|
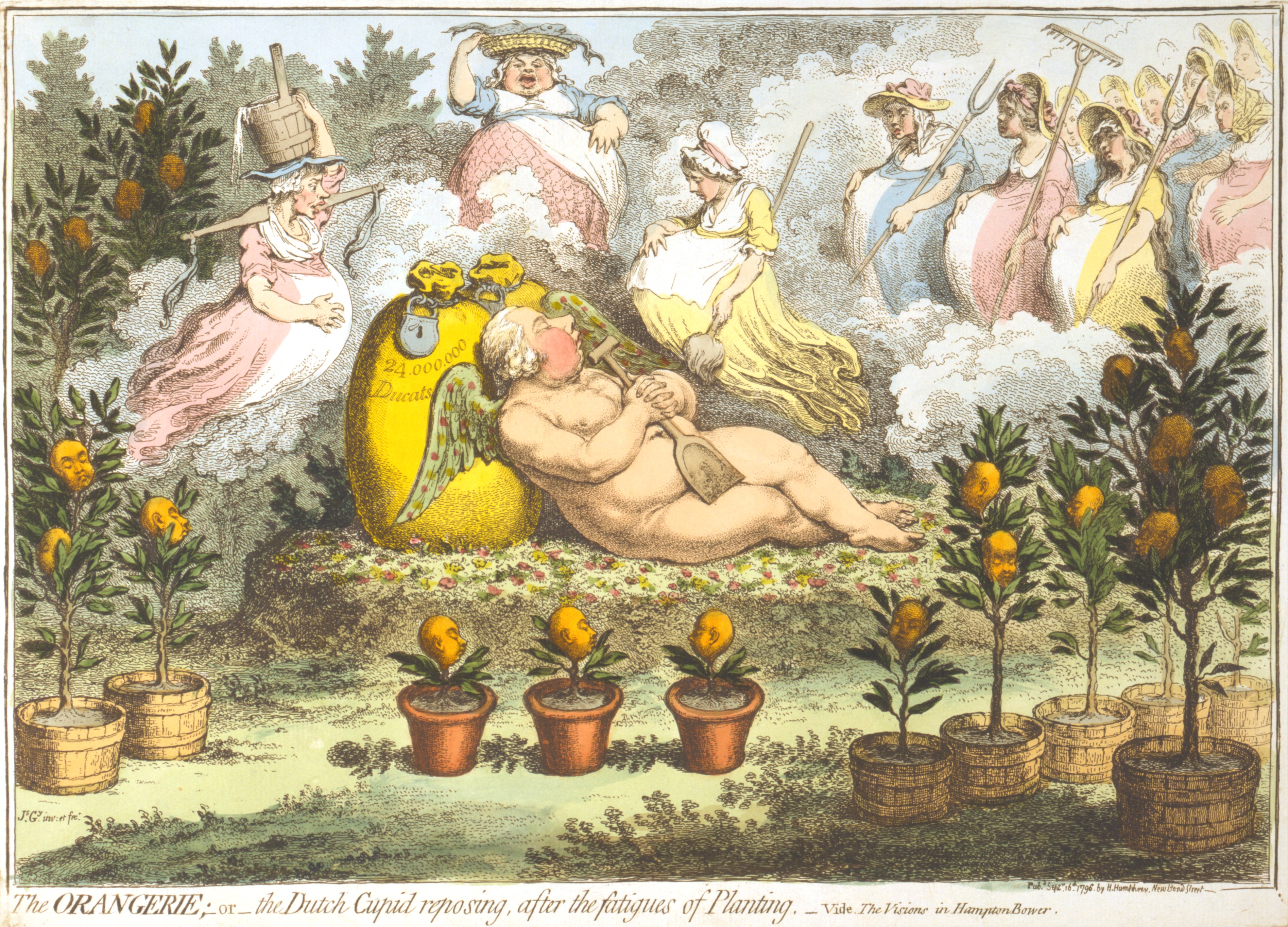
Capture Of The Dutch Fleet At Den Helder
The capture of the Dutch fleet at Den Helder on the night of 23 January 1795 presents a rare occurrence of an interaction between warships and cavalry, in which a French Revolutionary Hussar regiment came close to a Dutch fleet frozen at anchor in the Nieuwediep, just east of the town of Den Helder. After some of the Hussars had approached across the frozen Nieuwediep,De Jonge quoting correspondence with Lahure, notes that the French troops moved from Haarlem to Den Helder overland, which was more convenient, as there is no need to make a long detour across the Zuiderzee, whether there was ice on it or not; de Jonge, p. 187, note 1. Besides, on the basis of the testimony of eye witnesses he says that the ice on the Zuiderzee would not have been strong enough to carry a squadron of cavalry; de Jonge, p. 184. the French cavalry negotiated that all 14 Dutch warships would remain at anchor. A capture of ships by horsemen is an extremely rare feat in military history. The French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Countries Theatre Of The War Of The First Coalition
The Low Countries theatre of the War of the First Coalition, also known as the Flanders campaign, was a series of campaigns in the Low Countries conducted from 20 April 1792 to 7 June 1795 during the first years of the War of the First Coalition. As the French Revolution radicalised, the revolutionary National Convention and its predecessors broke the Catholic Church's power (1790), abolished the monarchy (1792) and even executed the deposed king Louis XVI of France (1793), vying to spread the Revolution beyond the new French Republic's borders, by violent means if necessary. The First Coalition, an alliance of reactionary states representing the Ancien Régime in Central and Western Europe – Habsburg Austria (including the Southern Netherlands), Prussia, Great Britain, the Dutch Republic (the Northern Netherlands), Hanover and Hesse-Kassel – mobilised military forces along all the French frontiers, threatening to invade Revolutionary France and violently restore the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IJsselmeer
The IJsselmeer (; , ), also known as Lake IJssel in English, is a closed-off freshwater lake in the central Netherlands bordering the Provinces of the Netherlands, provinces of Flevoland, North Holland and Friesland. It covers an area of with an average depth of . The river IJssel, after which the lake was named, flows into the IJsselmeer. The first two letters of the name are capitalized because IJ (digraph), IJ is a digraph (orthography), digraph sometimes considered a Typographic ligature, ligature in Dutch language, Dutch. History Two thousand years ago Pomponius Mela, a Ancient Rome, Roman geographer, mentioned a complex of lakes at the current location of the IJsselmeer. He called it ''Lake Flevo, Lacus Flevo''. Over the centuries, the lake banks crumbled away due to flooding and wave action, and the lake, now called the Almere (lake), Almere, grew considerably. During the 12th and 13th centuries, storm surges and sea level rise, rising sea levels flooded large areas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlieter Incident
In the Vlieter incident of 30 August 1799, a squadron of the Batavian Navy, commanded by '' Schout-bij-nacht'' Samuel Story, surrendered to the British navy. The incident occurred during the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland. It occurred in the tidal trench between Texel and the mainland that was known as ''De Vlieter'', near Wieringen. Background During the War of the First Coalition, the Dutch Republic was invaded in 1794 by the armies of the French Republic, which led to the flight of Stadtholder William V, Prince of Orange, to England, and the proclamation of the Batavian Republic. The Dutch now changed sides in the war, entering into an offensive and defensive alliance with France. In the course of the War of the Second Coalition, which actually was a continuation of the first war, without France, Great Britain, or the Batavian Republic having concluded a peace, Great Britain and Russia decided to launch an invasion of the Batavian Republic in the peninsula of North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helder Morel-Fatio
Helder may refer to: * Den Helder or The Helder, a municipality and a city in the Netherlands * Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland in 1799, or expedition to the "Helder" People * Anne-Marie Helder (21st century), British singer-songwriter * Glenn Helder (born 1968), Dutch footballer * Lilian Helder (born 1973), Dutch politician * Liza Helder (born 1989), Aruban model and Miss Aruba 2012 * Luke Helder (born 1981), American bomber * John Helder Wedge (1793–1872), Tasmanian politician Arts * Helder (comics), "Helder" (comics), a short comics story by Chester Brown See also * Hélder, a Portuguese masculine given name {{DEFAULTSORT:Helder Dutch-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlieter Incident
In the Vlieter incident of 30 August 1799, a squadron of the Batavian Navy, commanded by '' Schout-bij-nacht'' Samuel Story, surrendered to the British navy. The incident occurred during the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland. It occurred in the tidal trench between Texel and the mainland that was known as ''De Vlieter'', near Wieringen. Background During the War of the First Coalition, the Dutch Republic was invaded in 1794 by the armies of the French Republic, which led to the flight of Stadtholder William V, Prince of Orange, to England, and the proclamation of the Batavian Republic. The Dutch now changed sides in the war, entering into an offensive and defensive alliance with France. In the course of the War of the Second Coalition, which actually was a continuation of the first war, without France, Great Britain, or the Batavian Republic having concluded a peace, Great Britain and Russia decided to launch an invasion of the Batavian Republic in the peninsula of North ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HNLMS De Ruyter
HNLMS ''De Ruyter'' () may refer to one of nine ships of the Dutch States Navy or Royal Netherlands Navy named after Admiral Michiel de Ruyter (1607–1676): * '' Admiraal de Ruijter'', a 68-gun Batavian ship of the line that the British navy captured in the 1799 Vlieter incident and took into service as the 64-gun storeship HMS ''De Ruyter''. She was on her way to Falmouth, Jamaica to serve as a prison hulk in September 1804 when the Antigua–Charleston hurricane caused her to be washed ashore and wrecked with the loss of one sailor. * , a 54-gun frigate converted to steam power and then into a broadside ironclad in 1863 * , an unprotected cruiser * , a * , an . She was renamed ''Van Ghent'' to make way for the 1935 ''De Ruyter''. She served in World War II and was wrecked on Bamidjo reef on 15 February 1942 * , a unique light cruiser. She served in World War II and was sunk in the battle of the Java Sea The Battle of the Java Sea (, ) was a decisive naval battle of the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of The Hague (1795)
The Treaty of The Hague (also known as the Hedges Treaty) was signed on May 16, 1795, between representatives of the French First Republic and the Batavian Republic. Based on the terms of the treaty, the Batavian Republic ceded to France the territories of Maastricht, Venlo, and Zeelandic Flanders. Moreover, the accord established a defensive alliance between the two nations, which rapidly involved the Netherlands in the war against Great Britain and Austria. Furthermore, the Dutch agreed to pay an indemnity of 100 million guilders for their part in the war of the First Coalition, and to provide the French Republic a large loan against a low rate of interest. The "barrier forts" in the former Austrian Netherlands were dismantled. The port of Flushing was to be placed under a co-dominion. Finally, in a secret clause, the Dutch agreed to pay for a French army of occupation of 25,000 till the war was ended. The treaty brought the Revolutionary War between France and the Dutch Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apure River
The Apure River is a river of southwestern Venezuela, formed by the confluence of the Sarare and Uribante near Guasdualito, in Venezuela, at , and flowing across the Llanos into the Orinoco. It provides significant transportation in the area. Origin Most of the streams that ultimately form the Apure originate in the Venezuelan highlands of the Cordillera de Mérida and only some minor affluents of the Sarare River come from the Cordillera Oriental in the Colombian Andes, entering Venezuela at the confluence with the Oirá River which has a very narrow and steep valley and forms the border between the two countries for . The Oirá River starts in Venezuela and its thalweg forms that border for several kilometres downstream. The Uribante River is longer than the Sarare and flows from the Táchira-Mérida border, near the town of Pregonero. The Apure's drainage area thus includes the slopes of both the Colombian (less than 0.5 percent of its total area) and the Venezuelan Andes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Antonio Páez
José Antonio Páez Herrera (; 13 June 1790 – 6 May 1873) was a Venezuelan politician and military officer who served as the president of Venezuela three times. The first as the 5th president from 1830 to 1835, the second as the 8th president from 1839 to 1843, and the third as the 15th president from 1861 to 1863. He fought against the Spanish Crown for Simón Bolívar during the Venezuelan War of Independence. Páez later led Venezuela's independence from Gran Colombia. Páez dominated the country's politics for most of the next three decades once the country had achieved independence from Gran Colombia, serving either as president or as the power behind puppet presidents. He is considered a prime example of a 19th-century South American caudillo, saddling the country with a legacy of authoritarian rule that lasted with only a few breaks until 1958. He lived in Buenos Aires and New York City during his years in exile and died in the latter in 1873. Biography Early life P� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Camperdown
The Battle of Camperdown (Dutch language, Dutch: ''Zeeslag bij Kamperduin'') was fought on 11 October 1797 between the Royal Navy's Commander-in-Chief, North Sea, North Sea Fleet under Admiral Adam Duncan, 1st Viscount Duncan, Adam Duncan and a Batavian Navy fleet led by Vice-Admiral Jan Willem de Winter. Duncan's fleet won a complete victory over de Winter's in what was the most significant engagement between British and Batavian forces during the French Revolutionary Wars, capturing eleven ships without losing any of their own. In 1795, the Dutch Republic was Low Countries theatre of the War of the First Coalition, overrun by French First Republic, France and reorganised into the Batavian Republic, a French sister republic. After several French Navy campaigns ended in disaster, the Batavian navy was ordered move to Brest, France, Brest in 1797. This rendezvous never occurred, as the French and their allies failed to capitalise on the Spithead and Nore mutinies that paralysed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William V, Prince Of Orange
William V (Willem Batavus; 8 March 1748 – 9 April 1806) was Prince of Orange and the last Stadtholder of the Dutch Republic. He went into exile to London in 1795. He was furthermore ruler of the Principality of Orange-Nassau until his death in 1806. In that capacity, he was succeeded by his son William I of the Netherlands, William. Early life William Batavus was born in The Hague on 8 March 1748, the only son of William IV, Prince of Orange, William IV, who had the year before been restored as stadtholder of the United Provinces. He was only three years old when his father died in 1751, and a long regency began. His regents were: *Anne, Princess Royal and Princess of Orange, Dowager Princess Anne, his mother, from 1751 to her death in 1759; *Landgravine Marie Louise of Hesse-Kassel, Dowager Princess Marie Louise, his grandmother, from 1759 to her death in 1765; *Duke Louis Ernest of Brunswick-Lüneburg, from 1759 to 1766, and kept on as a privy counsellor, in accordance with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |