent legionary fortresses in later Roman Britain and, unlike the other sites at Chester and York, its archaeological remains lie relatively undisturbed beneath fields and the town of Caerleon and provide a unique opportunity to study the Roman legions in Britain. Excavations continue to unearth new discoveries; in the late 20th century a complex of very large monumental buildings outside the fortress b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
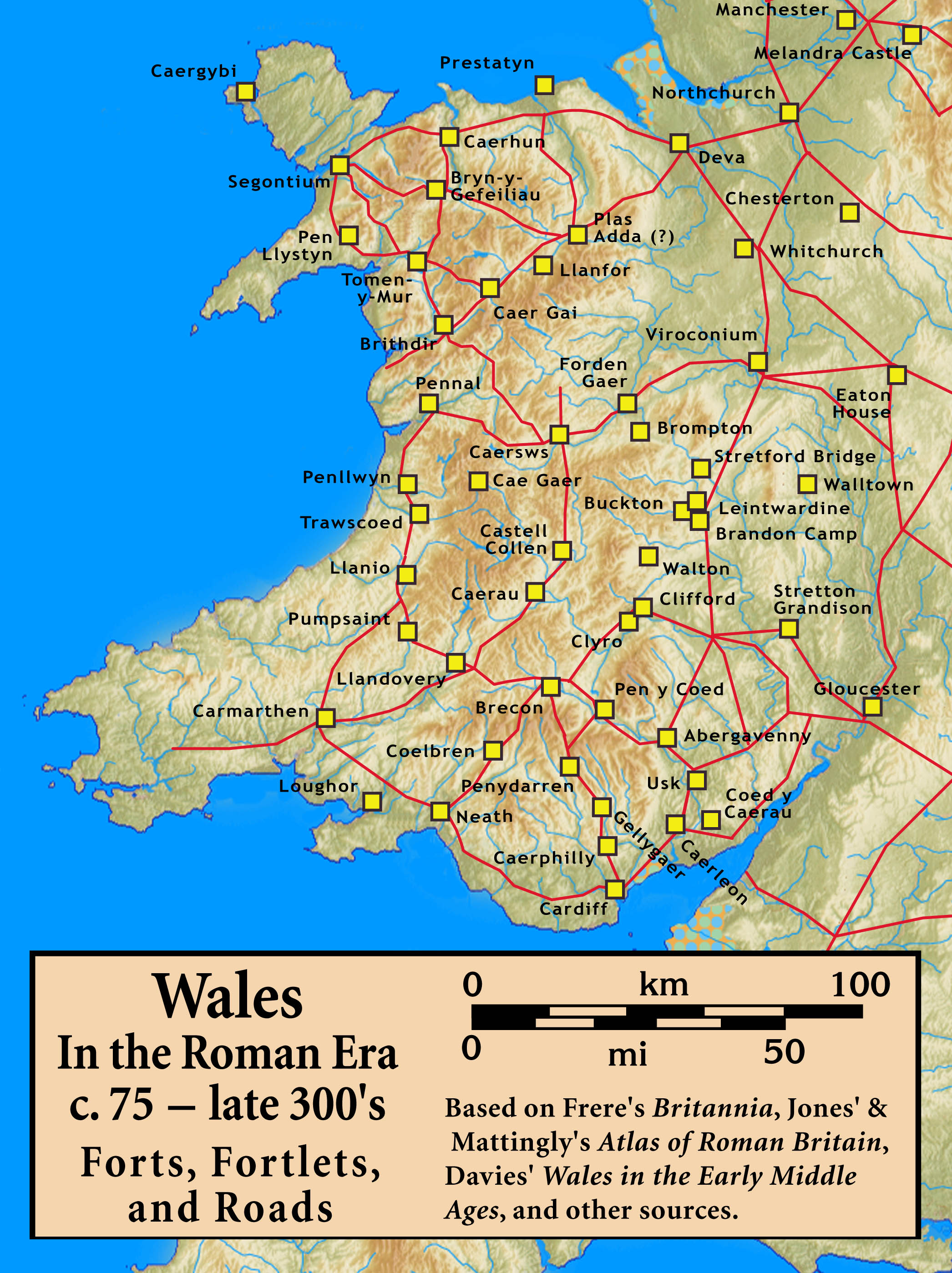
Wales In The Roman Era
The Roman era in the area of modern Wales began in 48 AD, with a military invasion by the Roman governor, imperial governor of Roman Britain. The conquest was completed by 78 AD, and Roman rule endured until the End of Roman rule in Britain, region was abandoned in 383 AD. The Roman Empire held a military occupation in most of Wales, except for the southern coastal region of South Wales, east of the Gower Peninsula, where there is a legacy of Romanization (cultural), Romanisation #Romanisation, in the region, and some southern sites such as Carmarthen, which was the civitas capital of the Demetae, Demetae tribe. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is in South Wales. Wales was a rich source of #Mining, mineral wealth, and the Romans used Roman engineering, their engineering Roman technology, technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper, and lead, as well as modest amounts of some other metals such as zinc and silver. The Roman #Roman invasion and conq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Amphitheatre
Roman amphitheatres are theatres — large, circular or oval open-air venues with tiered seating — built by the ancient Romans. They were used for events such as gladiator combats, ''venationes'' (animal slayings) and executions. About List of Roman amphitheatres, 230 Roman amphitheatres have been found across the area of the Roman Empire. Early amphitheatres date from the Roman Republic, Republican period, though they became more monumental during the Roman Empire, Imperial era.Bomgardner, 61. Amphitheatres are distinguished from Roman circus, circuses and hippodromes, which were usually rectangular and built mainly for racing events, and Stadium, stadia, built for sport, athletics, but several of these terms have at times been used for one and the same venue. The word ''amphitheatrum'' means "theatre all around". Thus, an amphitheatre is distinguished from the traditional semicircular Roman theatre (structure), Roman theatres by being circular or oval in shape.Bomgardner, 37. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary (, "Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is an , a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly in part from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes the roads of the Roman Empire. Owing to the scarcity of other extant records of this type, it is a valuable historical record. Publication History Manuscripts Almost nothing is known of its author or the conditions of its compilation. Numerous manuscripts survive, the eight oldest dating to some point between the 7th to 10th centuries after the onset of the Carolingian Renaissance. Despite the title seeming to ascribe the work to the patronage of the 2nd-century Antoninus Pius, all surviving editions seem to trace to an original towards the end of the reign of Diocletian in the early 4th century. The most likely imperial patron—if the work had one—would have been Caracalla. Stemma There are many manuscripts preserving the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Celtic Tribes
This is a list of ancient Celts, Celtic peoples and tribes. Continental Celts Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a large part of mainland Western Europe and large parts of Western Southern Europe (Iberian Peninsula), southern Central Europe and some regions of the Balkans and Anatolia. They were most of the population in Gallia, today's France, Switzerland, possibly Belgica – far France, Northern France, Belgium and far Southern Netherlands, large parts of Hispania, i.e. Iberian Peninsula – Spain and Portugal, in the northern, central and western regions; southern Central Europe – upper Danube basin and neighbouring regions, large parts of the middle Danube basin and the inland region of Central Asia Minor or Anatolia. They lived in these many regions forming a large arc stretching across from Iberia in the west to the Balkans and Anatolia in the ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetae
The Demetae were a Celtic people of Iron Age and Roman period, who inhabited modern Pembrokeshire and Carmarthenshire in south-west Wales. The tribe also gave their name to the medieval Kingdom of Dyfed, the modern area and county of Dyfed and the distinct dialect of Welsh spoken in modern south-west Wales, Dyfedeg. Etymology and relationship to Dyfed The tribal name Demetae is thought to derive from a Common Celtic element related to the modern Welsh word ''defaid'' (sheep) as well as the Ancient Brythonic word ''defod'' (wealth, property or riches). This element persists in the name for the area of West Wales that the tribe inhabited, with the post-Roman Kingdom of Dyfed (proto-Celtic *dametos') a clear continuation of the Pre-Roman etymon. The name even survived the Norman conquest of Wales and the introduction of the Shire system, with Thomas Morgan noting that the Welsh inhabitants of Pembrokeshire still referred to the area as ''Dyfed'' in the nineteenth century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civitas
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by Roman law, law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on the one hand and rights of citizenship on the other. The agreement () has a life of its own, creating a or "public entity" (synonymous with ), into which individuals are born or accepted, and from which they die or are Exile, ejected. The is not just the collective body of all the citizens, it is the contract binding them all together, because each of them is a . is an abstract formed from . Claude Nicolet traces the first word and concept for the citizen at Rome to the first known instance resulting from the synoecism of Romans and Sabines presented in the legends of the Roman Kingdom. According to Livy, the two peoples participated in a ceremony of union after which they were named Quirites after the Sabine town of Cures, Sabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |